
Concept explainers
(a)
To find: The
(a)
Answer to Problem 43UYK
Solution: The probability is 0.9953.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: When a coin is tossed, there are two possible outcomes, “heads” or “tails.” The probability of the heads coming up in a coin toss is calculated as:
The average of the sample proportion is calculated as:
The standard deviation of the sample proportion is calculated as:
Hence, the average value and standard deviation are 0.5 and 0.03536, respectively. Now, calculate the z-score,
The lower bound is
Calculate the z-score for the upper bound
Now, Excel is used to calculate the left tailed areas between the z scores. Use the formula
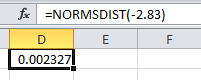
Use the formula
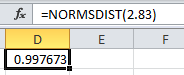
The area between them is calculated by subtracting the above values as:
Hence, the probability is 0.9953.
(b)
To find: The probability of the sample proportion of heads between 0.45 and 0.55 by using normal to the binomial approximate.
(b)
Answer to Problem 43UYK
Solution: The probability is 0.8426.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: When a coin is tossed, there are two possible outcomes, “heads” or “tails.”
The probability of the heads coming up in a coin toss is calculated as:
The average of the sample proportion is calculated as:
The standard deviation of the sample proportion is calculated as:
Hence, the average value and standard deviation are 0.5 and 0.03536 respectively. Now, calculate the z-score,
The lower bound is
Calculate the z-score for the upper bound
Now, Excel is used to calculate the left tailed areas between the z scores. Use the formula
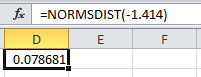
Use the formula
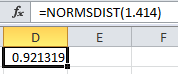
The area between them is calculated by subtracting the above values as:
Hence, the probability is 0.8426
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics: w/CrunchIt/EESEE Access Card
- 2. Which of the following statements are (not) true? lim sup{An U Bn} 818 lim sup{A, B} 818 lim inf{An U Bn} 818 818 lim inf{A, B} An An A, Bn- A, BnB →B = = = lim sup A, U lim sup Bn; 818 818 lim sup A, lim sup Bn; 818 81U lim inf A, U lim inf Bn; 818 818 lim inf A, lim inf Bn; n→X 818 An U BRAUB as no; An OBRANB as n→∞.arrow_forwardThroughout, A, B, (An, n≥ 1), and (Bn, n≥ 1) are subsets of 2. 1. Show that AAB (ANB) U (BA) = (AUB) (AB), Α' Δ Β = Α Δ Β, {A₁ U A2} A {B₁ U B2) C (A1 A B₁}U{A2 A B2).arrow_forward16. Show that, if X and Y are independent random variables, such that E|X|< ∞, and B is an arbitrary Borel set, then EXI{Y B} = EX P(YE B).arrow_forward
- Proposition 1.1 Suppose that X1, X2,... are random variables. The following quantities are random variables: (a) max{X1, X2) and min(X1, X2); (b) sup, Xn and inf, Xn; (c) lim sup∞ X and lim inf∞ Xn- (d) If Xn(w) converges for (almost) every w as n→ ∞, then lim- random variable. → Xn is aarrow_forwardExercise 4.2 Prove that, if A and B are independent, then so are A and B, Ac and B, and A and B.arrow_forward8. Show that, if {Xn, n ≥ 1) are independent random variables, then sup X A) < ∞ for some A.arrow_forward
- 8- 6. Show that, for any random variable, X, and a > 0, 8 心 P(xarrow_forward15. This problem extends Problem 20.6. Let X, Y be random variables with finite mean. Show that 00 (P(X ≤ x ≤ Y) - P(X ≤ x ≤ X))dx = E Y — E X.arrow_forward(b) Define a simple random variable. Provide an example.arrow_forward17. (a) Define the distribution of a random variable X. (b) Define the distribution function of a random variable X. (c) State the properties of a distribution function. (d) Explain the difference between the distribution and the distribution function of X.arrow_forward16. (a) Show that IA(w) is a random variable if and only if A E Farrow_forward15. Let 2 {1, 2,..., 6} and Fo({1, 2, 3, 4), (3, 4, 5, 6}). (a) Is the function X (w) = 21(3, 4) (w)+711.2,5,6) (w) a random variable? Explain. (b) Provide a function from 2 to R that is not a random variable with respect to (N, F). (c) Write the distribution of X. (d) Write and plot the distribution function of X.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

