
(a)
To draw:
Tree diagram for the given data
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Percentage of employees who use drugs
Percentage of employees whose drug test gave false positive result
Percentage of employees whose drug test gave false negative result
Let the
The event of “employees who do not take illegal drugs” be denoted by ND.
The event of “employees whose result was positive” be denoted by P.
The event of “employees whose result was negative” be denoted by N.
Graph:
The tree diagram is
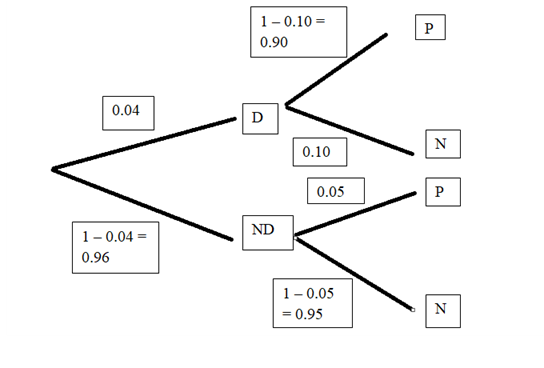
(b)
To calculate:
(b)
Answer to Problem R5.7RE
Probability that the drug test result positive is 0.084.
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Calculation:
From the tree diagram in the sub part a,
(c)
To calculate: Probability that an employee uses illegal drugs given the result is positive.
(c)
Answer to Problem R5.7RE
Probability that an employee uses illegal drugs given the result is positive is 0.42857.
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Calculation:
From the sub part b,
Chapter 5 Solutions
PRACTICE OF STATISTICS F/AP EXAM
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Introductory Statistics
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
- Please could you explain why 0.5 was added to each upper limpit of the intervals.Thanksarrow_forward28. (a) Under what conditions do we say that two random variables X and Y are independent? (b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) = E(X)E(Y); (e) Show by a counter example that the converse of (ii) is not necessarily true.arrow_forward1. Let X and Y be random variables and suppose that A = F. Prove that Z XI(A)+YI(A) is a random variable.arrow_forward
- (c) Utilize Fubini's Theorem to demonstrate that E(X)= = (1- F(x))dx.arrow_forward(c) Describe the positive and negative parts of a random variable. How is the integral defined for a general random variable using these components?arrow_forward26. (a) Provide an example where X, X but E(X,) does not converge to E(X).arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





