
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
Step – 1
The skeletal structure and charge has to be drawn.
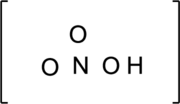
Step – 2
The total number of valence electrons is determined.
Step – 3
Connect the atoms using single bond.
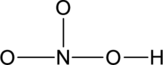
Step – 4
Start placing the lone pairs electrons around the atoms, giving each an octet. Do not exceed the 24 available electrons.
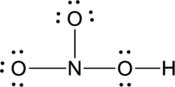
Step – 5
A final electron count indicates that each atom has eight valence electrons surrounding it.
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
Step – 1
The skeletal structure and charge has to be drawn.
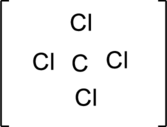
Step – 2
The total number of valence electrons is determined.
Step – 3
Connect the atoms using single bond.
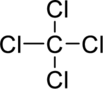
Step – 4
Start placing the lone pairs electrons around the atoms, giving each an octet. Do not exceed the 32 available electrons.
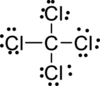
Step – 5
A final electron count indicates that each atom has eight valence electrons surrounding it.
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
Step – 1
The skeletal structure and charge has to be drawn.
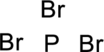
Step – 2
The total number of valence electrons is determined.
Step – 3
Connect the atoms using single bond.
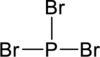
Step – 4
Start placing the lone pairs electrons around the atoms, giving each an octet. Do not exceed the 26 available electrons.
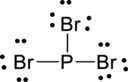
Step – 5
A final electron count indicates that each atom has eight valence electrons surrounding it.
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
Step – 1
The skeletal structure and charge has to be drawn.
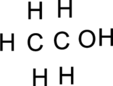
Step – 2
The total number of valence electrons is determined.
Step – 3
Connect the atoms using single bond.
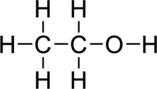
Step – 4
Start placing the lone pairs electrons around the atoms, giving each an octet. Do not exceed the 20 available electrons.
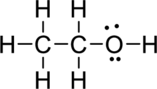
Step – 5
A final electron count indicates that each atom has eight valence electrons surrounding it.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biochemistry
- (f) SO: Best Lewis Structure 3 e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:, (g) CF2CF2 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: (h) (NH4)2SO4 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward1. Problem Set 3b Chem 141 For each of the following compounds draw the BEST Lewis Structure then sketch the molecule (showing bond angles). Identify (i) electron group geometry (ii) shape around EACH central atom (iii) whether the molecule is polar or non-polar (iv) (a) SeF4 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: (b) AsOBr3 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward(c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





