
Physics (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780321976444
Author: James S. Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 30PCE
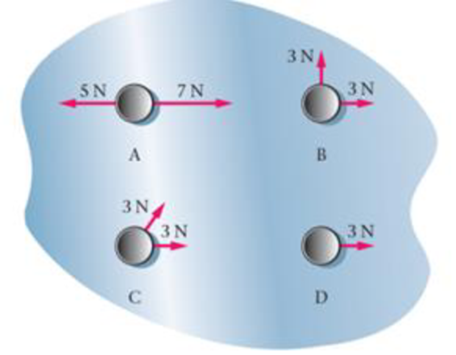
A hockey puck is acted on by one or more forces as shown in Figure 5-34. Rank the four cases. A, B, C, and D, in order of the magnitude of the puck's acceleration, starting with the smallest Indicate ties where appropriate.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please solve and answer the problem step by step with explanations along side each step stating what's been done correctly please. Thank you!! ( preferably type out everything)
Answer this
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics (5th Edition)
Ch. 5.1 - Two forces have magnitudes F1 and F2. If these...Ch. 5.2 - Which of the following statements is correct? A: A...Ch. 5.3 - The acceleration of an object has a magnitude a....Ch. 5.4 - A force F pushes on three boxes that slide without...Ch. 5.5 - An object is acted on by a single force that is at...Ch. 5.6 - When a certain person steps onto a scale on solid...Ch. 5.7 - Figure 5-23 shows four identical bricks that are...Ch. 5 - Driving down the road, you hit the brakes...Ch. 5 - Youve probably seen pictures of someone pulling a...Ch. 5 - As you read this, you are most likely sitting...
Ch. 5 - When a dog gets wet, it shakes its body from head...Ch. 5 - A young girl slides down a rope. As she slides...Ch. 5 - A block of mass m hangs from a string attached to...Ch. 5 - An astronaut on a space walk discovers that his...Ch. 5 - Two untethered astronauts on a space walk decide...Ch. 5 - In Figure 5-25 Wilbur asks Mr. Ed, the talking...Ch. 5 - A whole brick has more mass than half a brick,...Ch. 5 - The force exerted by gravity on a whole brick is...Ch. 5 - Is it possible for an object at rest to have only...Ch. 5 - Is it possible for an object to be in motion and...Ch. 5 - A bird cage, with a parrot inside, hangs from a...Ch. 5 - Suppose you jump from the cliffs of Acapulco and...Ch. 5 - A friend tells you that since his car is at rest,...Ch. 5 - Since all objects are weightless in orbit, how is...Ch. 5 - To clean a rug, you can hang it from a clothesline...Ch. 5 - If you step off a high board and drop to the water...Ch. 5 - Is it possible for an object to be moving in one...Ch. 5 - Since a bucket of water is weightless in space,...Ch. 5 - In the movie The Rocketeer, a teenager discovers a...Ch. 5 - List three common objects that have a weight of...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m is initially at rest. After a...Ch. 5 - On a planet far, far away, an astronaut picks up a...Ch. 5 - In a grocery store, you push a 15.4-kg shopping...Ch. 5 - You are pulling your little sister on her sled...Ch. 5 - A 0.53-kg billiard ball initially at rest is given...Ch. 5 - A 92-kg water skier floating in a lake is pulled...Ch. 5 - A 0.5-kg object is acted on by a force whose x...Ch. 5 - Predict/Explain You drop two balls of equal...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate A 42.0-kg parachutist is moving...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate In baseball, a pitcher can...Ch. 5 - A major-league catcher gloves a 92 mi/h pitch and...Ch. 5 - Driving home from school one day, you spot a ball...Ch. 5 - Stopping a 747 A 747 jetliner lands and begins to...Ch. 5 - The Ux-versus-time graph for a 1.8-kg object is...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate A drag racer crosses the finish...Ch. 5 - Predict/Explain A small car collides with a large...Ch. 5 - Predict/Explain A small car collides with a large...Ch. 5 - As you catch a 0.14-kg ball it accelerates at...Ch. 5 - BIO Woodpecker Concussion Prevention A woodpecker...Ch. 5 - On vacation, your 1400-kg car pulls a 560-kg...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate An 85-kg parent and a ?4-kg...Ch. 5 - A force of magnitude 7.50 N pushes three boxes...Ch. 5 - A force of magnitude 7.50 N pushes three boxes...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate Two boxes sit side-by-side on a...Ch. 5 - A skateboarder on a ramp is accelerated by a...Ch. 5 - Three objects, A, B, and C, have x and y...Ch. 5 - A farm tractor tows a 3300-kg trailer up a 14...Ch. 5 - A shopper pushes a 7 5-kg shopping cart up a 13...Ch. 5 - Two crewmen pull a rail through a lock, as shown...Ch. 5 - A hockey puck is acted on by one or more forces as...Ch. 5 - To give a 19-kg child a ride, two teenagers pull...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate A 65-kg skier speeds down a...Ch. 5 - An object acted on by three forces moves with...Ch. 5 - A train is traveling up a 2 88 incline at a speed...Ch. 5 - The Force Exerted on the Moon In Figure 5-37 we...Ch. 5 - You pull upward on a stuffed suitcase with a force...Ch. 5 - BIO Brain Growth A newborn babys brain grows...Ch. 5 - Suppose a rocket launches with an acceleration of...Ch. 5 - During an episode of turbulence in an airplane you...Ch. 5 - At the bow of a ship on a stormy sea, a crewman...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate As part of a physics experiment...Ch. 5 - When you weigh yourself on good old terra firma...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate BIO Flight of the Samara A...Ch. 5 - When you lift a bowling ball with a force of 82 N,...Ch. 5 - A 23-kg suitcase is pulled with constant speed by...Ch. 5 - (a) Draw a free-body diagram for the skier in...Ch. 5 - A 9.3-kg child sits in a 3.7-kg high chair. (a)...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-39 shows the normal force N experienced...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-40 shows the normal force N as a function...Ch. 5 - A 5.0-kg bag of potatoes sits on the bottom of a...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate (a) Find the normal force...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate A gardener mows a lawn with an...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-41 Problems 53 53 An ant walks slowly...Ch. 5 - CE Predict/Explain Riding in an elevator moving...Ch. 5 - CE Predict/Explain Riding in an elevator moving...Ch. 5 - CE Give the direction of the net force acting on...Ch. 5 - CE Predict/Explain You jump out of an airplane and...Ch. 5 - In a tennis serve, a 0.070-kg ball can be...Ch. 5 - BIO Human Heart Force The left ventricle of the...Ch. 5 - A 51 5-kg swimmer with an initial speed of 1.25...Ch. 5 - The ax-versus-time graph for a 2.0-kg object is...Ch. 5 - A skateboarder starts from rest and rolls down a...Ch. 5 - The rotors of a 15,200-kg heavy-lift helicopter...Ch. 5 - As it pulls itself up to a branch, a chimpanzee...Ch. 5 - CE Each of the three identical hockey pucks shown...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate The VASIMR Rocket NASA plans to...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m = 5.95 kg has an acceleration...Ch. 5 - At the local grocery store, you push a 14.5-kg...Ch. 5 - BIO Predict/Calculate The Force of Running...Ch. 5 - BIO Predict/Calculate Grasshopper Liftoff To...Ch. 5 - Takeoff from an Aircraft Carrier On an aircraft...Ch. 5 - The Ux-versus-time graph for a 1.8-kg object is...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate An archer shoots a 0.024-kg...Ch. 5 - An apple of mass m = 0.13 kg falls out of a tree...Ch. 5 - BIO The Fall of T. rex Paleontologists estimate...Ch. 5 - Deep Space 1 The NASA spacecraft Deep Space 1 was...Ch. 5 - Your groceries are in a bag with paper handles....Ch. 5 - BIO A Leafhopper's Leap The motion of jumping...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate At the airport, you observe some...Ch. 5 - Prob. 80GPCh. 5 - Two boxes are at rest on a smooth, horizontal...Ch. 5 - You have been hired to help improve the material...Ch. 5 - Prob. 83GPCh. 5 - A baseball of mass m and initial speed U strikes a...Ch. 5 - When two people push in the same direction on an...Ch. 5 - An air-track cart of mass m1 = 0.14 kg is moving...Ch. 5 - BIO Increasing Safety in a Collision Safety...Ch. 5 - BIO Increasing Safety in a Collision Safety...Ch. 5 - BIO Increasing Safety in a Collision Safety...Ch. 5 - BIO Increasing Safety in a Collision Safety...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 5-8 Suppose...Ch. 5 - Referring to Example 5-8 Suppose the force of 30.0...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Figure 5-13 Suppose...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Figure 5-13 Suppose...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
35. Consider the reaction.
The graph shows the concentration of Br2 as a function of time.
a. Use the g...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
10.71 Identify each of the following as an acid or a base: (10.1)
H2SO4
RbOH
Ca(OH)2
HI
...
