
Mathematics for Machine Technology
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781133281450
Author: John C. Peterson, Robert D. Smith
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 56, Problem 13AR
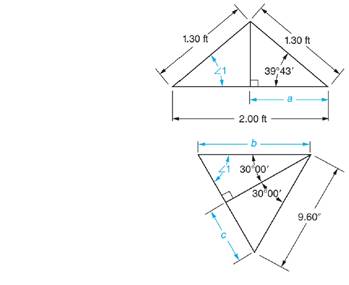
a. Determine:
(1)
(2) Side a
b. Determine:
(1)
(2) Side b
(3) Side c
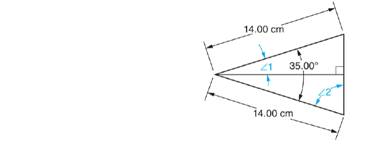
c. Determine:
(1)
(2)
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Evaluate the following integrals, where in each case y is the unit circle taken once
anticlockwise. (Standard results may be quoted without proof.)
(i) [|z|dz
(ii) L
cos(1/2)
dz;
(iii) z +31² dz;
(iv)
L
exp(22)
tan z dz;
dz.
z(x+4)
State Liouville's Theorem on entire functions and the Maximum Modulus Principle.
Let p(z) = z″ + an−12″ ¹ + ... + a1z + ao be a nonconstant polynomial. Show
that there is a number R> 0 such that
|2|n
|p(z)|≥
for |z|> R.
2
By considering f(z) =
in C.
P(2)
and using the results above, deduce that p has a zero
A power series Σan has radius of convergence R > 0 and defines a function
f(z) on {z C || < R}. Write down the power series for the functions f'(z)
and f(22), and state without proof their radii of convergence.
Show that there is an entire function ƒ : C→ C, expressible as the sum of a power
series, such that
f(0) = 0, f'(0) = 0, and f"(z) = exp(22) for all z Є C.
Chapter 56 Solutions
Mathematics for Machine Technology
Ch. 56 - Add, subtract, multiply, or divide each of the...Ch. 56 - Determine A.Ch. 56 - Prob. 3ARCh. 56 - Express 68.85 as degrees and minutes.Ch. 56 - Express 64.1420 as degrees, minutes, and seconds.Ch. 56 - Express 3723' as decimal degrees to 2 decimal...Ch. 56 - Express 10338'43" as decimal degrees to 4 decimal...Ch. 56 - Using a simple protractor, measure each of the...Ch. 56 - Prob. 9ARCh. 56 - Write the complement of each of the following...
Ch. 56 - Write the complement of each of the following...Ch. 56 - Given: ABCD and FEGH . Determine the value of each...Ch. 56 - a. Determine: (1) 1 (2) Side a b. Determine: (1) 1...Ch. 56 - a. Given: a=8.400 and b=9.200 . Find c. b. Given:...Ch. 56 - Compute 1.Ch. 56 - Determine the circumference of a circle that has a...Ch. 56 - Determine the diameter of a circle that has a...Ch. 56 - a. Given: CD=184 mm and CE=118 mm. Determine CF...Ch. 56 - a. Given: EB=5.150. Determine AE . b. Given:...Ch. 56 - Given: Points A and E are tangent points. EB is a...Ch. 56 - a. Given: AC=110andr=4.700 Compute arc length AC...Ch. 56 - a. Given: Dia H=14.520 and d=8.300. Compute Dia M....Ch. 56 - Prob. 23ARCh. 56 - a. Given: x=360 inches and y=5.10 inches. Compute...Ch. 56 - Prob. 25ARCh. 56 - A flat is cut on a circular piece as shown....Ch. 56 - A spur gear is shown. Pitch circles of spur gears...Ch. 56 - Determine the arc length from point C to point D...Ch. 56 - Prob. 29ARCh. 56 - Determine dimension x to 3 decimal places.Ch. 56 - Refer to the drill jig shown. Determine 1.Ch. 56 - Prob. 32ARCh. 56 - Prob. 33ARCh. 56 - Lay out the template shown. Make the layout full...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A polynomial p of degree n has all its zeros in the disc of radius R centred at 0. Quoting a theorem from the course, write down the value of 1 2πί La P(z) 'p'(z) dz, where is the circle of radius 2R centred at 0. γarrow_forwardCalculate the following integrals using complex variable techniques. ᏧᎾ 2π (i) S 1+8 cos20 (ii) I COS x dz x²-2x+5 Leave your answers in terms of real functions of real variables.arrow_forwardFor each of the following functions determine whether it is the real part of a differentiable function defined on C. If it is, determine a corresponding imaginary part. (i) u(x, y) = x² - y²+4xy; (ii) u(x, y) = x³ — y³ + 3x²y. -arrow_forward
- Let A be an algebra and X C A a subset. Recall that the centraliser of X in A is defined to be == C(X) = {a A | ax = xa for all x = X}. Let U = { (o b) : a, b, c & R} ≤ M₂(R). C as in Question 1. (i) Show that the centraliser of U in M₂(R) is: C(U) = {(o 9 ) ; a € R} . 0 : (ii) Let M=R2, the natural module for U. Show that Endu (M) = R. (iii) Find all one-dimensional submodules of M. (iv) Is MXY for some submodules X, Y of M? (no proof is required for this part.)arrow_forwardLet A be a finite-dimensional algebra. Prove that A is a semisimple algebra if and only if every left ideal I of A admits a complement (so there exists a left ideal J such that A = I J as vector spaces). You I may assume that if a module M can be written as a sum of simple modules M = S₁+ S₂++ Sn, then we can find a subset R C {1, 2, ………, n} such that DER ST is a direct sum of simples. You may also assume that every non-zero finite-dimensional module has a simple submodule. M =arrow_forwardShow that these two matrices generate the algebra M₂(Q) over the field Q. 0 1 S := and T = == -1 - -1 (13)arrow_forward
- Let G = S3, the symmetric group on 3 letters. Show that K(X,Y) KG - (X21, YX XY², Y³ —– 1) ' - (Hint: Write S3 (12) and Y X S3 as a group.) = {id, (12), (23), (13), (123), (132)}. Consider the map from → (123). You may assume that these two elements generatearrow_forwardConsider a simplified two-joint robotic arm where the two joints are connected by rigid links.Each joint has a mass, and the links are modeled as idealized rods. The motion of each jointaffects the other through the coupling of forces. The system can be modeled by the followingsecond-order coupled ODEs: m1θ1" + k1(θ1 − θrest) + k3(θ1 − θ2) = 0 (equation 1)m2θ2" + k2(θ2 − θrest) + k3(θ2 − θ1) = 0 (equation 2) where θ1(t) and θ2(t) represent the angular positions of the first and second joints, respec-tively. m1 and m2 are the effective masses at each joint. k1, k2 and k3 are the stiffnessconstants representing the elastic restoring forces in the joints and links. θrest = 0 representsthe equilibrium position for each joint.The parameters are:m1 = 1, m2 = 1, θrest = 0, k1 = 1, k2 = 2, k3 = 3, θrest = 0The initial conditions are:θ1(0) = 1, θ2(0) = 2Please solve by hand to get θ1(t) and θ2(t) using eigenvectors and eigenvalues. Show all steps/calculations, and provide a written description…arrow_forward3feet in 1secound; 21feet in x secondsarrow_forward
- (15 pts) Show your work to get full credit! Compute a QR factorization of the matrixarrow_forward(5) Let G be a group. Show that G acts on itself via the action g⚫a (i.e. using the binary operation of G) for all g, a Є G. [ for each of the three axioms, plus 1 for conclusion] = gaarrow_forward= (2) Let H {id, (12) (34), (13)(24), (14)(23)}. Prove that H is a sub- group of the symmetric group S4 of degree 4. each of the four axioms, plus 1 for the conclusion] 1 forarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:9780395977224
Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:McDougal Littell
Points, Lines, Planes, Segments, & Rays - Collinear vs Coplanar Points - Geometry; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dDWjhRfBsKM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Naming Points, Lines, and Planes; Author: Florida PASS Program;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F-LxiLSSaLg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY