
Concept explainers
The beam AB supports a uniformly distributed load of 480 lb/ft and two concentrated loads P and Q. The normal stress due to bending on the bottom edge of the lower flange is +14.85 ksi at D and +10.65 ksi at E. (a) Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the beam. (b) Determine the maximum normal stress due to bending that occurs in the beam.
Fig. P5.63
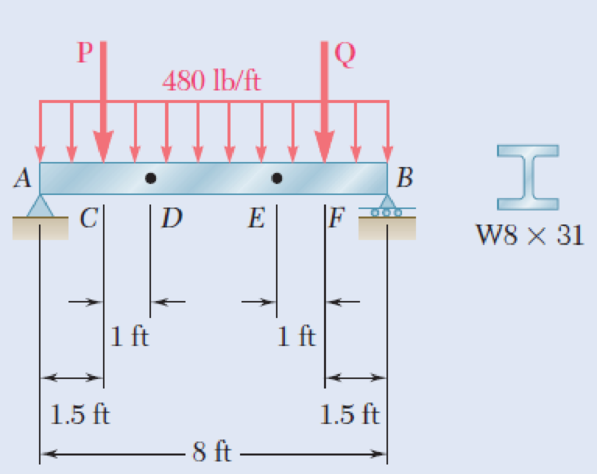
(a)
Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the beam.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The normal stress due to bending at the point D is
The normal stress due to bending at the point E is
Refer to Appendix C “Properties of Rolled-Steel Sections” in the textbook.
The section modulus (S) for
Determine the bending moment at point D
Here, the normal stress at point D is
Substitute 14.85 ksi for
Determine the bending moment at point E
Here, the normal stress at point E is
Substitute 10.65 ksi for
Show the free-body diagram of the region DE as in Figure 1.
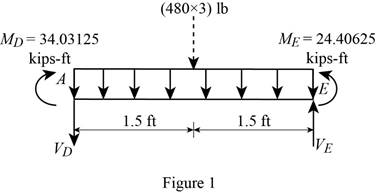
Determine the vertical reaction at point D by taking moment about point E.
Show the free body diagram of the region ACD as in Figure 2.
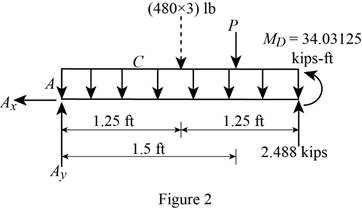
Determine the magnitude of the load P by taking moment about the point A.
Determine the vertical reaction at point A by resolving the vertical component of forces.
Show the free body diagram of the entire beam as in Figure 3.
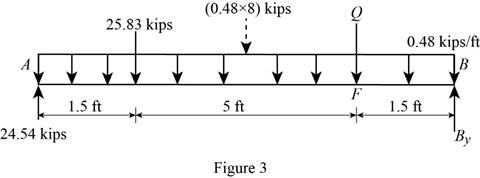
Determine the magnitude of the load P by taking moment about the point B.
Determine the vertical reaction at point A by resolving the vertical component of forces.
Shear force:
Show the calculation of shear force as follows;
Show the calculated shear force values as in Table 1.
| Location (x) ft | Shear force (V) kips |
| A | 24.54 |
| C (Left) | 23.82 |
| C (Right) | –2.01 |
| F (Left) | –4.41 |
| F (Right) | –13.12 |
| B | –13.84 |
Plot the shear force diagram as in Figure 4.
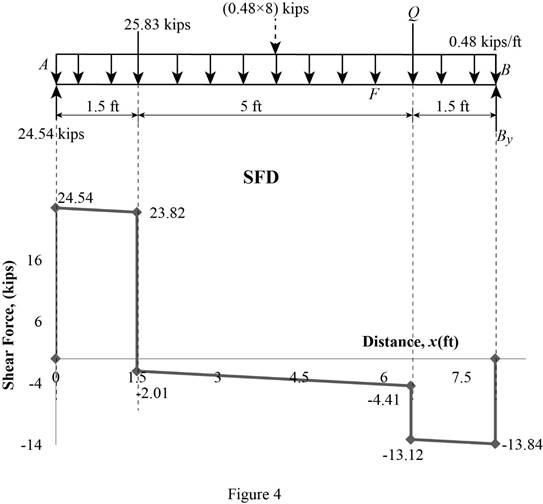
Bending moment:
Show the calculation of the bending moment as follows;
Show the calculated bending moment values as in Table 2.
| Location (x) ft | Bending moment (M) kips-ft |
| A | 0 |
| C | 36.27 |
| F | 19.77 |
| B | 0 |
Plot the bending moment diagram as in Figure 5.
