
Concept explainers
Cervical Cancer Incidence in HPV-Positive Women
A persistent infection with one of about 10 strains of genital HPV (human papillomavirus) is the main risk factor for cervical cancer. The virus spreads easily by sexual contact, but vaccines that prevent infection have been available since 2006. The vaccines consist of viral proteins that self-assemble into virus-like particles. The particles are not infectious (they contain no viral DNA), but their component proteins trigger an immune response that can prevent HPV infection and the cervical cancer it causes.
In 2003, Michelle Khan and her coworkers published results of their 10-year study correlating HPV status with cervical cancer incidence in women (FIGURE 37.23). All 20,514 participants were free of cervical cancer when the study began.
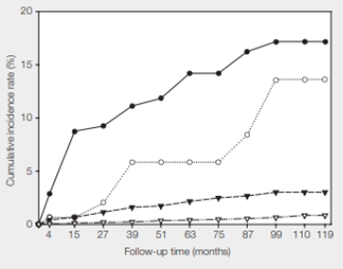
FIGURE 37.23 Cumulative incidence rate of cervical cancer correlated with HPV status.
● HPV16 positive
○ HPV16 negative and HPV18 positive
▾ All other cancer-causing HPV types combined
▿ No cancer-causing HPV types was detected.
At 110 months into the study, what percentage of women who were not infected with any type of cancer-causing HPV had cervical cancer? What percentage of women who were infected with HPV16 also had cancer?
To determine: The percentage of women who were not infected with any type of cancer-causing HPV, but had cervical cancer.
Introduction: The researchers in the given study attempted to make a connection between the presence of various HPV viral infections and the incidence of cervical cancer. Cervical cancer arises from the cervix, which occurs due to the abnormal growth of the cells that have the capability to invade or spread to other body parts.
Explanation of Solution
The given study showed that approximately one percent of the women who had no cancer-causing HPV infections developed cervical cancer. The study shows that the infection with the genital HPV is the main risk factor for cervical cancer. The women who have not been infected with cancer-causing HPV have a small chance of having cervical cancer. HPV is not the only cause of cervical cancer. It can also be caused due to a weakened immune system, long-term mental stress, giving birth at a very young age, several pregnancies, birth control pills, and so on.
In the given study, 1% of women who were not infected with any type of cancer-causing HPV had cervical cancer.
To determine: The percentage of the women who were infected with HPV16 had cancer.
Introduction: The researchers in this study attempted to make a connection between the presence of various HPV viral infections and the incidence of cervical cancer. Cervical cancer arises from the cervix, which occurs due to the abnormal growth of the cells that have the capability to invade or spread to other body parts.
Explanation of Solution
At 110 months, 17 percent of the women who tested positive for HPV16 had cervical cancer. Human papillomavirus that spreads easily by sexual contact is a risk factor for cervical cancer. The study indicates that those women who are HPV-positive have a high risk of getting cervical cancer.
The HPV positive women, who have the habit of smoking and have HIV influence, are more likely to develop cervical cancer. If the virus infection is left untreated, the pre-cancerous cells will develop to cancer cells, but it will take 10 to 15 years.
