
Interpretation:
The planar densities for planes
Concept introduction:
Planar density is the ratio of the area of the plane to the number of atoms in a plane.
Answer to Problem 3.71P
Planar densities for the plane:
Plane (110) is denser (closely packed) than others.
Explanation of Solution
Planar density is expressed as,
P = No. of atom/Area of plane =Z/A
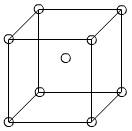
(a) For plane
(b) For plane
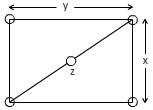
BCC unit cell with the plane (110) is rectangular.
Area of rectangular
Where
Diagonal length =4R.
Using Pythagoras theorem,
Number of atoms in the plane (110),
1 atom at every four corners and 1 center atom within the cell.
Planar density =
[Planar density]2 =
(c) For plane
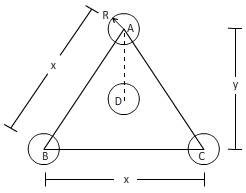
Plane (111)inthe BCC unit cell is having a triangular section.
Now, to calculate middle line length y is from the figure,
Now,
A plane with higher plane density is highly dense.
Plane density for plane
By comparing values of planar density, the plane
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Essentials Of Materials Science And Engineering
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





