
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780100546714
Author: Katz
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 30, Problem 11PQ
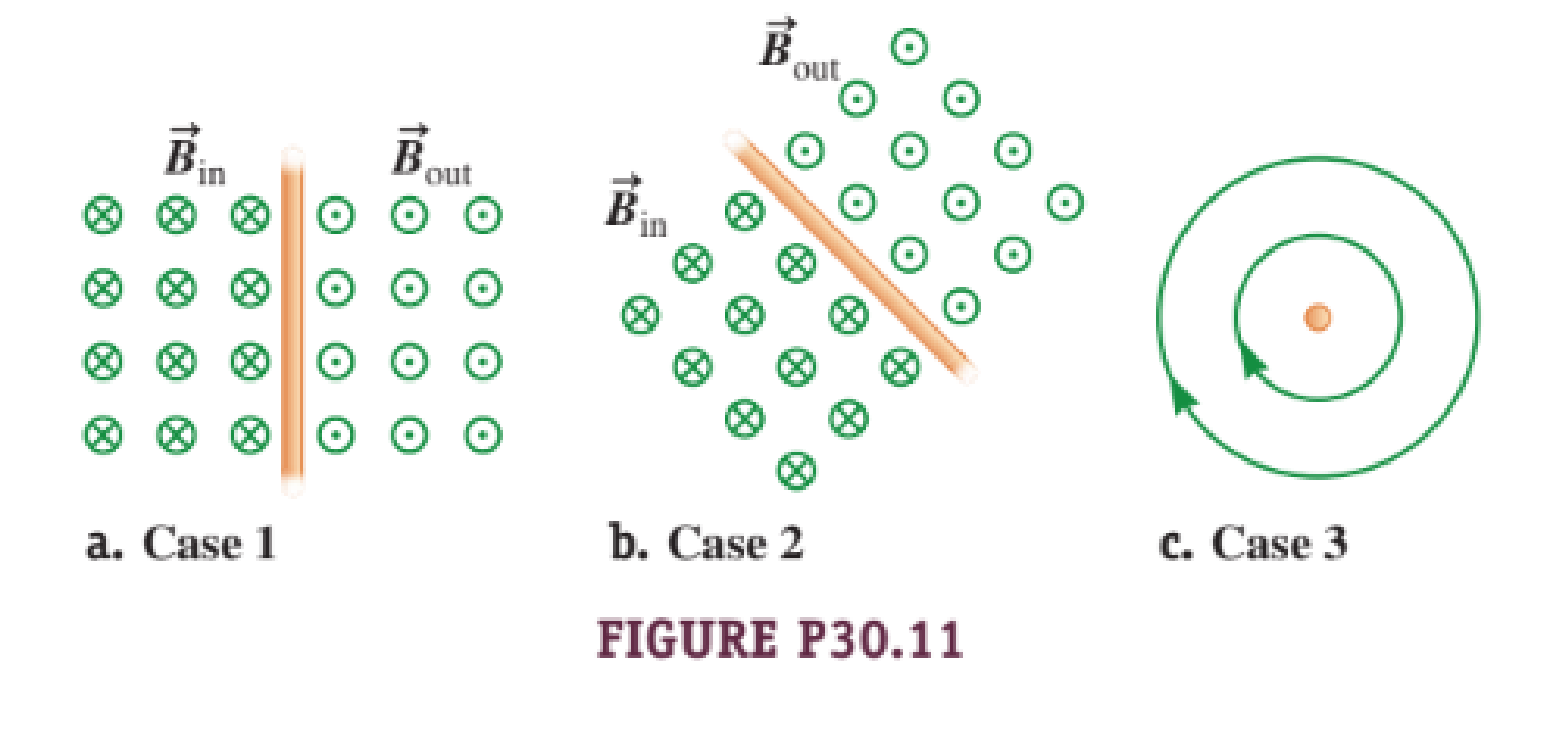
Figure P30.11 shows three configurations of wires and the resultant magnetic fields due to current in the wires. What is the direction of the current that gives the resultant magnetic field shown in each case?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 30 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
Ch. 30.2 - Prob. 30.1CECh. 30.3 - Prob. 30.2CECh. 30.4 - Prob. 30.3CECh. 30.8 - Cosmic rays are high-energy charged particles...Ch. 30.9 - The Earths Van Allen belts (Fig. 30.34) are a...Ch. 30.10 - Prob. 30.6CECh. 30.10 - Prob. 30.7CECh. 30.12 - Prob. 30.8CECh. 30 - A yoga teacher tells her students to imagine their...Ch. 30 - Prob. 2PQ
Ch. 30 - Prob. 3PQCh. 30 - Prob. 4PQCh. 30 - Prob. 5PQCh. 30 - Copy Figure P30.6 and sketch the magnetic field...Ch. 30 - Prob. 7PQCh. 30 - Prob. 9PQCh. 30 - Figure P30.10 shows a circular current-carrying...Ch. 30 - Figure P30.11 shows three configurations of wires...Ch. 30 - Review A proton is accelerated from rest through a...Ch. 30 - An electron moves in a circle of radius r at...Ch. 30 - One common type of cosmic ray is a proton...Ch. 30 - Prob. 15PQCh. 30 - Prob. 16PQCh. 30 - Prob. 17PQCh. 30 - A Two long, straight, parallel wires are shown in...Ch. 30 - Prob. 19PQCh. 30 - Two long, straight, parallel wires carry current...Ch. 30 - Prob. 21PQCh. 30 - Two long, straight wires carry the same current as...Ch. 30 - Prob. 23PQCh. 30 - A wire is bent in the form of a square loop with...Ch. 30 - Prob. 25PQCh. 30 - A Derive an expression for the magnetic field...Ch. 30 - Prob. 27PQCh. 30 - Prob. 28PQCh. 30 - Prob. 29PQCh. 30 - Prob. 30PQCh. 30 - Prob. 31PQCh. 30 - Prob. 32PQCh. 30 - Prob. 33PQCh. 30 - Prob. 34PQCh. 30 - Normally a refrigerator is not magnetized. If you...Ch. 30 - Prob. 36PQCh. 30 - Prob. 37PQCh. 30 - The magnetic field in a region is given by...Ch. 30 - Prob. 39PQCh. 30 - Prob. 40PQCh. 30 - Prob. 41PQCh. 30 - The velocity vector of a singly charged helium ion...Ch. 30 - Prob. 43PQCh. 30 - Can you use a mass spectrometer to measure the...Ch. 30 - In a laboratory experiment, a beam of electrons is...Ch. 30 - Prob. 46PQCh. 30 - Prob. 47PQCh. 30 - Prob. 48PQCh. 30 - A proton and a helium nucleus (consisting of two...Ch. 30 - Two ions are accelerated from rest in a mass...Ch. 30 - Prob. 51PQCh. 30 - Prob. 52PQCh. 30 - A rectangular silver strip is 2.50 cm wide and...Ch. 30 - For both sketches in Figure P30.56, there is a...Ch. 30 - A 1.40-m section of a straight wire oriented along...Ch. 30 - Professor Edward Ney was the founder of infrared...Ch. 30 - Prob. 59PQCh. 30 - A wire with a current of I = 8.00 A directed along...Ch. 30 - Prob. 61PQCh. 30 - The triangular loop of wire shown in Figure P30.62...Ch. 30 - Prob. 63PQCh. 30 - Consider the wires described in Problem 