
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133104261
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 35P
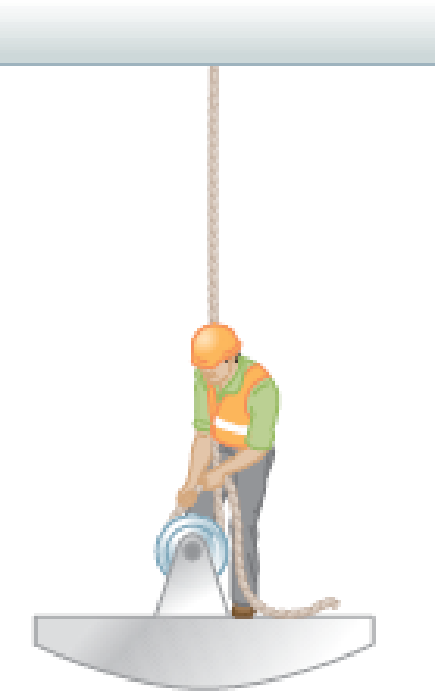
In Figure P4.35, the man and the platform together weigh 950 N. The pulley can be modeled as frictionless. Determine how hard the man has to pull on the rope to lift himself steadily upward above the ground. (Or is it impossible? If so, explain why.)
Figure P4.35
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
a cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?
Calculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were:
222.22 800.00
61.11 641.67
0.00 588.89
11.11 588.89
8.33 588.89
11.11 588.89
5.56 586.11
2.78 583.33
Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 4 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Ch. 4.1 - Which of the following statements is most correct?...Ch. 4.4 - An object experiences no acceleration. Which of...Ch. 4.4 - You push an object, initially at rest, across a...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 4.4QQCh. 4.6 - (i) If a fly collides with the windshield of a...Ch. 4.6 - Which of the following is the reaction force to...Ch. 4.7 - Consider the two situations shown in Figure 4.8,...Ch. 4 - Prob. 1OQCh. 4 - Prob. 2OQCh. 4 - Prob. 3OQ
Ch. 4 - Prob. 4OQCh. 4 - Prob. 5OQCh. 4 - Prob. 6OQCh. 4 - Prob. 1CQCh. 4 - If a car is traveling due westward with a constant...Ch. 4 - A person holds a ball in her hand. (a) Identify...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4CQCh. 4 - If you hold a horizontal metal bar several...Ch. 4 - Prob. 6CQCh. 4 - Prob. 7CQCh. 4 - Prob. 8CQCh. 4 - Balancing carefully, three boys inch out onto a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 10CQCh. 4 - Prob. 11CQCh. 4 - Prob. 12CQCh. 4 - Prob. 13CQCh. 4 - Give reasons for the answers to each of the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 15CQCh. 4 - In Figure CQ4.16, the light, taut, unstretchable...Ch. 4 - Prob. 17CQCh. 4 - Prob. 18CQCh. 4 - Prob. 19CQCh. 4 - A force F applied to an object of mass m1 produces...Ch. 4 - (a) A car with a mass of 850 kg is moving to the...Ch. 4 - A toy rocket engine is securely fastened to a...Ch. 4 - Two forces, F1=(6i4j)N and F2=(3i+7j)N, act on a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 5PCh. 4 - Prob. 6PCh. 4 - Two forces F1 and F2 act on a 5.00-kg object....Ch. 4 - A 3.00-kg object is moving in a plane, with its x...Ch. 4 - A woman weighs 120 lb. Determine (a) her weight in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 10PCh. 4 - Prob. 11PCh. 4 - Prob. 12PCh. 4 - Prob. 13PCh. 4 - Prob. 14PCh. 4 - Prob. 15PCh. 4 - You stand on the seat of a chair and then hop off....Ch. 4 - Prob. 17PCh. 4 - A block slides down a frictionless plane having an...Ch. 4 - Prob. 19PCh. 4 - A setup similar to the one shown in Figure P4.20...Ch. 4 - Prob. 21PCh. 4 - The systems shown in Figure P4.22 are in...Ch. 4 - A bag of cement weighing 325 N hangs in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 24PCh. 4 - In Example 4.6, we investigated the apparent...Ch. 4 - Figure P4.26 shows loads hanging from the ceiling...Ch. 4 - Prob. 27PCh. 4 - An object of mass m1 = 5.00 kg placed on a...Ch. 4 - An object of mass m = 1.00 kg is observed to have...Ch. 4 - Two objects are connected by a light string that...Ch. 4 - Prob. 31PCh. 4 - A car is stuck in the mud. A tow truck pulls on...Ch. 4 - Two blocks, each of mass m = 3.50 kg, are hung...Ch. 4 - Two blocks, each of mass m, are hung from the...Ch. 4 - In Figure P4.35, the man and the platform together...Ch. 4 - Two objects with masses of 3.00 kg and 5.00 kg are...Ch. 4 - A frictionless plane is 10.0 m long and inclined...Ch. 4 - Prob. 39PCh. 4 - An object of mass m1 hangs from a string that...Ch. 4 - A young woman buys an inexpensive used car for...Ch. 4 - A 1 000-kg car is pulling a 300-kg trailer....Ch. 4 - An object of mass M is held in place by an applied...Ch. 4 - Prob. 44PCh. 4 - An inventive child named Nick wants to reach an...Ch. 4 - In the situation described in Problem 45 and...Ch. 4 - Two blocks of mass 3.50 kg and 8.00 kg are...Ch. 4 - Prob. 48PCh. 4 - In Example 4.5, we pushed on two blocks on a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 50PCh. 4 - Prob. 51PCh. 4 - Prob. 52PCh. 4 - Review. A block of mass m = 2.00 kg is released...Ch. 4 - A student is asked to measure the acceleration of...Ch. 4 - Prob. 55PCh. 4 - Prob. 56PCh. 4 - A car accelerates down a hill (Fig. P4.57), going...Ch. 4 - Prob. 58PCh. 4 - In Figure P4.53, the incline has mass M and is...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forwardFrom number 2 and 3 I just want to show all problems step by step please do not short cut look for formulaarrow_forward
- Look at the answer and please show all work step by steparrow_forward3. As a woman, who's eyes are h = 1.5 m above the ground, looks down the road sees a tree with height H = 9.0 m. Below the tree is what appears to be a reflection of the tree. The observation of this apparent reflection gives the illusion of water on the roadway. This effect is commonly called a mirage. Use the results of questions 1 and 2 and the principle of ray reversibility to analyze the diagram below. Assume that light leaving the top of the tree bends toward the horizontal until it just grazes ground level. After that, the ray bends upward eventually reaching the woman's eyes. The woman interprets this incoming light as if it came from an image of the tree. Determine the size, H', of the image. (Answer 8.8 m) please show all work step by steparrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Newton's Third Law of Motion: Action and Reaction; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y61_VPKH2B4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY