
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
In the marked carbon atom, one s and three p orbital hybridize forming four
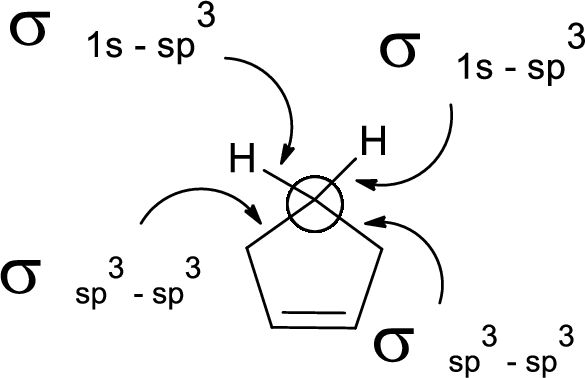
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
(b)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(b)
Explanation of Solution
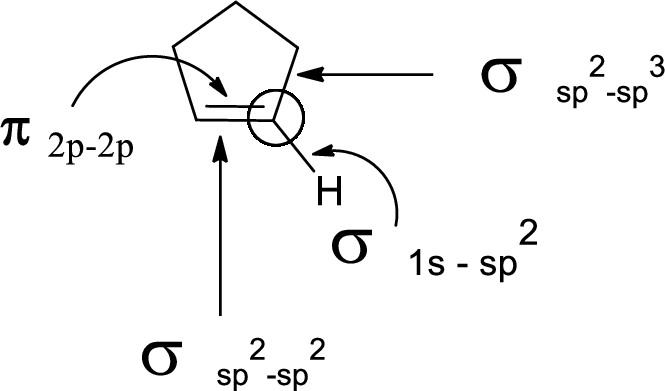
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
(c)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(c)
Explanation of Solution
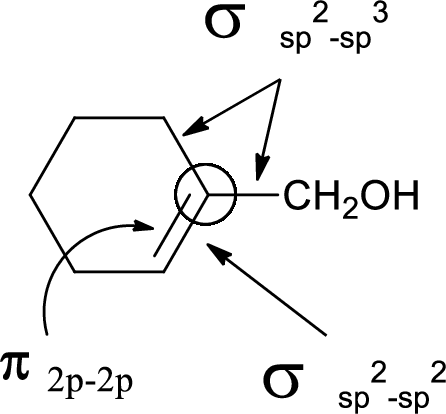
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
(d)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(d)
Explanation of Solution
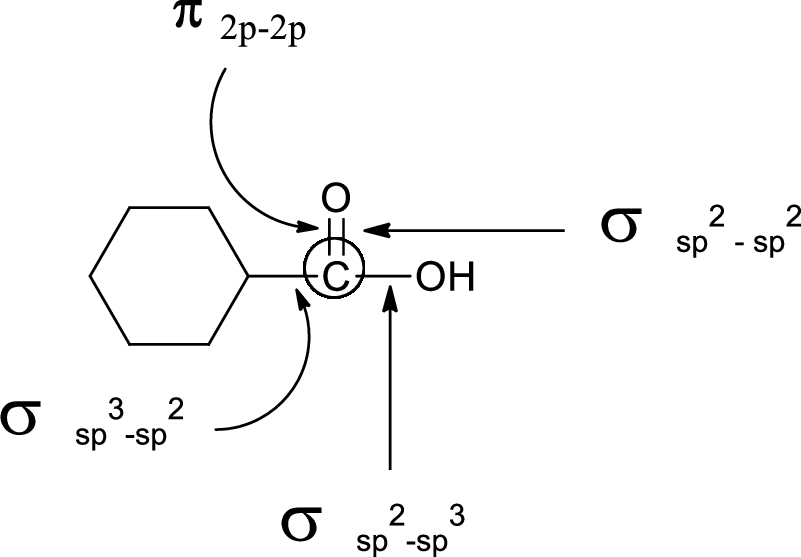
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
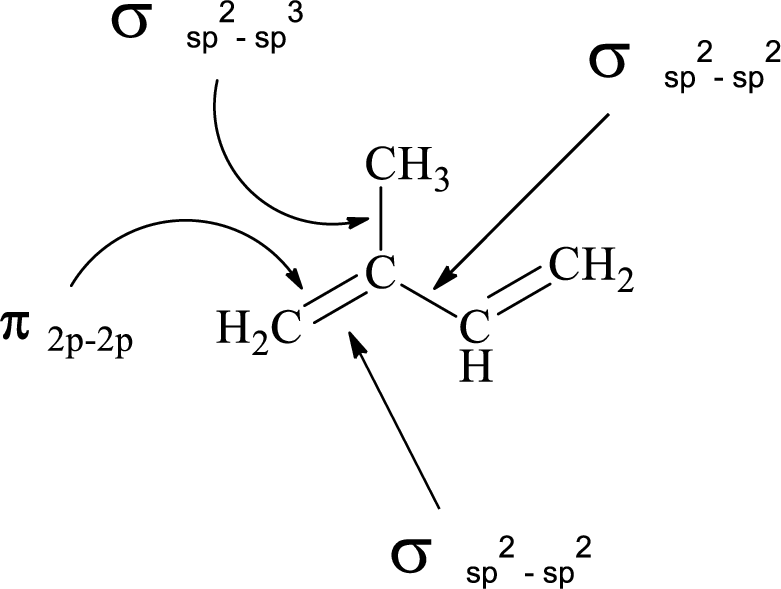
(e)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(e)
Explanation of Solution
In the marked carbon atom, one s and one p orbital hybridize forming two
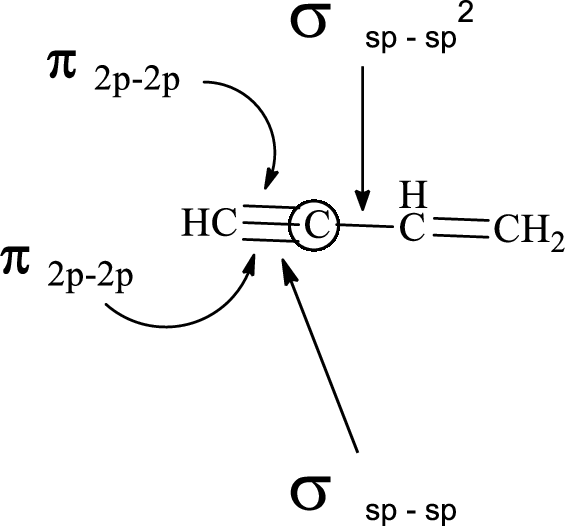
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
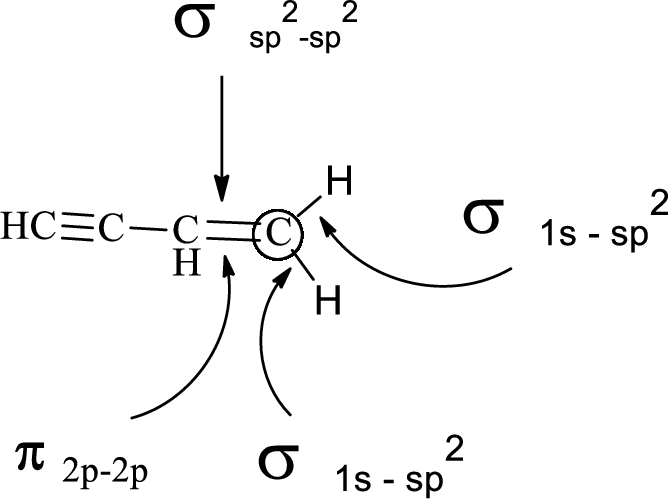
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