63. Find...Ch. 30 - Prob. 65PQCh. 30 - Prob. 66PQCh. 30 - A Three parallel current-carrying wires are shown...Ch. 30 - Prob. 68PQCh. 30 - Prob. 69PQCh. 30 - Prob. 70PQCh. 30 - Prob. 71PQCh. 30 - Prob. 72PQCh. 30 - A circular coil 15.0 cm in radius and composed of...Ch. 30 - Prob. 74PQCh. 30 - Prob. 75PQCh. 30 - Prob. 76PQCh. 30 - Prob. 77PQCh. 30 - Two long, straight, current-carrying wires run...Ch. 30 - Prob. 79PQCh. 30 - Prob. 80PQCh. 30 - Prob. 81PQCh. 30 - Prob. 82PQCh. 30 - Two infinitely long current-carrying wires run...Ch. 30 - Prob. 84PQCh. 30 - Prob. 85PQCh. 30 - Prob. 86PQCh. 30 - A charged particle with charge q and velocity...Ch. 30 - Prob. 88PQCh. 30 - Prob. 89PQCh. 30 - A mass spectrometer (Fig. 30.40, page 956)...Ch. 30 - Three long, current-carrying wires are parallel to...Ch. 30 - Prob. 92PQCh. 30 - A current-carrying conductor PQ of mass m and...Ch. 30 - A proton enters a region with a uniform electric...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A uniform magnetic field B=5.44104iT passes through a closed surface with a slanted top as shown in Figure P31.59. a. Given the dimensions and orientation of the closed surface shown, what is the magnetic flux through the slanted top of the surface? b. What is the net magnetic flux through the entire closed surface?arrow_forwardFigure P30.10 shows a circular current-carrying wire. Using the coordinate system indicated (with the z axis out of the page), state the direction of the magnetic field at points A and B.arrow_forwardDetermine the initial direction of the deflection of charged particles as they enter the magnetic fields as shown in Figure P22.2. Figure P22.2.arrow_forward
- A toroid has a major radius R and a minor radius r and is tightly wound with N turns of wire on a hollow cardboard torus. Figure P31.6 shows half of this toroid, allowing us to see its cross section. If R r, the magnetic field in the region enclosed by the wire is essentially the same as the magnetic field of a solenoid that has been bent into a large circle of radius R. Modeling the field as the uniform field of a long solenoid, show that the inductance of such a toroid is approximately L=120N2r2R Figure P31.6arrow_forwardAn electron in a TV CRT moves with a speed of 6.0107 m/s, in a direction perpendicular to Earth's field, which has a strength of 5.0105 T. (a) What strength electric field must be applied perpendicular to the Earth’s field to make the election moves in a straight line? (b) If this is done between plates separated by 1.00 cm, what is the voltage applied? (Note that TVs are usually surrounded by a ferromagnetic material to shield against external magnetic fields and avoid the need for such a collection,)arrow_forwardOne common type of cosmic ray is a proton traveling at close to the speed of light. If the proton is traveling downward, as shown in Figure P30.14, at a speed of 1.00 107 m/s, what are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point B?arrow_forward
