
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 3, Problem 3.6P
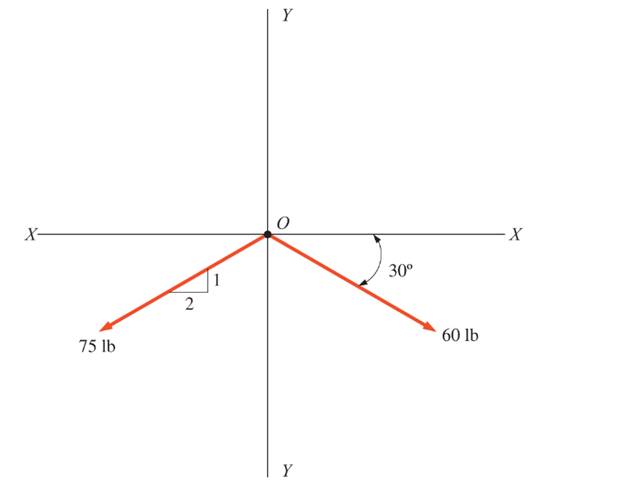
through 3.6 Solve Problem 3.1  through 3.3
through 3.3  using the method of components.
using the method of components.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule06:07
Students have asked these similar questions
2. A spur gear made of bronze drives a mid steel pinion with angular velocity ratio of 32: 1. The
pressure angle is 14½. It transmits 5 kW at 1800 r.p.m. of pinion. Considering only strength, design
the smallest diameter gears and find also necessary face width. The number of teeth should not be less
than 15 teeth on either gear. The elastic strength of bronze may be taken as 84 MPa and of steel as 105
MPa. Lewis factor for 14½½ pressure angle may be taken
0.684
0.124
y =
No. of teeth
as
[Ans. m 3 mm; b= 35 mm; Dp = 48 mm; D= 168 mm]
Q2. Determine the safety factors for the bracket rod shown in Figure 2 based on both the
distortion-energy theory and the maximum shear theory and compare them.
Given: The material is 2024-T4 aluminum with a yield strength of 47 000 psi.
The rod length /= 6 in. and arm a = 8 in. The rod outside diameter od 1.5 in., id = 1 in, h=2 in.,
t=0.5 in., Load F= 1000 lb.
Assumptions: The load is static and the assembly is at room temperature. Consider
shear due to transverse loading as well as other stresses. (Note: solve in SI units)
wall
tube
Figure 2
arm
The question has been set up with all the cuts needed to accurately derive expressions for V(x) and M(x). Using the cuts free body diagrams set up below, derive expressions for V(x) and M(x). If you use the method of cuts then validate your answers using calculus or vice versa.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 3 - through 3.3 Determine the magnitude, direction,...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude, direction, and sense of...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude, direction, and sense of...Ch. 3 - Solve Problem 3.1 through 3.3 using the method of...Ch. 3 - Solve Problem 3.1 through 3.3 using the method of...Ch. 3 - through 3.6 Solve Problem 3.1 through 3.3 using...Ch. 3 - The 150-lb force shown is the resultant of two...Ch. 3 - Find the resultant force P exerted on the tree.Ch. 3 - Find the resultant force R exerted on the pole.Ch. 3 - Calculate the resultant force on the screw eye....
Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant of the coplanar concurrent...Ch. 3 - Use the parallelogram law to find the following...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.13PCh. 3 - Determine the resultant of the coplanar concurrent...Ch. 3 - The resultant of the concurrent force system shown...Ch. 3 - Three force of 900 lb, 1000 lb, and 600 lb are...Ch. 3 - The four forces shown hade parallel lines of...Ch. 3 - Three coplanar concurrent forces act as shown. a....Ch. 3 - Four coplanar concurrent forces act as shown a....Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant of the four forces of...Ch. 3 - For the concrete wall and footing shown: a....Ch. 3 - Calculate the moment of the 550-lb force about...Ch. 3 - In Problem 3.22 , calculate the moment about point...Ch. 3 - Compute the moment about point A for the linkage...Ch. 3 - Compute the moment of the force F about point A...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant and its location for the...Ch. 3 - Compute the magnitude, sense, and location of the...Ch. 3 - Compute the magnitude, sense, and location of the...Ch. 3 - Compute the magnitude and location of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude and location of the...Ch. 3 - Fresh water is impounded behind a dam to a height...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude and location of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude and location of the...Ch. 3 - Compute the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 3 - Compute the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 3 - Compute the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 3 - A body is subjected to the following three...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude, direction, and sense of...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude, direction, and sense of...Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant of the load system shown....Ch. 3 - For the concrete structure shown, determine the...Ch. 3 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 3 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 3 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 3 - 3.49 Determine the magnitude, direction, and sense...Ch. 3 - The resultant and one-component force of a...Ch. 3 - The resultant force of a concurrent force system...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitudes of forces P1 and P2 such...Ch. 3 - The resultant force of a concurrent force system...Ch. 3 - A hockey puck is acted on simultaneously by two...Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant force for each of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant force for each of the...Ch. 3 - The resultant of the three concurrent forces shown...Ch. 3 - The transmission tower shown is subjected to a...Ch. 3 - A gravity-type masonry dam, as shown, depends on...Ch. 3 - The transfomer (as shown) must be lifted...Ch. 3 - Refer to the diagram for Problem 3.60 /. Assume...Ch. 3 - The plastic barrel tent anchor of Problem 2.11...Ch. 3 - Calculate the moment of the forces shown with...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude and location of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the moment (about point A) of the appied...Ch. 3 - The lift force on the wing of an aircraft is...Ch. 3 - A beam is subjected to distributed loads as shown....Ch. 3 - For the concrete gravity wall shown, determine the...Ch. 3 - Fresh water is impounded to a height of 8 ft...Ch. 3 - Plank, 2 in. by 10 in. in cross section and 5 ft...Ch. 3 - a. Compute the moment (about point A) of the...Ch. 3 - Determine the resultant of the three forces acting...Ch. 3 - a. Calculate the moments about points A and B due...Ch. 3 - Determine the magnitude of F1 and F2 shown such...Ch. 3 - Calculate the magnitude, direction, and sense of...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Show that for circular motion, force = mass * velocity squared/radius.
