
Analyzing the Motion of a Projectile A projectile is fired from a cliff
Where
At what horizontal distance from the face of the cliff is the height of the projectile a maximum?
Find the maximum height of the projectile.
At what horizontal distance from the face of the cliff will the projectile strike the water?
Graph the function
Use a graphing utility to verify the solutions found in parts
When the height of the projectile is
(a)
To calculate: The horizontal distance from face of the cliff at which the height of the projectile is a maximum.
Answer to Problem 73AYU
Solution:
The height of projectile is maximum at a distance of
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A projectile is fired from a cliff 200 feet above the water at an inclination of
Formula used:
The graph of the function
Calculation:
A projectile is fired from a cliff 200 feet above the water at an inclination of
The graph of the function
Compare
Hence, the height of projectile is maximum at a distance
(b)
To calculate: The maximum height of the projectile.
Answer to Problem 73AYU
Solution:
The maximum height of the projectile is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A projectile is fired from a cliff 200 feet above the water at an inclination of
Formula used:
The graph of the function
Calculation:
A projectile is fired from a cliff 200 feet above the water at an inclination of
The graph of the function
Compare
The maximum height of projectile is
(c)
To calculate: The horizontal distance from the face of the cliff at which the projectile will strike the water.
Answer to Problem 73AYU
Solution:
The projectile will strike the water at
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A projectile is fired from a cliff 200 feet above the water at an inclination of
Formula used:
When the projectile touches the water the height of the projectile becomes zero.
Calculation:
A projectile is fired from a cliff 200 feet above the water at an inclination of
When the projectile touches the water the height of the projectile becomes zero.
The least common denominator is
Divide by
The equation
As
The projectile will strike the water at
(d)
To graph: To graph
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Graph:
The equation of
To graph
Step 1: Press Y= and enter the expression
Press [2nd][MATH] to write the inequality
Press [2nd][MATH][
Step 2: Press [GRAPH].
The graph will be as given below
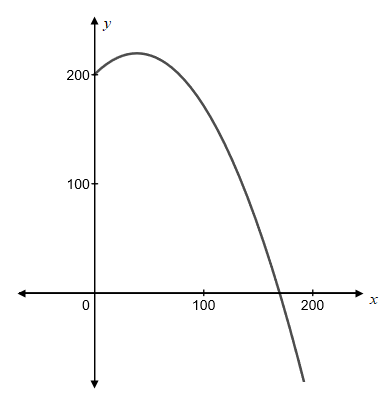
Interpretation:
The graph of the equation
(e)
To calculate: The maximum and zeros of
Answer to Problem 73AYU
Solution:
Maximum of
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Calculation:
The equation of
To find the zero and maximum of
Step 1: Press Y= and enter the expression
Step 2: Press [2nd][TRACE] to get the CALC. Under CALC menu choose 2: zero and press
ENTER.
Step 3: Move the cursor( use arrow keys ) to left of observed zero location. Press ENTER.
Step 4: Move the cursor( use arrow keys ) to right of observed zero location. Press ENTER.
Step 5: When last screen asks for guess press ENTER.
The coordinates of zeros are
As the distance and height can’t be negative, the co-ordinate of zero is
Step 6: Press [2ND][TRACE] to get the CALC. Under CALC menu choose 3: maximum and press ENTER.
Step 7: Move the cursor (use arrow keys) to left of observed maximum location. Press ENTER.
Step 8: Move the cursor( use arrow keys ) to right of observed maximum location. Press ENTER.
Step 9: When last screen asks for guess, press ENTER
The coordinate of maximum value is
From part (b) the maximum height is
Hence, using graphical utility the maximum height and the zero of the function coincides with the answers from part (b) and part (c).
(f)
To calculate: The distance of the projectile from the cliff, when it is 100 feet above the water.
Answer to Problem 73AYU
Solution:
The distance of projectile from the cliff is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A projectile is fired from a cliff 200 feet above the water at an inclination of
Formula used:
Calculation:
A projectile is fired from a cliff 200 feet above the water at an inclination of
Where
The projectile is 100 feet above the water.
The least common denominator is
Divide by
Add
The equation
As
The distance of projectile from the cliff is
Chapter 3 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Glencoe Math Accelerated, Student Edition
Precalculus: Concepts Through Functions, A Unit Circle Approach to Trigonometry (4th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Precalculus (10th Edition)
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities (7th Edition)
Calculus, Single Variable: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





