
Concept explainers
One Tough Bug The genus Ferroplasma consists of a few species of acid-loving archaea. One species, Ferroplasma acidarmanus, was discovered in one of the most contaminated sites in the United States: Iron Mountain Mine in California. F. acidarmamus is the main constituent of .slime streamers (a type of biofilm) growing in water draining from this abandoned copper mine (right). The water is hot (about 40°C, or 104°F), heavily laden with arsenic and other toxic metals, and has a pH of zero.
F. acidarmanus cells have an ancient energy-harvesting pathway that uses electrons pulled from iron-sulfur compounds in minerals such as pyrite. Removing electrons from these compounds dissolves the minerals, so groundwater in the mine ends up with extremely high concentrations of solutes, including metal ions such as copper, zinc, cadmium, and arsenic. The pathway also produces .sulfuric acid, which lowers the pH of the water around the cell to zero.
F. acidarmanus cells keep their internal pH at a cozy 5.0 despite Living in an environment similar to hot battery acid. However, most of the cell’s enzymes function best al much lower pH (FIGURE 5.13). Thus, researchers think F. acidarmanus may have an unknown type of internal compartment that keeps their enzymes in a highly acidic environmental.

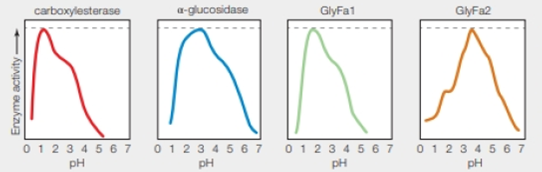
FIGURE 5.13 pH anomaly of Ferroplasma acidarmanus.
Left graphs showing pH activity profile of four enzymes isolated from Ferraplasma acidarmanus Researchers had expected all of these enzymes to function best at the calls’ cytoplasmic pH (5.0).
What do the dashed lines in the graphs signify?
To determine: What do the dashed lines in the graphs signify.
Concept introduction: Enzymes are the protein molecules that enhance the rate of the reactions without being changed by them. It acts as a biocatalyst. Each enzyme works the best within a certain range of environmental conditions that include temperature, pH, and salt concentration.
Explanation of Solution
The isolated bacteria Ferroplasma acidarmanus grow well at acidic environment (pH zero) of copper mine where the water temperature is about 40 ºC and heavily laden with arsenic and other toxic metals.
The F. acidarmanus has an ancient energy harvesting pathway. It uses the electrons from iron-sulfur compounds in the mineral such as pyrite. Removing electrons from these compounds dissolve the minerals that lead to the high concentration of metal ions such as copper, zinc, cadmium, and arsenic in groundwater. This also produces sulfuric acid which lowers the pH of the water around the cells to zero.
Despite the surrounding environment the internal pH of the bacteria is 5.0. However, most of the enzymes in bacteria functions best at much lower pH. This causes a thinking of presence of the unknown type of internal environment in the bacteria that keeps their enzymes in a highly acidic environment.
Refer to Fig. 5.13 “pH anomaly of Ferroplasma acidarmanus”, there are four different enzymes carboxylesterase, α-glucosidase, GlyFa1, and GlyFa2 which works best around pH 1.5, 3, 1.8, and 3.8 respectively. The dashed line shows the optimum activity for each enzyme.
The dashed line indicates the optimum enzyme activity for each enzyme.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- Selection of Traits What adaptations do scavengers have for locating and feeding on prey? What adaptations do predators have for capturing and consuming prey?arrow_forwardCompetition Between Species What natural processes limit populations from growing too large? What are some resources organisms can compete over in their natural habitat?arrow_forwardSpecies Interactions Explain how predators, prey and scavengers interact. Explain whether predators and scavengers are necessary or beneficial for an ecosystem.arrow_forward
- magine that you are conducting research on fruit type and seed dispersal. You submitted a paper to a peer-reviewed journal that addresses the factors that impact fruit type and seed dispersal mechanisms in plants of Central America. The editor of the journal communicates that your paper may be published if you make ‘minor revisions’ to the document. Describe two characteristics that you would expect in seeds that are dispersed by the wind. Contrast this with what you would expect for seeds that are gathered, buried or eaten by animals, and explain why they are different. (Editor’s note: Providing this information in your discussion will help readers to consider the significance of the research).arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between Uniporters, Symporters and Antiporters? Which of these are examples of active transport?arrow_forwardWhat are coupled transporters?arrow_forward
- How do histamine and prostaglandins help in the mobilization of leukocytes to an injury site? What are chemotactic factors? How do they affect inflammation process?arrow_forwardCompare and contrast neutrophils and macrophages. Describe two ways they are different and two ways they are similar.arrow_forwardDescribe the effects of three cytokines (not involved in the initial inflammation response). What cells release them?arrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





