
EBK SHIGLEY'S MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DE
10th Edition
ISBN: 8220100256431
Author: BUDYNAS
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 54P
Solve Prob. 6-17 except include a steady torque of 2500 lbf · in being transmitted through the shaft between the points of application of the forces.
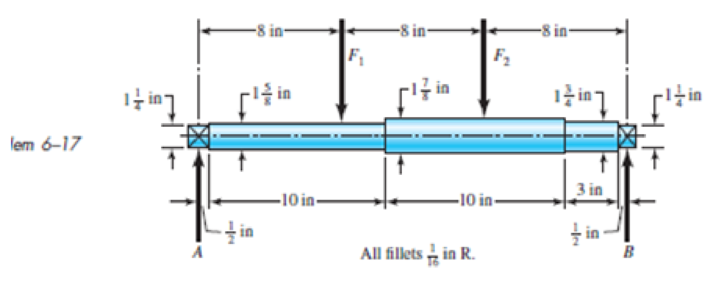
6-17 The shaft shown in the figure is machined from AIS1 1040 CD steel. The shaft rotates at 1600 rpm and is supported in rolling bearings at A and B. The applied forces are F1 = 2500 Ibf and F2 = 1000 Ibf. Determine the minimum fatigue factor of safety based on achieving infinite life. If infinite life is not predicted, estimate the number of cycles to failure. Also check for yielding.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Figure below shows a portion of a pump that is gear-driven at uniform load and speed. The 25 mm diameter solod shaft supported by
the bearings is to be made of machined AISI 1045 CD steel. The helical gear is subjected to the axial force F =499 y a radial
load F = 741 N and a tangential load of F=2,006 N. Assume the component is operating at room temperature of 70°F and the
material has 50% reliability factor.
25-mm solid
Bending K, = 2.0
round shaft Fillet Torsional K = 1.5
F.
F,
Axial K, = 1.8
F
Pump
Helical
spur gear
50 mm
-250-mm dia.-
FIGURE
1. Identify the critical location(s) of stress and show it clearly in a diagram.
2. Identify cleary, all the components of stresses (at the critical point) that will be calculated (by drawing and clearly showing
the XYZ axes) and show it in a matrix form. Show which components of stresses will have a value zero or non-zero.
3. Calculate the principal stresses and principal directions. Show the principal stresses clearly in a stress element…
The solid steel rotating shaft in the figure is supported at B and C, and is driven by a gear, not seen, which is linked to spur gear D which has a pitch diameter of 150 mm. The drive gear force F acts at a pressure angle of 20 degrees. The shaft transmits a torque to point A of Ta-350 N.m. The properties of machined steel shaft are Sy-420 MPa and Sut-560MPa. Use a safety factor of 2.5 and determine the minimum allowable diameter in section B and C. Assume sharp felt radii at the bearing shoulders to estimate the stress concentration factors.Explain.
5-63
The figure shows a shaft mounted in bearings at A and D and having pulleys at B and C. The
forces shown acting on the pulley surfaces represent the belt tensions. The shaft is to be made of
AISI 1035 CD steel. Using a conservative failure theory with a design factor of 2, determine the
minimum shaft diameter to avoid yielding.
f-in R
300 Ibf
50 lbf
59 Ibf
392 lbf D
Problem 5-63
C 6 in
8-in D.
8 in
B
8 in
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK SHIGLEY'S MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DE
Ch. 6 - A 10-mm steel drill rod was heat-treated and...Ch. 6 - Prob. 2PCh. 6 - A steel rotating-beam test specimen has an...Ch. 6 - A steel rotating-beam test specimen has an...Ch. 6 - A steel rotating-beam test specimen has an...Ch. 6 - Repeat Prob. 6-5 with the specimen having an...Ch. 6 - A steel rotating-beam test specimen has an...Ch. 6 - Derive Eq. (6-17). Rearrange the equation to solve...Ch. 6 - For the interval 103 N 106 cycles, develop an...Ch. 6 - Estimate the endurance strength of a...
