
Concept explainers
What is each compound’s systematic name?
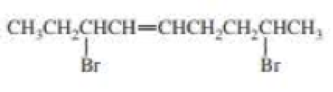
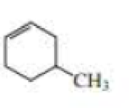
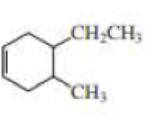
(a)
Interpretation:
Systematic name of the given compound should be determined.
Concept introduction:
- IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
- Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
- Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
- For alkenes, suffix will be ‘ene’.
- Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
- When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Answer to Problem 36P
Systematic name for given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given compound is,
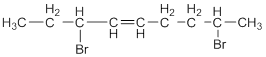
This reveals that the molecule contains a nine carbon chain with a double bond on the fourth carbon atom and two bromo groups on the third and eighth carbon atom respectively.
Therefore,
According with the IUPAC conventions the systematic name of the compound is,
(b)
Interpretation:
Systematic name of the given compound should be determined.
Concept introduction:
- IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
- Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
- Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
- For alkenes, suffix will be ‘ene’.
- Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
- When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
- E-Z designators are used as like cis-trans terminology for non-similar groups attached alkenes.
- In E-Z designations, the groups attached to vinylic positions are checked by their priority on the basis of higher molecular weight. If the higher priority groups are on the same sides, then the configuration is designated as Z. If the higher priority groups are on the opposite sides, then the configuration is designated as E.
Answer to Problem 36P
Systematic name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
Given,
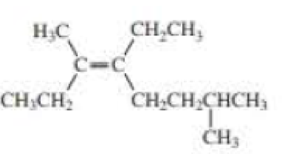
Compound is,
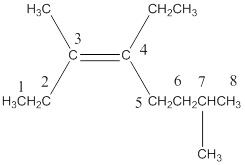
This reveals that the longest chain in the molecule contains eight carbon atoms with a double bond on third carbon atom and an ethyl group attached on the fourth carbon atom.
Two methyl groups were attached on the third and seventh carbon atom.
Therefore,
The systematic name of the compound is
(c)
Interpretation:
Systematic name of the given compound should be determined.
Concept introduction:
- IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
- Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
- Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
- For alkenes, suffix will be ‘ene’.
- Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
- When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Answer to Problem 36P
Systematic name of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
Given,
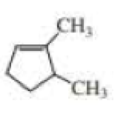
The structure of the compound is,
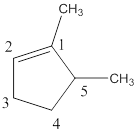
Structure of the compound reveals that that the given compound contains five membered carbon chain with double bond and on the first and fifth carbon atom methyl groups were attached.
Therefore,
The systematic name of the compound in accordance with IUPAC is,
(d)
Interpretation:
Systematic name of the given compound should be determined.
Concept introduction:
- IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
- Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
- Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
- For alkenes, suffix will be ‘ene’.
- Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
- When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
- E-Z designators are used as like cis-trans terminology for non-similar groups attached alkenes.
- In E-Z designations, the groups attached to vinylic positions are checked by their priority on the basis of higher molecular weight. If the higher priority groups are on the same sides, then the configuration is designated as Z. If the higher priority groups are on the opposite sides, then the configuration is designated as E.
Answer to Problem 36P
Systematic name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
Given,
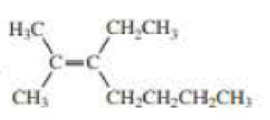
Structure of the compound is,
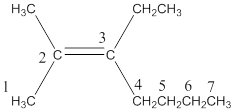
The structure of the compound reveals the molecule contains seven membered carbon chain with a double bond on the second carbon. On the third and second carbon atoms one ethyl and methyl group were attached.
Therefore the systematic name of the compound is
(e)
Interpretation:
Systematic name of the given compound should be determined.
Concept introduction:
- IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
- Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
- Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
- For alkenes, suffix will be ‘ene’.
- Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
- When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Answer to Problem 36P
Systematic name of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The struicture of the compound is,
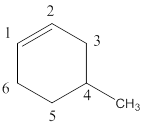
Structure of the compound reveals that that the given compound contains six membered carbon chain with double bond and on the fourth carbon atom one methyl group was attached.
Therefore,
The systematic name of the compound in accordance with IUPAC is,
4-methylcyclohexene.
(f)
Interpretation:
Systematic name of the given compound should be determined.
Concept introduction:
- IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
- Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
- Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
- For alkenes, suffix will be ‘ene’.
- Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
- When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Answer to Problem 36P
Systematic name of the given compound
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The structure of the compound is,
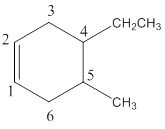
Structure of the compound reveals that that the given compound contains six membered carbon chain with double bond and on the fourth and fifth carbon atoms one ethyl and methyl group was attached respectively.
Therefore,
The systematic name of the compound in accordance with IUPAC’s rules and regulations is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