- The current density in the long, cylindrical wire shown in the accompanying figure varies with distance r from the center of the wire according to J = cr. where c is a constant (a) What is the current through the wire? (b) What is the magnetic field produced by this current for r < R? For rR ?arrow_forwardA Derive an expression for the magnetic field produced at point P due to the current-carrying wire shown in Figure P30.26. The curved parts of the wire are pieces of concentric circles. Point P is at their center.arrow_forwardThe Hall effect finds important application in the electronics industry. It is used to find the sign and density of the carriers of electric current in semiconductor chips. The arrangement is shown in Figure P22.66. A semiconducting block of thickness t and width d carries a current I in the x direction. A uniform magnetic field B is applied in the y direction. If the charge carriers are positive, the magnetic force deflects them in the z direction. Positive charge accumulates on the top surface of the sample and negative charge on the bottom surface, creating a downward electric field. In equilibrium, the downward electric force on the charge carriers balances the upward magnetic force and the carriers move through the sample without deflection. The Hall voltage ΔVH = Vc − Va between the top and bottom surfaces is measured, and the density of the charge carriers can be calculated from it. (a) Demonstrate that if the charge carriers are negative the Hall voltage will be negative. Hence, the Hall effect reveals the sign of the charge carriers, so the sample can be classified as p-type (with positive majority charge carriers) or n-type (with negative). (b) Determine the number of charge carriers per unit volume n in terms of I, t, B, ΔVH, and the magnitude q of the carrier charge. Figure P22.66arrow_forward
- Electromagnetic braking can be achieved by applying a strong magnetic field to a pinning metal disk attached to a shaft. (a) How can a magnetic field slow the spinning of a disk? (b) Would the brakes work if the disk was made of plastic instead of metal?arrow_forwardA cube of edge length l=2.50 cm is positioned as shown in Figure P30.47. A uniform magnetic field given by B = (5 i + 4j + 3k) T exists throughout the region. (a) Calculate the magnetic flux through the shaded face. (b) What is the total flux through the six faces?arrow_forwardA uniform magnetic field of magnitude is directed parallel to the z-axis. A proton enters the field with a velocity v=(4j+3k)106m/s and travels in a helical path with a radius of 5.0 cm. (a) What is the value of B? (b) What is the time required for one trip around the helix? (c) Where is the proton 5.0107s after entering the field?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Magnets and Magnetic Fields; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IgtIdttfGVw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY