
Concept explainers
To review:
The role of aquaporins in the uptake of water from the soil by root cells.
Given:
The oocytes of the frog Xenopus laevis were taken by the researchers and injected with the messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) of plant tonoplast intrinsic protein (TIP). They are large in size and have a low osmotic cell permeability. The, mRNA of a nontransport protein is taken in the second case and injected into the oocytes. Some of the oocytes were not injected at all and this became the third case of the experiment. These cells were observed after giving incubation of 2 days in isotonic medium and a treatment with hypotonic solution. The following graph was made by plotted changes in relative volume on the y-axis and time on x-axis:
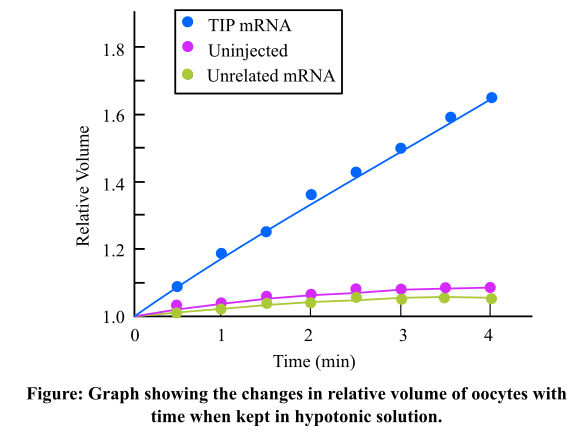
The oocytes which had TIP mRNA burst after sometime while the oocytes, which were injected with a different nontransport protein, and the oocytes which were not injected do not burst. The following table depicts the osmotic water permeability of the three conditions as calculated by the researchers:

Introduction:
Aquaporins are the integral membrane proteins which are responsible for the transport of molecules of lower weight across the bilipid layer. They transport across the concentration gradient and does not require energy.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 34 Solutions
Life: The Science of Biology
- i. Based on Figure 2, identify the structure that regulates the movement of water and minerals towards the xylem in the root ii. Predict what will happen to the transportation of water and minerals through the plasma membrane if the root was poisoned and no cellular respiration occurred. iii. . Nitrate and phosphate are important anions for plants. Explain how the movement of protons (H+) influence the anions uptake across the plasma membrane of the root hair cellsarrow_forwardDescribe how the water potential of a leaf changes throughout the course of a 24-hour period. What is driving this change? How does the water potential of this leaf compare to the water potential of a root in the same plant during the same period? How does it compare to the soil underneath the plant? Please fast and properly explain.arrow_forwardName the pressure which is responsible for the movement of water molecules across the cortical cells of root.arrow_forward
- Describe the pathway water would take up the stem to the leaf of a plant. Describe the water's movement through any cells, tissues, and/or systems of the plant body.arrow_forwardWhich one of the following statement is wrong? Options Water is absorbed mainly by unicellular root hairs Cellulosic cell wall is a semi permeable membrane Pure water has maximum diffusic pressure Facilitated diffusion requires special membrane proteinsarrow_forwardWhat would enhance water uptake by a plant cell?(A) decreasing the Ψ of the surrounding solution(B) positive pressure on the surrounding solution(C) the loss of solutes from the cell(D) increasing the Ψ of the cytoplasmarrow_forward
- (b) Water absorbed by plant roots travels by different pathways from the root hairs to the xylem. Figure 5 shows these pathways in a plant root. cell A xylem vessel root hair key pathway B Tissue D Tissue E * pathway C Figure 5: Schematic representation of water movement through the tissues of a plant root (PLEASE TURN OVER) Page 6 CONT'D from Page 5 i. Explain how water moves from the root hair to the xylem vessels in the root. ii. Identify cellA, pathway B, pathway C, tissue D and tissue E in Figure 5.arrow_forwardDRAW IT Draw a simple sketch of cation exchange, showinga root hair, a soil particle with anions, and a hydrogen iondisplacing a mineral cation.arrow_forwardWhen leaf water potential increases why does hydraulic conductivity increase as well in plants?arrow_forward
- What is the relationship between osmotic potential and plants when water with salinated water is used to water plants? E.G: How does it inhibit growth and why if the plant isn't salt tolerantarrow_forwardB) If you have a mesophyll cell in a leaf (a living, parenchyma cell in a leaf) with a slight positive turgor pressure (Yp = 0.01 MPa) and solutes (Ys = -3.0 MPa), and it is next to a xylem vessel element with very few solutes in the xylem sap (Ys = -0.01 MPa) but high physical tension (Yp = - 2.0 MPa), which way will water flow? a) from the mesophyll cell into the vessel element b) from the vessel element into the mesophyll cell c) neither direction. They are at equilibrium. Activa GoroSearrow_forwardAmong the three pathways of water movements in plants, which is the most used? Explain the reasons behind. (i) Figure 1: Water droplets on leaf blades (IPM, University of Missouri) Explain the phenomenon shown in Figure 1 by providing the specific term, elucidating the reason, conditions and plant structure involved. (ii)arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





