
Concept explainers
Assuming that the front and rear axle loads remain in the same ratio as for the truck of Prob. 5.96, determine how much heavier a truck could safely cross the bridge designed in that problem.
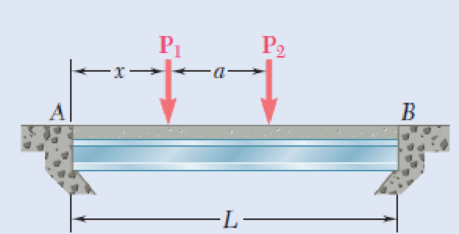
5.96 A bridge of length L = 48 ft is to be built on a secondary road whose access to trucks is limited to two-axle vehicles of medium weight. It will consist of a concrete slab and of simply supported steel beams with an ultimate strength σU = 60 ksi. The combined weight of the slab and beams can be approximated by a uniformly distributed load w = 0.75 kips/ft on each beam. For the purpose of the design, it is assumed that a truck with axles located at a distance a = 14 ft from each other will be driven across the bridge and that the resulting concentrated loads P1 and P2 exerted on each beam could be as large as 24 kips and 6 kips, respectively. Determine the most economical wide-flange shape for the beams, using LRFD with the load factors γD = 1.25, γL = 1.75 and the resistance factor ϕ = 0.9. [Hint: It can be shown that the maximum value of |ML| occurs under the larger load when that load is located to the left of the center of the beam at a distance equal to aP2/2(P1 + P2).]
Fig. P5.96
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
- I need answer as soon as possible, do correctly pleasearrow_forwardProblem 5 Rigid member ABC is supported with two links BE and CD which have a cross section area of 230 and 300 mm? respectively. Determine the maximum applied force Q knowing that the maximum movement of point E is 0.45 mm. D Brass E - 105 GPa 230 mm B C E Aluminum E = 70 GPa 150 mm 65 mm 230 mm Area given is for member AB not BE Cross section area of links AB and CD are 230 and 300 mm^2 respectively.arrow_forwardQ.I. An I-section beam, 150 mm wide by 250 mm deep, with flange and web of thickness 20 mm is used as a simply supported beam over a span of 7 m. The beam carries a distributed load of 6 kN/m and a concentrated load of 30 kN at mid-span. Determine: (a) the second moment of area of the cross- section of the girder, (b) the maximum stress set-up. 20 mm 150 mm B 20 mm 250 mm 20 mmarrow_forward
- The left half of the simply supported beam carries a uniformlydistributed load of intensity 600 N/m. If E = 10 GPa, determinethe smallest value of I that limits the midspan displacement to1/360th of the span.arrow_forwardI need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forwardThe cantilever beam BC is attached to the steel cable AB as shown. Knowing that the cable is initially taut, determine the tension in the cable caused by the distributed load shown. Use E = 200 GPa.arrow_forward
- 4. For the braced beam and loading shown; (a) draw free body diagram, (b) determine the magnitude force of member BE, and (c) determine the magnitude of the force on the support A | 50 N 20 KNAM D 15 m * 1m 3 m 30° Earrow_forwardHomework A timber beam AB of length L and rectangular cross section carries a single concentrated load P at its midpoint C. (a) Show that the ratio Tm/Tm of the maximum values of the shearing and normal stresses in the beam is equal to h/2L, where h and L are, respectively, the depth and the length of the beam. (b) Determine the depth h and the width b of the beam, knowing that L = 2 m, P = 40 KN, T, = 960 kPa, and om = 12 MPa. m · L/2 C - L/2· A Вarrow_forwardThe load on the beam shown increases uniformly from 0 at point A to w = 63 N/m at point B over a length of L= 26 meters. Determine the magnitude of the support reaction at point B. Carrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





