
Concept explainers
For the following cases, determine the allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity of the foundation. Use Terzaghi’s equation and assume general shear failure in soil. Use FS = 4.
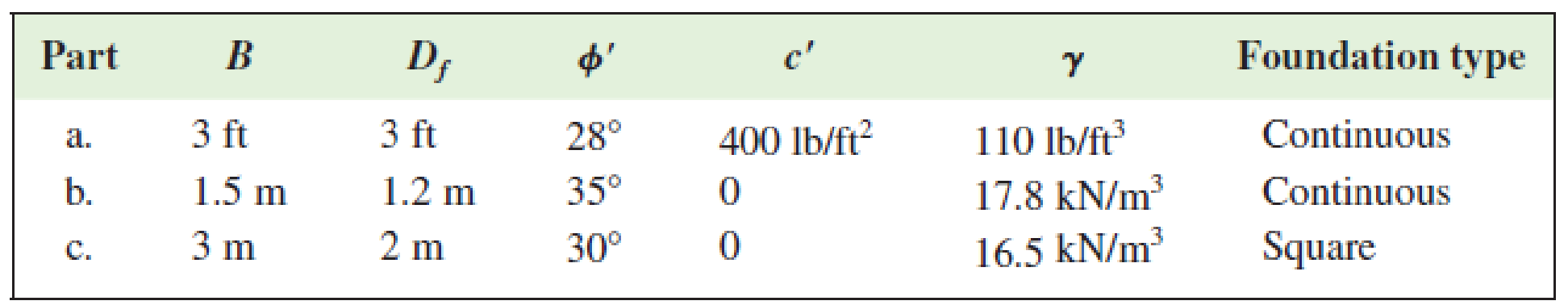
Parameters for Problem 6.1
a)
Find the allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity of the continuous foundation.
Answer to Problem 6.1P
The allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity of the continuous foundation is
Explanation of Solution
Given information;
The width (B) of the foundation is 3 ft.
The depth
The angle of friction
The cohesion
The specific weight
The factor of safety is (FS) is 4.0.
Calculation:
Refer Table (6.1), “Terzaghi’s bearing capacity factors” in the text book.
For
Take the value of
Take the value of
Take the value of
Determine the ultimate load bearing capacity
Determine the allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity
Hence, the allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity
b)
Find the allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity of the continuous foundation.
Answer to Problem 6.1P
The allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity of the continuous foundation is
Explanation of Solution
Given information;
The width (B) of the foundation is 1.5 m.
The depth
The angle of friction
The cohesion
The specific weight
The factor of safety is (FS) is 4.0.
Calculation:
Refer Table (6.1), “Terzaghi’s bearing capacity factors” in the text book.
For
Take the value of
Take the value of
Take the value of
Determine the ultimate load bearing capacity
Determine the allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity
Hence, the allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity
c)
Find the allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity of the square foundation.
Answer to Problem 6.1P
The allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity of the square foundation is
Explanation of Solution
Given information;
The width (B) of the foundation is 3.0 m.
The depth
The angle of friction
The cohesion
The specific weight
The factor of safety is (FS) is 4.0.
Calculation:
Refer Table (6.1), “Terzaghi’s bearing capacity factors” in the text book.
For
Take the value of
Take the value of
Take the value of
Determine the ultimate load bearing capacity
Determine the allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity
Hence, the allowable gross vertical load-bearing capacity
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- Problem 2. A rectangular channel with a width of 5 m and slope of 0.0075 carries 38 m³/s. If Manning's n is 0.015, determine normal depth, whether the flow is subcritical or supercritical and the conjugate depth.arrow_forwardProblem 5. Water flows in a rectangular open channel through a width constriction. If the upstream depth is y₁ = 5 ft when the flow is 300 cfs, what is the minimum width, Bmin that will prevent yi from exceeding 5 ft? Neglect head losses. 10 ft Bminarrow_forwardProblem 3. A trapezoidal channel has a bottom width B = 48.5 ft and side slopes of m = 1.5. Calculate critical depth when the flow is 1146 cfs. Check your answer with the attached chart.arrow_forward
- Problem 4. A drainage channel (n = 0.018) has a bottom width of 5 ft and side slopes of m = 2. The flow is 65.0 cfs and the slope is 0.0025. a. Calculate normal depth for the channel. b. Calculate the Froude Number. Is the flow subcritical or supercritical?arrow_forwardFor this exercise consider the single-bay building framing plan shown below, which you have considered previously. It has been decided to change from concrete framing to structural steel framing. A steel deck and concrete slab with a total thickness of five inches spans between the steel beams, and the steel beams are supported by steel girders along two edges. Assume all beams and girders are simple span and design the interior beams and edge girders. Use a design live load of 80 pounds per square foot. The slab dead load is 70 pounds per square foot, which includes the weight of the slab, beams, girders, and superimposed dead loads (mechanical, ceiling, floor finish, etc.). The beams may be assumed to have continuous lateral support from the floor slab. The girders should be assumed to be braced only by the beams (i.e., unbraced length equals beam spacing). The columns supporting the framing have been designed and do not need to be considered. Use steel yield strength Fy = 50 ksi for…arrow_forwardFor the following floor plan design member M3 as a T-shape beam. Use the following information: slab thickness = 3.5 in. f'c = 4000 psi fy = 60000 psi. = 103 psf WD=82 psf (not including the weight of the slab) Make sure to include the weight of the self weight of the slab when calculating M₁. Include a drawing of the final cross section of the beam Ensure that M, is not more than 10% of м. Make sure that you complete all the checks. Ignore serviceability check.arrow_forward
- 12-23. A particle is moving along a straight line such that its acceleration is defined as a = (-2v) m/s², where v is in meters per second. If v = 20 m/s when s = 0 and t = 0, determine the particle's position, velocity, and acceleration as functions of time.arrow_forwardoutline the key components of a safety plan for residential and highway construction project, how do they different?arrow_forwardDetermine all reactions for the beam by applying the Moment Distribution Method. Provide detailed steps.Iterate until all carry over moments are less than 1 kN*m. EI is constant. ( No wrong or incomplete solutions). Previous Ans. was incorrect.arrow_forward
- 2. A concrete slab of uniform thickness is continuous for six spans and is supported by 12-inch-wide concrete beams at 10 ft o.c. The following loads are applied to the slab: DL 100 psf (includes self-weight) and LL = 50 psf Determine all moments and shears. = -10 ft- -10 ft- -10 ft- -10 ft- -10 ft- -10 ft- 12 in. (TYP.)arrow_forward1. Compute V for the cross sections below. Use f'c = 4000 psi, fy = 40,000 psi, and assume λ = 1.0. T 24" No. 3 stirrups at 8" o.c. 25" 12" + No. 4 stirrups at 10" o.c. 6" 14" 20" 15" 5" 5" 8"arrow_forwardDetermine all reactions for the beam by applying the Moment Distribution Method. Provide detailed steps.Iterate until all carry over moments are less than 1 kN*m. EI is constant. ( No wrong or incomplete solutions). Thanks!arrow_forward
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning

