Problem 6.1QP: Define these terms: system, surroundings, open system, closed system, isolated system, thermal... Problem 6.2QP: What is heat? How does heat differ from thermal energy? Under what condition is heat transferred... Problem 6.3QP: What are the units for energy commonly employed in chemistry? Problem 6.4QP: A truck initially traveling at 60 km per hour is brought to a complete stop at a traffic light. Does... Problem 6.5QP: These are various forms of energy: chemical, heat, light, mechanical, and electrical. Suggest ways... Problem 6.7QP: Define these terms: thermochemistry, exothermic process, endothermic process. Problem 6.8QP: Stoichiometry is based on the law of conservation of mass. On what law is thermochemistry based? Problem 6.9QP: Describe two exothermic processes and two endothermic processes. Problem 6.10QP: Decomposition reactions are usually endothermic, whereas combination reactions are usually... Problem 6.11QP: On what law is the first law of thermodynamics based? Explain the sign conventions in the equation U... Problem 6.12QP: Explain what is meant by a state function. Give two examples of quantities that are state functions... Problem 6.13QP: The internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on its temperature. Do a first-law analysis of this... Problem 6.14QP: Consider these changes: (a) Hg(l)Hg(g) (b) 3O2(g)2O3(g) (c) CuSO45H2O(s)CuSO4(s)+5H2O(g) (d)... Problem 6.15QP: A sample of nitrogen gas expands in volume from 1.6 L to 5.4 L at constant temperature. Calculate... Problem 6.16QP: A gas expands in volume from 26.7 mL to 89.3 mL at constant temperature. Calculate the work done (in... Problem 6.17QP: A gas expands and does P-V work on the surroundings equal to 325 J. At the same time, it absorbs 127... Problem 6.18QP: The work done to compress a gas is 74 J. As a result, 26 J of heat is given off to the surroundings.... Problem 6.19QP: Calculate the work done when 50.0 g of tin dissolves in excess acid at 1.00 atm and 25C:... Problem 6.20QP: Calculate the work done in joules when 1.0 mole of water vaporizes at 1.0 atm and 100C. Assume that... Problem 6.21QP Problem 6.22QP: In writing thermochemical equations, why is it important to indicate the physical state (that is,... Problem 6.23QP: Explain the meaning of this thermochemical equation: 4NH3(g)+5O2(g)4NO(g)+6H2O(g)H=904kJ/mol Problem 6.24QP: Consider this reaction: 2CH3OH(l)+3O2(g)4H2O(l)+2CO2(g)H=1452.8kJ/mol What is the value of H if (a)... Problem 6.25QP: The first step in the industrial recovery of zinc from the zinc sulfide ore is roasting, that is,... Problem 6.26QP: Determine the amount of heat (in kJ) given off when 1.26 104 g of NO2 are produced according to the... Problem 6.27QP: Consider the reaction 2H2O(g)2H2(g)+O2(g)H=483.6kJ/mol If 2.0 moles of H2O(g) are converted to H2(g)... Problem 6.28QP: Consider the reaction H2(g)+Cl2(g)2HCl(g)H=184.6kJ/mol If 3 moles of H2 react with 3 moles of Cl2 to... Problem 6.29QP: What is the difference between specific heat and heat capacity? What are the units for these two... Problem 6.30QP: Define calorimetry and describe two commonly used calorimeters. In a calorimetric measurement, why... Problem 6.31QP: Consider the following data: Metal Al Cu Mass (g) 10 30 Specific heat (J/g C) 0.900 0.385... Problem 6.32QP: A piece of silver of mass 362 g has a heat capacity of 85.7 J/C. What is the specific heat of... Problem 6.33QP: A 6.22-kg piece of copper metal is heated from 20.5C to 324.3C. Calculate the heat absorbed (in kJ)... Problem 6.34QP: Calculate the amount of heat liberated (in kJ) from 366 g of mercury when it cools from 77.0C to... Problem 6.35QP: A sheet of gold weighing 10.0 g and at a temperature of 18.0C is placed flat on a sheet of iron... Problem 6.36QP: To a sample of water at 23.4C in a constant-pressure calorimeter of negligible heat capacity is... Problem 6.37QP: A 0.1375-g sample of solid magnesium is burned in a constant-volume bomb calorimeter that has a heat... Problem 6.38QP: A quantity of 85.0 mL of 0.900 M HCl is mixed with 85.0 mL of 0.900 M KOH in a constant-pressure... Problem 6.39QP: What is meant by the standard-state condition? Problem 6.40QP: How are the standard enthalpies of an element and a compound determined? Problem 6.41QP: What is meant by the standard enthalpy of a reaction? Problem 6.42QP: Write the equation for calculating the enthalpy of a reaction. Define all the terms. Problem 6.43QP: State Hesss law. Explain, with one example, the usefulness of this law in thermochemistry. Problem 6.44QP: Describe how chemists use Hesss law to determine the Hfo of a compound by measuring its heat... Problem 6.45QP: Which of the following standard enthalpy of formation values is not zero at 25C? Na(s), Ne(g),... Problem 6.46QP: The Hfo values of the two allotropes of oxygen, O2 and O3, are o and 142.2 kJ/mol, respectively, at... Problem 6.47QP: Which is the more negative quantity at 25C: Hfo for H2O(l) or Hfo for H2O(g)? Problem 6.48QP: Predict the value of Hfo (greater than, less than, or equal to zero) for these elements at 25C: (a)... Problem 6.49QP: In general, compounds with negative Hfo values are more stable than those with positive Hfo values.... Problem 6.50QP: Suggest ways (with appropriate equations) that would enable you to measure the Hfo values of Ag2O(s)... Problem 6.51QP: Calculate the heat of decomposition for this process at constant pressure and 25C:... Problem 6.52QP: The standard enthalpies of formation of ions in aqueous solutions are obtained by arbitrarily... Problem 6.53QP: Calculate the heats of combustion for the following reactions from the standard enthalpies of... Problem 6.54QP: Calculate the heats of combustion for the following reactions from the standard enthalpies of... Problem 6.55QP: Methanol, ethanol, and n-propanol are three common alcohols. When 1.00 g of each of these alcohols... Problem 6.56QP: The standard enthalpy change for the following reaction is 436.4 kJ/mol: H2(g)H(g)+H(g) Calculate... Problem 6.57QP: From the standard enthalpies of formation, calculate Hrxno for the reaction... Problem 6.58QP: Pentaborane-9, B5H9, is a colorless, highly reactive liquid that will burst into flame when exposed... Problem 6.59QP: Determine the amount of heat (in kJ) given off when 1.26 104 g of ammonia are produced according to... Problem 6.60QP: At 850C, CaCO3 undergoes substantial decomposition to yield CaO and CO2. Assuming that the values of... Problem 6.61QP: From these data, S(rhombic)+O2(g)SO2(g)Hrxno=296.06kJ/molS(monoclinic)+O2(g)SO2(g)Hrxno=296.36kJ/mol... Problem 6.62QP: From the following data,... Problem 6.63QP: From the following heats of combustion,... Problem 6.64QP: Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the reaction 2Al(s)+Fe2O3(s)2Fe(s)+Al2O3(s) given that... Problem 6.65QP Problem 6.66QP: Why is the lattice energy of a solid always a positive quantity? Why is the hydration of ions always... Problem 6.67QP: Consider two ionic compounds A and B. A has a larger lattice energy than B. Which of the two... Problem 6.68QP: Mg2+ is a smaller cation than Na+ and also carries more positive charge. Which of the two species... Problem 6.70QP: Why is it dangerous to add water to a concentrated acid such as sulfuric acid in a dilution process? Problem 6.71QP: Which of the following does not have Hfo=O at 25C? He(g) Fe(s) Cl(g) S8(s) O2(g) Br2(l) Problem 6.72QP: Calculate the expansion work done when 3.70 moles of ethanol are converted to vapor at its boiling... Problem 6.73QP Problem 6.74QP: Given the thermochemical equations: Br2(l)+F2(g)2BrF(g)Ho=188kJ/molBr2(l)+3F2(g)2BrF3(g)Ho=768kJ/mol... Problem 6.75QP: The standard enthalpy change H for the thermal decomposition of silver nitrate according to the... Problem 6.76QP: Hydrazine, N2H4, decomposes according to the following reaction: 3N2H4(l)4NH3(g)+N2(g) (a) Given... Problem 6.77QP: A quantity of 2.00 102 mL of 0.862 M HCl is mixed with an equal volume of 0.431 M Ba(OH)2 in a... Problem 6.78QP: A 3.53-g sample of ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) was added to 80.0 mL of water in a constant-pressure... Problem 6.79QP: Consider the reaction N2(g)+3H2(g)2NH3(g)Hrxno=92.6kJ/mol If 2.0 moles of N2 react with 6.0 moles of... Problem 6.80QP Problem 6.81QP Problem 6.82QP: A 2.10-mole sample of crystalline acetic acid, initially at 17.0C, is allowed to melt at 17.0C and... Problem 6.83QP Problem 6.84QP: You are given the following data:... Problem 6.85QP: A gaseous mixture consists of 28.4 mole percent of hydrogen and 71.6 mole percent of methane. A... Problem 6.86QP: When 2.740 g of Ba reacts with O2 at 298 K and 1 atm to form BaO, 11.14 kJ of heat are released.... Problem 6.87QP: Methanol (CH3OH) is an organic solvent and is also used as a fuel in some automobile engines. From... Problem 6.88QP: A 44.0-g sample of an unknown metal at 99.0C was placed in a constant-pressure calorimeter... Problem 6.89QP: Using the data in Appendix 2, calculate the enthalpy change for the gaseous reaction shown here.... Problem 6.90QP: Producer gas (carbon monoxide) is prepared by passing air over red-hot coke: C(s)+12O2(g)CO(g) Water... Problem 6.91QP Problem 6.92QP Problem 6.93QP: Ethanol (C2H5OH) and gasoline (assumed to be all octane, C8H18) are both used as automobile fuel. If... Problem 6.94QP: The combustion of what volume of ethane (C2H6), measured at 23.0C and 752 mmHg, would be required to... Problem 6.95QP Problem 6.96QP Problem 6.97QP: Explain the cooling effect experienced when ethanol is rubbed on your skin, given that... Problem 6.98QP: For which of the following reactions does Hrxno=Hfo? (a) H2(g)+S(rhombic)H2S(g) (b)... Problem 6.99QP Problem 6.100QP: A quantity of 0.020 mole of a gas initially at 0.050 L and 20C undergoes a constant-temperature... Problem 6.101QP Problem 6.102QP Problem 6.103QP Problem 6.104QP Problem 6.105QP: A person ate 0.50 pound of cheese (an energy intake of 4000 kJ). Suppose that none of the energy was... Problem 6.106QP Problem 6.107QP Problem 6.108QP: The enthalpy of combustion of benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) is commonly used as the standard for... Problem 6.109QP Problem 6.110QP Problem 6.111QP: Glaubers salt, sodium sulfate decahydrate (Na2SO4 10H2O), undergoes a phase transition (that is,... Problem 6.112QP: A balloon 16 m in diameter is inflated with helium at 18C. (a) Calculate the mass of He in the... Problem 6.113QP: Acetylene (C2H2) can be hydrogenated (reacting with hydrogen) first to ethylene (C2H4) and then to... Problem 6.114QP Problem 6.115QP: An excess of zinc metal is added to 50.0 mL of a 0.100 M AgNO3 solution in a constant-pressure... Problem 6.116QP: (a) A person drinks four glasses of cold water (3.0C) every day. The volume of each glass is 2.5 ... Problem 6.118QP Problem 6.119QP: Why are cold, damp air and hot, humid air more uncomfortable than dry air at the same temperatures?... Problem 6.120QP Problem 6.121QP Problem 6.122QP Problem 6.123QP Problem 6.124QP: Determine the standard enthalpy of formation of ethanol (C2H5OH) from its standard enthalpy of... Problem 6.125QP Problem 6.126QP: Ice at 0C is placed in a Styrofoam cup containing 361 g of a soft drink at 23C. The specific heat of... Problem 6.127QP Problem 6.128QP Problem 6.130QP: Calculate the internal energy of a Goodyear blimp filled with helium gas at 1.2 105 Pa. The volume... Problem 6.131QP Problem 6.132QP: Acetylene (C2H2) can be made by reacting calcium carbide (CaC2) with water. (a) Write an equation... Problem 6.133QP: The average temperature in deserts is high during the day but quite cool at night, whereas that in... Problem 6.135QP: From a thermochemical point of view, explain why a carbon dioxide fire extinguisher or water should... Problem 6.136QP: Calculate the U for the following reaction at 298 K: 2H2(g)+O2(g)2H2O(l) Problem 6.137QP: Lime is a term that includes calcium oxide (CaO, also called quicklime) and calcium hydroxide... Problem 6.138QP: A 4.117-g impure sample of glucose (C6H12O6) was burned in a constant-volume calorimeter having a... Problem 6.139QP: Construct a table with the headings q, w, U, and H. For each of the following processes, deduce... Problem 6.140QP: The combustion of 0.4196 g of a hydrocarbon releases 17.55 kJ of heat. The masses of the products... Problem 6.141QP: Metabolic activity in the human body releases approximately 1.0 104 kJ of heat per day. Assuming... Problem 6.142QP: Give an example for each of the following situations: (a) Adding heat to a system raises its... Problem 6.143QP: From the following data, calculate the heat of solution for KI: Problem 6.144QP: Starting at A, an ideal gas undergoes a cyclic process involving expansion and compression, as shown... Problem 6.145QP: For reactions in condensed phases (liquids and solids), the difference between H and U is usually... Problem 6.146QP: The diagrams (a)(d) represent various physical and chemical processes: (a) 2A(g) A2(g); (b) MX(s) ... Problem 6.147QP: A 20.3-g sample of an unknown metal and a 28.5-g sample of copper, both at 80.6C, are added to 100 g... Problem 6.148QP Problem 6.149QP Problem 6.150QP: The fastest serve in tennis is about 150 mph. Can the kinetic energy of a tennis ball traveling at... Problem 6.151QP Problem 6.152QP: It has been estimated that 3 trillion standard cubic feet of methane is released into the atmosphere... Problem 6.153QP Problem 6.154QP Problem 6.155QP Problem 6.156QP: We hear a lot about how the burning of hydrocarbons produces the greenhouse gas CO2, but what about... format_list_bulleted

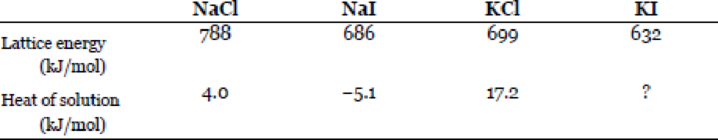
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStaxChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStaxChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co