Ch. 6 - Two steels are being considered for manufacture of...Ch. 6 - A 1-in-diamctcr solid round bar has a groove...Ch. 6 - A solid square rod is cantilevered at one end. The...Ch. 6 - A rectangular bar is cut from an AISI 1020...Ch. 6 - A solid round bar with diameter of 2 in has a...Ch. 6 - The rotating shaft shown in the figure is machined...Ch. 6 - The shaft shown in the figure is machined from...Ch. 6 - Solve Prob. 6-17 except with forces F1 = 1200 lbf...Ch. 6 - Bearing reactions R1 and R2 are exerted on the...Ch. 6 - A bar of steel has the minimum properties Se = 40...Ch. 6 - Repeat Prob. 6-20 but with a steady torsional...Ch. 6 - Repeat Prob. 6-20 but with a steady torsional...Ch. 6 - Repeat Prob. 6-20 but with an alternating...Ch. 6 - A bar of steel has the minimum properties Se = 40...Ch. 6 - The cold-drawn AISI KUO steel bar shown in the...Ch. 6 - Repeat Prob. 6-25 for a load that fluctuates from...Ch. 6 - An M14 2 hex-head bolt with a nut is used to...Ch. 6 - The figure shows a formed round-wire cantilever...Ch. 6 - The figure is a drawing of a 4- by 20-mm latching...Ch. 6 - The figure shows the free-body diagram of a...Ch. 6 - Solve Prob. 6-30 except let w1 = 2.5 in. w2 = l.5...Ch. 6 - For the part in Prob. 630, recommend a fillet...Ch. 6 - Prob. 33PCh. 6 - Prob. 34PCh. 6 - A part is loaded with a combination of bending,...Ch. 6 - Repeat the requirements of Prob. 6-35 with the...Ch. 6 - 6-37 to 6-46For the problem specified in the build...Ch. 6 - 6-37 to 6-46For the problem specified in the build...Ch. 6 - 637 to 646 For the problem specified in the table,...Ch. 6 - For the problem specified in the table, build upon...Ch. 6 - 6-37 to 6-46 For the problem specified in the...Ch. 6 - 6-37 to 6-46 For the problem specified in the...Ch. 6 - 6-37 to 6-46 For the problem specified in the...Ch. 6 - Problem Number Original Problem, Page Number 637...Ch. 6 - 6-37 to 6-46 For the problem specified in the...Ch. 6 - 6-37 to 6-46 For the problem specified in the...Ch. 6 - 6-47 to 6-50 For the problem specified in the...Ch. 6 - 6-47 to 6-50 For the problem specified in the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 49PCh. 6 - Prob. 50PCh. 6 - 6-51 to 6-53 For the problem specified in the...Ch. 6 - 6-51 to 6-53 For the problem specified in the...Ch. 6 - 6-51 to 6-53 For the problem specified in the...Ch. 6 - Solve Prob. 6-17 except include a steady torque of...Ch. 6 - Solve Prob. 618 except include a steady torque of...Ch. 6 - In the figure shown, shaft A, made of AISI 1020...Ch. 6 - A schematic of a clutch-testing machine is shown....Ch. 6 - For the clutch of Prob. 657, the external load P...Ch. 6 - A flat leaf spring has fluctuating stress of max =...Ch. 6 - A rotating-beam specimen with an endurance limit...Ch. 6 - A machine part will be cycled at 350 MPa for 5...Ch. 6 - The material properties of a machine part are Sut...Ch. 6 - Repeat Prob. 662 using the Goodman criterion....
