
Concept explainers
The U.S. Coast Guard (USCG) provides a wide variety of information on boating accidents including the wind condition at the time of the accident. The following table shows the results obtained for 4401 accidents (USCG website, November 8, 2012). 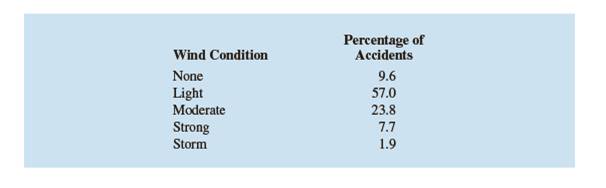
Let x be a random variable reflecting the known wind condition at the time of each accident.
Set
a. a
b. Compute the
c. Compute the variance and standard deviation for x.
d. Comment on what your results imply about the wind conditions during boating accidents.
a.
The probability distribution of x.
Answer to Problem 59SE
The probability distribution is:
| 0 | 0.096 |
| 1 | 0.57 |
| 2 | 0.238 |
| 3 | 0.077 |
| 4 | 0.019 |
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The results of wind condition at the time of 4401 accident are as given in the following table:
| Wind condition | Percentage of Accident |
| None | 9.6 |
| Light | 57 |
| Moderate | 23.8 |
| Strong | 7.7 |
| Strom | 1.9 |
Formula used:
The formulas are:
Calculation:
Consider,
Set
That is,
Thus, the required probability distribution of
|
|
|
| 0 | 0.096 |
| 1 | 0.57 |
| 2 | 0.238 |
| 3 | 0.077 |
| 4 | 0.019 |
b.
To find:The expected value of
Answer to Problem 59SE
The expected value of x is 1.353.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The expected value of x can be computed as:
Hence, the expected value of x is 1.353.
c.
To find: The standard deviation and variance of x.
Answer to Problem 59SE
The variance and standard deviation of x are 0.68839 and 0.8296 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The variance and standard deviation of x can be computed as:
Hence, the variance and standard deviation of x are 0.68839 and 0.8296 respectively.
d.
To explain: The wind condition during boating accidents.
Explanation of Solution
The wind condition during the boating accidents can be understood from the results obtained in part b and c. That is,
On an average the wind condition during the boating accidents is 1.353 and the dispersion or the variance in the wind condition is 0.68839.
In other words, the wind condition on an average is approximately 135.3% and variability of wind condition is nearly 68.839% during the boating accidents.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Essentials of Modern Business Statistics with Microsoft Office Excel (Book Only)
- 2. Which of the following statements are (not) true? lim sup{An U Bn} 818 lim sup{A, B} 818 lim inf{An U Bn} 818 818 lim inf{A, B} An An A, Bn- A, BnB →B = = = lim sup A, U lim sup Bn; 818 818 lim sup A, lim sup Bn; 818 81U lim inf A, U lim inf Bn; 818 818 lim inf A, lim inf Bn; n→X 818 An U BRAUB as no; An OBRANB as n→∞.arrow_forwardThroughout, A, B, (An, n≥ 1), and (Bn, n≥ 1) are subsets of 2. 1. Show that AAB (ANB) U (BA) = (AUB) (AB), Α' Δ Β = Α Δ Β, {A₁ U A2} A {B₁ U B2) C (A1 A B₁}U{A2 A B2).arrow_forward16. Show that, if X and Y are independent random variables, such that E|X|< ∞, and B is an arbitrary Borel set, then EXI{Y B} = EX P(YE B).arrow_forward
- Proposition 1.1 Suppose that X1, X2,... are random variables. The following quantities are random variables: (a) max{X1, X2) and min(X1, X2); (b) sup, Xn and inf, Xn; (c) lim sup∞ X and lim inf∞ Xn- (d) If Xn(w) converges for (almost) every w as n→ ∞, then lim- random variable. → Xn is aarrow_forwardExercise 4.2 Prove that, if A and B are independent, then so are A and B, Ac and B, and A and B.arrow_forward8. Show that, if {Xn, n ≥ 1) are independent random variables, then sup X A) < ∞ for some A.arrow_forward
- 8- 6. Show that, for any random variable, X, and a > 0, 8 心 P(xarrow_forward15. This problem extends Problem 20.6. Let X, Y be random variables with finite mean. Show that 00 (P(X ≤ x ≤ Y) - P(X ≤ x ≤ X))dx = E Y — E X.arrow_forward(b) Define a simple random variable. Provide an example.arrow_forward17. (a) Define the distribution of a random variable X. (b) Define the distribution function of a random variable X. (c) State the properties of a distribution function. (d) Explain the difference between the distribution and the distribution function of X.arrow_forward16. (a) Show that IA(w) is a random variable if and only if A E Farrow_forward15. Let 2 {1, 2,..., 6} and Fo({1, 2, 3, 4), (3, 4, 5, 6}). (a) Is the function X (w) = 21(3, 4) (w)+711.2,5,6) (w) a random variable? Explain. (b) Provide a function from 2 to R that is not a random variable with respect to (N, F). (c) Write the distribution of X. (d) Write and plot the distribution function of X.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage