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Explain all answers clearly, using complete sentence and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
This molecular drawing shows images of acetone molecules before and after a change. Was the change chemical or ...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Carefully examine the common sedimentary rocks shown In Figure 2.13. Use these photos and the preceding discuss...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
[14.110] The following mechanism has been proposed for the gas-phase reaction of chloroform (CHCI3) and chlorin...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvote instantarrow_forwardKirchoff's Laws. A circuit contains 3 known resistors, 2 known batteries, and 3 unknown currents as shown. Assume the current flows through the circuit as shown (this is our initial guess, the actual currents may be reverse). Use the sign convention that a potential drop is negative and a potential gain is positive. E₂ = 8V R₁₁ = 50 R₂ = 80 b с w 11 www 12 13 E₁ = 6V R3 = 20 a) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop abefa in the clockwise direction starting at point a. (2 pt). b) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop bcdeb in the clockwise direction starting at point b. (2 pt). c) Apply Kirchoff's Junction Rule at junction b (1 pt). d) Solve the above 3 equations for the unknown currents I1, 12, and 13 and specify the direction of the current around each loop. (5 pts) I1 = A 12 = A 13 = A Direction of current around loop abef Direction of current around loop bcde (CW or CCW) (CW or CCW)arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 4.) The diagram shows the electric field lines of a positively charged conducting sphere of radius R and charge Q. A B Points A and B are located on the same field line. A proton is placed at A and released from rest. The magnitude of the work done by the electric field in moving the proton from A to B is 1.7×10-16 J. Point A is at a distance of 5.0×10-2m from the centre of the sphere. Point B is at a distance of 1.0×10-1 m from the centre of the sphere. (a) Explain why the electric potential decreases from A to B. [2] (b) Draw, on the axes, the variation of electric potential V with distance r from the centre of the sphere. R [2] (c(i)) Calculate the electric potential difference between points A and B. [1] (c(ii)) Determine the charge Q of the sphere. [2] (d) The concept of potential is also used in the context of gravitational fields. Suggest why scientists developed a common terminology to describe different types of fields. [1]arrow_forward3.) The graph shows how current I varies with potential difference V across a component X. 904 80- 70- 60- 50- I/MA 40- 30- 20- 10- 0+ 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 VIV Component X and a cell of negligible internal resistance are placed in a circuit. A variable resistor R is connected in series with component X. The ammeter reads 20mA. 4.0V 4.0V Component X and the cell are now placed in a potential divider circuit. (a) Outline why component X is considered non-ohmic. [1] (b(i)) Determine the resistance of the variable resistor. [3] (b(ii)) Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit. [1] (c(i)) State the range of current that the ammeter can measure as the slider S of the potential divider is moved from Q to P. [1] (c(ii)) Describe, by reference to your answer for (c)(i), the advantage of the potential divider arrangement over the arrangement in (b).arrow_forward1.) Two long parallel current-carrying wires P and Q are separated by 0.10 m. The current in wire P is 5.0 A. The magnetic force on a length of 0.50 m of wire P due to the current in wire Q is 2.0 × 10-s N. (a) State and explain the magnitude of the force on a length of 0.50 m of wire Q due to the current in P. [2] (b) Calculate the current in wire Q. [2] (c) Another current-carrying wire R is placed parallel to wires P and Q and halfway between them as shown. wire P wire R wire Q 0.05 m 0.05 m The net magnetic force on wire Q is now zero. (c.i) State the direction of the current in R, relative to the current in P.[1] (c.ii) Deduce the current in R. [2]arrow_forward
- 2.) A 50.0 resistor is connected to a cell of emf 3.00 V. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the circuit are ideal. V A 50.00 (a) The current in the ammeter is 59.0 mA. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell. The circuit is changed by connecting another resistor R in parallel to the 50.0 resistor. V A 50.00 R (b) Explain the effect of this change on R is made of a resistive wire of uniform cross-sectional area 3.1 × 10-8 m², resistivity 4.9 × 10-70m and length L. The resistance of R is given by the equation R = KL where k is a constant. (b.i) the reading of the ammeter. [2] (b.ii) the reading of the voltmeter. [2] (c) Calculate k. State an appropriate unit for your answer. [3] [2]arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- A rod 12.0 cm long is uniformly charged and has a total charge of -20.0 μc. Determine the magnitude and direction of the electric field along the axis of the rod at a point 32.0 cm from its center. 361000 ☑ magnitude What is the general expression for the electric field along the axis of a uniform rod? N/C direction toward the rodarrow_forwardA certain brand of freezer is advertised to use 730 kW h of energy per year. Part A Assuming the freezer operates for 5 hours each day, how much power does it require while operating? Express your answer in watts. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? P Submit Request Answer Part B W If the freezer keeps its interior at a temperature of -6.0° C in a 20.0° C room, what is its theoretical maximum performance coefficient? Enter your answer numerically. K = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer Part C What is the theoretical maximum amount of ice this freezer could make in an hour, starting with water at 20.0°C? Express your answer in kilograms. m = Ο ΑΣΦ kgarrow_forwardDescribe the development of rational choice theory in sociology. Please includearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY