
Concept explainers
Review. The use of superconductors has been proposed for power transmission lines. A single coaxial cable (Fig. P31.47) could carry a power of 1.00 × 103 MW (the output of a large power plant) at 200 kV, DC, over a distance of 1.00 × 103 km without loss. An inner wire of radius a = 2.00 cm, made from the superconductor Nb3Sn, carries the current I in one direction. A surrounding superconducting cylinder of radius b = 5.00 cm would carry the return current I. In such a system, what is the magnetic field (a) at the surface of the inner conductor and (b) at the inner surface of the outer conductor? (c) How much energy would he stored in the magnetic field in the space between the conductors in a 1.00 × 103 km superconducting line? (d) What is the pressure exerted on the outer conductor due to the current in the inner conductor?
Figure P31.47
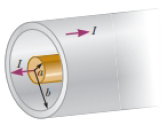
(a)
Answer to Problem 32.75AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The power carry by the coaxial cable is 1.00×103 MW, potential difference is 200 kV, total distance is 1.00×103 km inner radius is 2.00 cm and surrounding cylinder radius is 5.00 cm.
Formula to calculate the current flow in the coaxial cable is,
i=PΔV
Here,
i is the current flow in the coaxial cable.
P is the power deliver.
ΔV is the potential difference.
Substitute 1.00×103 MW for P and 200 kV for ΔV to find i.
i=1.00×103 MW×106 W1 MW200 kV×103 V1 kV=5×103 A
Thus, the current flow in the coaxial cable is 5×103 A.
Formula to calculate the magnetic field at inner conductor from Ampere’s law is,
Bin=μ0i2πa
Here,
Bin is the magnetic field at inner conductor.
μ0 is the absolute permeability of free space.
a is the radius of inner cable.
Substitute 4π×10−7 T⋅m/A for μ0, 5×103 A for i, and 2.00 cm for a to find the Bin.
Bin=4π×10−7 T⋅m/A×5×103 A2π×2.00 cm×10−2 m1 cm=0.050 T×103 mT1 T=50.0 mT
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnetic field at the surface of the inner conductor is 50.0 mT.
(b)
Answer to Problem 32.75AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The power carry by the coaxial cable is 1.00×103 MW, potential difference is 200 kV, total distance is 1.00×103 km inner radius is 2.00 cm and surrounding cylinder radius is 5.00 cm.
Formula to calculate the magnetic field at inner surface of outer conductor from Ampere’s law is,
Bout=μ0i2πb
Here,
Bout is the magnetic field at inner surface of outer conductor.
b is the radius of outer conductor.
Substitute 4π×10−7 T⋅m/A for μ0, 5×103 A for i, and 5.00 cm for b to find the Bin.
Bin=4π×10−7 T⋅m/A×5×103 A2π×5.00 cm×10−2 m1 cm=0.020 T×103 mT1 T=20.0 mT
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnetic field at the surface of the inner conductor is 20.0 mT.
(c)
Answer to Problem 32.75AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The power carry by the coaxial cable is 1.00×103 MW, potential difference is 200 kV, total distance is 1.00×103 km inner radius is 2.00 cm and surrounding cylinder radius is 5.00 cm.
Formula to calculate the energy density store in magnetic field is,
uB=B22μ0
Formula to calculate the total energy stored in the magnetic field in the space between the conductors is,
U=∫bauBdV (1)
Here,
U is the total energy stored in the magnetic field in the space between the conductors.
dV is the small arbitrary volume.
Write the expression for the small arbitrary volume.
dV=2πrldr
Here,
r is the distance from the center of the coaxial cable.
l is the length of the coaxial cable.
Formula to calculate the magnetic field from Ampere’s law is,
B=μ0i2πr
Substitute μ0i2πr for B and 2πrldr for dV in equation (1).
U=∫ba((μ0i2πr)22μ0)(2πrldr)=∫ba(μ0i28π2r2)(2πrldr)=μ0i2l4π∫ba(drr)
Integrate the above equation within limits.
μ0i2l4πln[ba]
Substitute 4π×10−7 T⋅m/A for μ0, 5×103 A for i, 2.00 cm for a, 5.00 cm for b, and 1.00×103 km for l.
U=(4π×10−7 T⋅m/A)(5×103 A)2(1.00×103 km×103 m1 km)4πln[5.00 cm2.00 cm]=(2.5×106)ln(2.5) J=2.29×106 J×10−6 MJ1 J=2.29 MJ
Conclusion:
Therefore, the energy that stored in the magnetic field in the space between the conductors is 2.29 MJ.
(d)
Answer to Problem 32.75AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The power carry by the coaxial cable is 1.00×103 MW, potential difference is 200 kV, total distance is 1.00×103 km inner radius is 2.00 cm and surrounding cylinder radius is 5.00 cm.
The magnetic field created by the inner conductor exerts a force of repulsion on the current in the outer sheath. The strength of this magnetic field is calculated in part (b) that is 20.0 mT.
Write the expression for the projection area of the outer conductor.
Ap=wl
Write the expression for the circumferential area of the outer conductor.
Cl=2πb
Formula to calculate the current flow in the outer cylinder is,
iout=i×ApCl
Here,
Ax is the projection area.
Cl is the circumferential length.
Substitute wl for Ap and 2πb for Ac.
iout=i×wl2πb
Substitute 5×103 A for i and 5.00 cm for b to find iout.
iout=(5×103 A)×wl2π(5.00 cm×10−2 m1 cm)=(105 A/m)wl2π
Formula to calculate the force experience by the outer conductor is,
F=ioutBl
Formula to calculate the pressure exerted on the conductor due to the current is,
P=FA
Substitute ioutBl for F and wl for A to find P.
P=ioutBlwl
Substitute (105 A/m)wl2π for iout, 20.0 mT for B.
P=((105 A/m)wl2π)(20.0 mT×10−3 T1 mT)wl=318 Pa
Conclusion:
Therefore, the pressure exerted on the conductor due to the current in the inner conductor is 318 Pa.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 32 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
- An object is placed 24.1 cm to the left of a diverging lens (f = -6.51 cm). A concave mirror (f= 14.8 cm) is placed 30.2 cm to the right of the lens to form an image of the first image formed by the lens. Find the final image distance, measured relative to the mirror. (b) Is the final image real or virtual? (c) Is the final image upright or inverted with respect to the original object?arrow_forwardConcept Simulation 26.4 provides the option of exploring the ray diagram that applies to this problem. The distance between an object and its image formed by a diverging lens is 5.90 cm. The focal length of the lens is -2.60 cm. Find (a) the image distance and (b) the object distance.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