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Repeat Problem 10.3-15 using L = 3.5 m, max = 3 mm, and EI = 800 kN·m2.arrow_forwardWhat is the maximum power that can be delivered by a hollow propeller shaft (outside diameter 50 mm, inside diameter 40 mm, and shear modulus of elasticity 80 GPa) turning at 600 rpm if the allowable shear stress is 100 MPa and the allowable rate of twist is 3.0°/m?arrow_forwardA crank arm consists of a solid segment of length bxand diameter rf, a segment of length bltand a segment of length byas shown in the figure. Two loads P act as shown: one parallel to — vand another parallel to —y. Each load P equals 1.2 kN. The crankshaft dimensions are A] = 75 mm, fr> = 125 mm, and b3= 35 mm. The diameter of the upper shaft isd = 22 mm, (a) Determine the maximum tensile, compressive, and shear stresses at point A, which is located on the surface of the shaft at the z axis. (b) Determine the maximum tensile, compressive, and shear stresses at point B, which is located on the surface of the shaft at the y axisarrow_forward
- A magnesium-alloy wire of diameter d = 4mm and length L rotates inside a flexible tube in order to open or close a switch from a remote location (see figure). A torque Tis applied manually (either clockwise or counterclockwise) at end 5, thus twisting the wire inside the tube. At the other end A, the rotation of the wire operates a handle that opens or closes the switch. A torque T0 = 0.2 N · m is required to operate the switch. The torsional stiffness of the tube, combined with friction between the tube and the wire, induces a distributed torque of constant intensity t = 0.04N m/m (torque per unit distance) acting along the entire length of the wire. (a) If the allowable shear stress in the wire is T allow = 30 MPa, what is the longest permissible length Lmaxof the wire?arrow_forwardA gear reduction unit uses the countershaft shown in the figure. Gear A receives power from another gear with the transmitted force FA applied at the 20 pressure angle as shown. The power is transmitted through the shaft and delivered through gear B through a transmitted force Fg at the pressure angle shown. For the steel countershaft shown below, assume the bearings have a maximum slope specification of 0.064" for good bearing life. Does the dia shown below meet the requirement? if not determine a suitable shaft diameter. 1.25-in da Gear A F₁-300- Gear B Sindia The minimum shaft diameter is in.arrow_forwardThe shaft shown in the figure is machined from AISI 1040 CD steel. The shaft rotates at 1600 rpm and is supported in rolling bearings at A and B. The applied forces are F1 = 2500 lbf and F2 = 2500 lbf. The location of critical bending moment from 10.5" from point A, where bending moment is 14 750 lbf·in. Determine the minimum fatigue factor of safety based on achieving infinite life. Yield strength is 71 kpsi. If infinite life is not predicted, estimate the number of cycles to failure. Also check for yielding. Note: for the given ratio of r/d = 0.0625/1.625 = 0.04, D/d = 1.875/1.625 = 1.15 the stress concentration is given by K, =1.95. Also, use the correction of the endurance limit based on the surface factor, ka, size factor, kb, and loading factor, ke -8 in- -8 in- -8 in- 3 in -10 in- -10 in in All fillets in R. 1/4arrow_forward
- The shaft shown in the figure is machined from AISI 1040 CD steel. The shaft rotates at 1600 rpm and is supported in rolling bearings at A and B. The applied forces are F₁ = 1600 lbf and F2 = 640 lbf. A steady torque of 1600 lbf-in is being transmitted through the shaft between the points of application of the forces. T A ↑ in -10 in- F₁ F₂ -10 in- All fillets in R. 12 in 3 in in- B T 3 NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. What is the value of the theoretical stress concentration factor for bending, the notch sensitivity, and the fatigue stress concentration factor? (You must provide an answer before moving to the next part.) The value of the theoretical stress concentration factor for bending is The value of the notch sensitivity is The value of the fatigue stress concentration factor isarrow_forwardA,B,C,D,E,F,G WHICH POINT PLS WRITE THE LETTER AS UR FINAL ANSWER THXarrow_forward7-5 A rotating step shaft is loaded as shown, where the forces FA and F3 are constant at 600 lbf and 300 lbf. respectively, and the torque T alternates from 0 to 1800 lbf - in. The shaft is to be considered simply supported at points O and C, and is made of AISI 1045 CD steel with a fully corrected endurance limit of S₂ = 40 kpsi. Let Kf = 2.1 and K = 1.7. For a design factor of 2.5 determine the minimal acceptable diameter of section BC using the (a) DE-Gerber criterion. (b) DE-Goodman criterion. n 6 in FA = 600 lbf 6 in FB = 300 lbf 6 in T, n Page 413arrow_forward
- The shaft shown in the figure is machined from AISI 1040 CD steel. The shaft rotates at 1600 rpm and is supported in rolling bearings at A and B. The applied forces are F1 = 1600 lbf and F2 = 640 lbf. A steady torque of 1600 lbf·in is being transmitted through the shaft between the points of application of the forces.arrow_forwardFrom our study guide, very hard to understand... please explain steps to solution in detail.arrow_forward6-28 The figure shows a formed round-wire cantilever spring subjected to a varying force. The hardness tests made on 50 springs gave a minimum hardness of 400 Brinell. It is apparent from the mounting details that there is no stress concentration. A visual inspection of the springs indicates that the surface finish corresponds closely to a hot- rolled finish. Ignore curvature effects on the bending stress. What number of applica- tions is likely to cause failure? Solve using: (a) Goodman criterion. (b) Gerber criterion. = 40 lbf max 12 in- = 20 lbf min Problem 6-28arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license