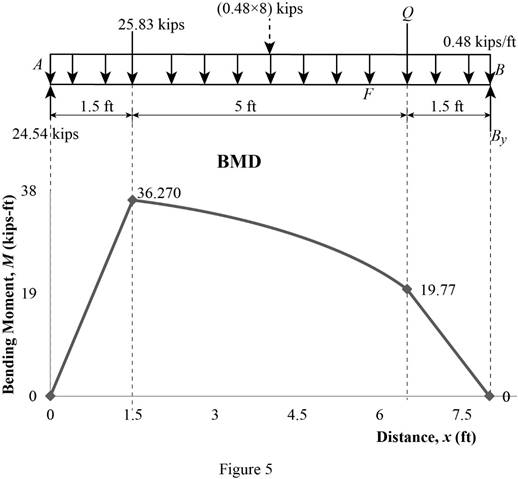
Refer to Figure 5;
The maximum absolute bending moment is
(b)
The maximum normal stress due to bending.
Answer to Problem 63P
The maximum normal stress due to bending is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Refer to Appendix C “Properties of Rolled-Steel Sections” in the textbook.
The section modulus (S) for
The maximum absolute bending moment is
Determine the maximum normal stress
Substitute
Therefore, the maximum normal stress due to bending is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
- (B) Q: The cantilever beam shown below has a circular cross section of 50mm outer diameter. Portion AB of the beam is hollow, with an inner diameter of 35mm. If the allowable bending stress is 140 MPa, determine (1) the largest allowable uniformly distributed load (w) that can be applied to the beam; (2) the bending stress at a point that is 7 mm below the top of the beam at section D. 50 mm W D B O! 35 mm A - 750 mm 250 mmarrow_forwardFind maximum bending stress and its location, bending stress at a point 20mm from the top of the beam on section Barrow_forward7arrow_forward
- 201 (A) Q: For the beam ABCD carries a uniformly distributed load (w) as shown in the figure below. Portions AB and CD of the beam is hollow. If the allowable bending stress is 60 MPa, determine (1) the largest allowable value of the uniformly distributed load (w) that can be applied to the beam; (2) the bending stresse at a point that is 30 mm above the bottom of the beam at the section of maximum positive moment. 20mm w kN/m 200mm 160mm 2m 2m 20mm A AT 2 m B 20mm H 60mm 20mm Sec. (AB), (CD) 100mm Sec. (BC)arrow_forward9. Draw the shearing-force and bending-moment diagrams for the following beams: A cantilever of length 20 m carrying a load of 10 kN at a distance of 15 m from the supported end. A cantilever of length 20 m carrying a load of 10 KN uniformly distributed over the inner 15 m of its length. A cantilever of length 12 m carrying a load of 8 kN, applied 5 m from the supported end, and a load of 2kN/m over its whole length. A beam, 20 m span, simply-supported at each end and carrying a vertical load of 20 kN at a distance 5 m from one support. A beam, 16 m span, simply-supported at each end and carrying a vertical load of 2.5 kN at a distance of 4 m from one support and the beam itself weighing 500 N per i. ii. iii. iv. V. metre.arrow_forward5.7 For the cantilever beam shown in the figure, find (a) the maximum bending stress and its location; and (b) the bending stress at a point 20 mm from the top of the beam on section B. 1.0 kN/m 150 mm C A 2 m- 50 mm 6 m FIG. PS.7arrow_forward
- 5.41 The inverted T-beam supports three concentrated loads as shown in the fig- ure. Find the maximum allowable value of Pif the bending stresses are not to exceed 3.5 ksi in tension and 8 ksi in compression. 14P 1.0 in. D 8 in. 1.0 in. 2 ft 3 ft 3 (t 2 tt - 4 int FIG. PS.41arrow_forwardStrength of Materialsarrow_forwardd 5.23 Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the beam and loading shown and determine the maximum normal stress due to bending. 80 kN/m 160 kN B C ID A E Hinge- W310 × 60 -2.4 m 1.5 m 1.5 m 0.6 marrow_forward
- Draw the shear and moment diagram. Find the maximum bending stress and its location.arrow_forwardDraw the shearing-force and bending-moment diagrams for the following beams: 1. A cantilever of length 20 m carrying a load of 10 kN at a distance of 15 m from the supported end. 2. A cantilever of length 20 m carrying a load of 10 kN is uniformly distributed over the inner 15 m of its length. 3. A cantilever of length 12 m carrying a load of 8 kN, applied 5 m from the supported end, and a load of 2kNlm over its whole length.arrow_forwardDraw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the beam and loading shown and determine the maximum normal stress due to bendingarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