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Determine the maximum force P that can be applied without causing movement of the 250-lb crate that has a cente...
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
software is generally feature complete, (supposedly) bug free and ready for use by the community.
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Look at the following code, which is the first line of a class definition: public class Tiger extends Felis In ...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Write a program that requests the current time and a waiting time as two integers for the number of hours and t...
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- It is required to treat 130 kmol/hr of chloroform-air feed gas mixture that contains 12% chloroform. It is required to remove 93% of chloroform using 150 kmol/hr of solvent that contains 99.6% water and 0.4% chloroform. The cross sectional area of the column is 0.8 m². Calculate the column height using the following data; kx'.a = 1.35 (kmol/m³.s (Ax)), and ky'.a = 0.06 (kmol/m³.s (Ay)), kx/ky = 1.35, and the equilibrium data are: X 0 0.0133 0.033 y 0 0.01 0.0266 0.049 0.064 0.0747 0.0933 0.1053 0.0433 0.06 0.0733 0.111 0.1 0.12 0.14arrow_forward४ B: Find the numerical solution for the 2D equation below and calculate the temperature values for each grid point shown in Fig. 2 (show all steps). (Do only one trail using following initial values and show the final matrix) [T1] T₂ T3 [T] 1 = [0] 0 0 d dx dx) (ka)+4(ka) = dy -20xy, k = 1 + 0.3 T ge L=3cm, 4x= Ay B.Cs.: at x=0=LT=0°C at y=0-L T=10°C Fig. (2)arrow_forward: +0 العنوان use only Two rods fins) having same dimensions, one made orass (k = 85 Wm K) and the mer of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having of their ends inserted into a furna. At a section 10.5 cm a way from furnace, the temperature of brass rod 120 Find the distance at which the ame temperature would be reached in the per rod ? both ends are ex osed to the same environment. ns 2.05 ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forward
- For the beam show below, draw A.F.D, S.F.D, B.M.D 6 kN/m 1 M B. 3 M Marrow_forward1. Two long rods of the same diameter-one made of brass (k=85w/m.k) and the other made of copper (k=375 w/m.k) have one of their ends inserted into a furnace (as shown in the following figure). Both rods are exposed to the same environment. At a distance of 105 mm from the furnace, the temperature of the brass rod is 120°C. At what distance from the furnace will the same temperature be reached in the copper rod? Furnace 105 mm T₁ Brass rod ⑪ h Too- x2- Ti Copper rodarrow_forward: +0 العنوان use only Two rods fins) having same dimensions, one made orass (k = 85 Wm K) and the mer of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having of their ends inserted into a furna. At a section 10.5 cm a way from furnace, the temperature of brass rod 120 Find the distance at which the ame temperature would be reached in the per rod ? both ends are ex osed to the same environment. ns 2.05 ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forward
- مشر on ۲/۱ Two rods (fins) having same dimensions, one made of brass(k=85 m K) and the other of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having one of their ends inserted into a furnace. At a section 10.5 cm a way from the furnace, the temperature brass rod 120°C. Find the distance at which the same temperature would be reached in the copper rod ? both ends are exposed to the same environment. 22.05 ofthearrow_forwardThe composite wall of oven with A= 1m² as in Fig.1 consists of three materials, two of with kA = 20 W/m K and kc = 50 W/m K with thickness, LA=0.3 m, L= 0.15 m and Lc 0.15 m. The inner surface temperature T1=900 K and the outer surface temperature T4 300 K, and an oven air temperature of To=1100 K, h=25 W/m². K. Determine kɛ and the temperatures T2 and T3 also draw the thermal resistance networkarrow_forwardTwo rods (fins) having same dimensions, one made of brass (k = 85 Wm K) and the other of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having one of their ends inserted into a furnace. At a section 10.5 cm a way from the furnace, the temperature of brass rod 120°C. Find the distance at which the same temperature would be reached in the copper rod ? both ends are exposed to the same environment. Ans 22.05arrow_forward
- A long wire (k-8 W/m °C.) with ro 5 mm and surface temperature Ts=180°C as shown in Fig.2. Heat is generated in the wire uniformly at a rate of 5 x107 W/m³. If the energy equation is given by: d 11(77) + - =0 k r dr dr Derive an expression for T(r) and determine the temperature at the center of the wire and at r=2 mm. Air Th T KA LA T2 T3 T Fig.1 KB kc 180°C Го Fig.2arrow_forwardB: Find the numerical solution for the 2D equation below and calculate the temperature values for each grid point shown in Fig. 2 (show all steps). (Do only one trail using following initial values and show the final matrix) T₂ 0 T3 0 I need a real solution, not artificial intelligence locarrow_forwardCan I solve this problem by calculating the initial kinetic energy with respect to G instead of A.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Solids: Lesson 53 - Slope and Deflection of Beams Intro; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I7lTq68JRmY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY