
Concept explainers
Figure P38.76 shows an object placed a distance do1 from one of two converging lenses separated by s = 1.00 m. The first lens has focal length f1 = 22.0 cm, and the second lens has focal length f2 = 45.0 cm. An image is formed by light passing through both lenses at a distance di2 = 15.0 cm to the left of the second lens. a. What is the value of do1 that will result in this image position? b. Is the final image formed by the two lenses real or virtual? c. What is the magnification of the final image? d. Is the final image upright or inverted?
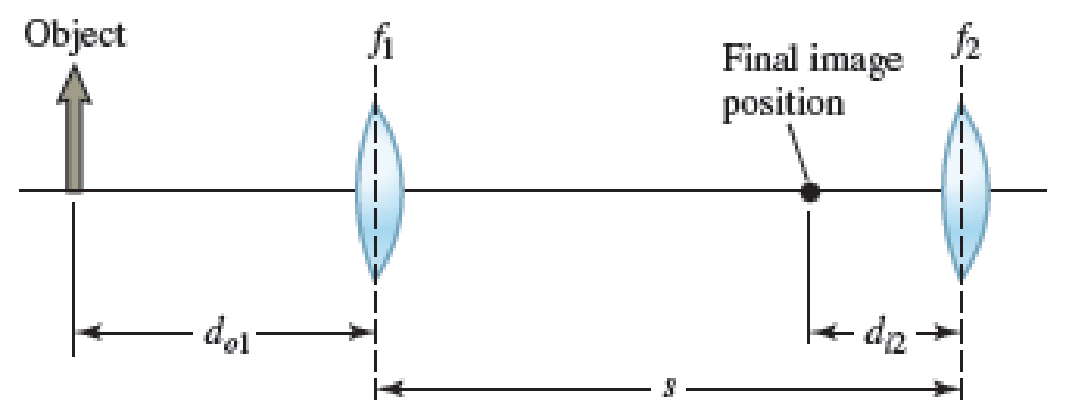
Figure P38.76
(a)
The value of
Answer to Problem 76PQ
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Write the thin lens equation for first lens.
Here,
Rearrange the above equation to find
Similarly,
The image of first lens acts as object for second lens. Hence, object distance for second lens is,
Conclusion:
Substitute
From equation (III), we get,
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the value of
(b)
Whether the image formed by the two lenses is real or virtual.
Answer to Problem 76PQ
The image formed by the two lenses is Virtual.
Explanation of Solution
Since, the image is formed on the left side of the second lens, the image is Virtual.
(c)
The magnification of the final image.
Answer to Problem 76PQ
The total magnification of the final image is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the total magnification of the final image.
Here,
Write the expression for the magnification of the first lens.
Here,
Write the expression for the magnification of the second lens.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute the equations (V) and equation (VI) in the equation (IV) to find
Substitute
Thus, the total magnification of the final image is
(d)
Whether the final image is upright or inverted.
Answer to Problem 76PQ
The final image produced will be inverted.
Explanation of Solution
Since, the total magnification has a negative sign, the image formed will be inverted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 38 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- look at answer show all work step by steparrow_forwardLook at the answer and please show all work step by steparrow_forward3. As a woman, who's eyes are h = 1.5 m above the ground, looks down the road sees a tree with height H = 9.0 m. Below the tree is what appears to be a reflection of the tree. The observation of this apparent reflection gives the illusion of water on the roadway. This effect is commonly called a mirage. Use the results of questions 1 and 2 and the principle of ray reversibility to analyze the diagram below. Assume that light leaving the top of the tree bends toward the horizontal until it just grazes ground level. After that, the ray bends upward eventually reaching the woman's eyes. The woman interprets this incoming light as if it came from an image of the tree. Determine the size, H', of the image. (Answer 8.8 m) please show all work step by steparrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