In the given study, 17 percent of the women who were infected with HPV16 had cancer.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 37 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Genetics: Analysis and Principles
- A potential cause of acquired autoimmunity is ___________ . tissue hypersensitivity molecular mimicry histamine release radiation exposurearrow_forwardAutoantibodies are probably involved in: reactions to poison ivy pollen allergies systemic lupus erythematosus HIV/AIDSarrow_forwardQuestion 50 Bonus. virus vaccines: All of the following vaccines contain live attenuated vaccine viruses EXCEPT (which one has inactivated vaccine virus?): O smallpox vaccine O Sabin polio vaccine/OPV Oral Polio Vaccine O Hepatitis A vaccine O Varicella-Zoster/Chickenpox-Shingles vaccines O MMR vaccine Question 51arrow_forward
- Mc 8 eBook References paragraph. Inoculated attenuated Sabin vaccination Salk Inactivated multiply three revert two prophylaxis infantile paralysis myasthenia gravis Poliomyelitis 00000000000 Drag the text blocks below into their correct order. In contrast, oral polio vaccine (OPV), developed by an in the 1960s, contains virus and can be easily administered by mouth making it useful still in polio eradication programs in developing countries today. OPV poses many risks, however, such as the attenuated virus can people and spread to others or it can making this vaccine virtually unusable in the U.S. today. In the past, this disease often affected small children and was called poliovirus vaccine was developed by in 1954 and is now the form used for all U.S. childhood vaccinations due to its low risk to individuals being vaccinated. in vaccinated to a neurovirulent strain causing disease, neuromuscular paralysis. There are against polio. is an acute enteroviral infection of the spinal…arrow_forwardSusceptibility/Predisposition to Infectious Disease Why is it that some people always seem to get the flu and others don't? Why are some individuals more susceptible to SARS CoV-2? 1) links between human genetic variation and susceptibility to a specific infectious disease (e.g., Neanderthal DNA and Covid), 2) link between aging and a specific infectious disease 3) links between stress, nutrition, or exercise and a specific infectious disease. Please be sure to mention: The factor you explored The disease(s) implicated How the factor affects susceptibility to disease (i.e., mechanism)arrow_forwardQuestion 1 Nursing. Innate lymphoid cells reside primarily in tissues such as the lungs, the lining of the gastrointestinal tract, and the skin, because these sites represent the major routes of entry of pathogens into the body. Several different subsets of innate lymphoid cells exist, and each is specialized to respond to a category of pathogen (e.g., viruses, extracellular bacteria, helminthic parasites, etc). a) True b) Falsearrow_forward
- All about the properties of Coronavirus as an Immunogen.arrow_forwardPart B - Viral Classification: The Baltimore Scheme The Baltimore classification scheme is based on the relationship between the virus' genome and its mRNA. For the following choices, indicate which viruses would fall into each classification: 1) require reverse transcriptase to copy the information in their own genome to DNA; 2) can replicate and be transcribed in the same manner as the cell's own genetic material; and 3) a replicative form of DNA must be produced and is used for both replication and transcription. Drag and drop choices to the bins they describe. double-stranded DNA viruses Requires reverse transcriptase double-stranded RNA viruses retroviruses double-stranded DNA viruses that have an RNA intermediate Functions similarly to cell's own genetic material plus-strand RNA viruses minus-strand RNA viruses Reset Help plus-strand DNA viruses Uses a replicative form of DNAarrow_forwardFill in the blanks. The parentheses represent the choices for the blank. Scientists already knew that a special type of virus called a bacteriophage inserts genetic information into a bacterial cell in order to force the bacterial cell to make more bacteriophage viruses. What scientists did not know, however, was whether that genetic information is carried by the (proteins, DNA) covering the outside of the bacteriophage virus or by the (proteins, DNA) inside the bacteriophage virus.arrow_forward
- From: "Towards a universal flu vaccine" Each year, the flu vaccine includes antigens from two strains of Influenza A and two strains of Influenza B. These antigens are from the head of the H spikes an area that sticks out from the virus and so, is very easy for human immune cells to detect. However, the problem with using the head of the H spike as an antigen is... O The H spike head mutates very rapidly, so quickly changes to forms not recognized by human immune cells. O The H spike head is exposed on the surface of the virus for only a short period of time. Viruses quickly pull the H spikes back inside the virus, shiclding them from human immune cells. O The H spike head is often too big for the human immune cells to attack. O The H spike head is often too small for the human immune cells to bind to.arrow_forwardplease tell me how bacteriophage and animal viruses multiply. please add both lytic and lysogenic cycles for bacteriophage, all steps, and the outcomes of both. For animal viruses, please include all steps and briefly explain the differences between their nucleic acids. i am having a hard trouble understanding this information if you could please explain in way where a child would understand it that would be amazingarrow_forwarddocs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAlpQLSen_DnlxjlAa6EoAyAOhS Gitcmj9fQ_M4bwAg1Wizsq5Yp4A/formResponse O YouTube Maps nanswers TaT4 are rUC Which of the following are true regarding testosterone? * (1) Testosterone acts on specific target cells to stimulate male sexual characteristics. (2) Testosterone is directly stimulated by the release of GnRH. (3) Testosterone produces a negative feedback mechanism to regulate GnRH. (4) If spermatogenesis is slow, testosterone production is stimulated. O A- If answers (1), (2) and (3) are TRUE B- If answers (1) and (3) are TRUE O C- If answers (2) and (4) are TRUE O D- If only answer (4) is TRUE O E- If answers (1), (2), (3) and (4) are TRUE Which is true of the following statements regarding COVID-19? (1) SARS-CoV-2 is the virus that causes COVID-19 (2) The new coronavirus can infect the upper or lower part respiratorv svstemarrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

