
Given the vectors
(a)
To sketch: The diagram for the vector sum
Explanation of Solution
Introduction: Graphical method or geographical construction of vectors is defined as a method that is used to add more than two vectors. The resultant vector is drawn from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector.
Section 1:
To sketch: The diagram for the vector sum,
Introduction: Graphical method or geographical construction of vectors is defined as a method that is used to add more than two vectors. The resultant vector is drawn from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector.
Given information:
Vector
Draw the vector diagram for vector sum,
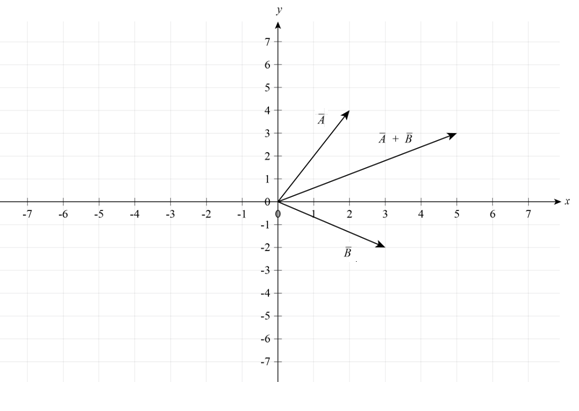
Figure I
Conclusion:
Therefore, the vector diagram for vector sum,
Section 2:
To sketch: The diagram for the vector difference,
Introduction: Graphical method or geographical construction of vectors is defined as a method that is used to add more than two vectors. The resultant vector is drawn from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector.
Given information:
Vector
Draw the vector diagram for vector difference,
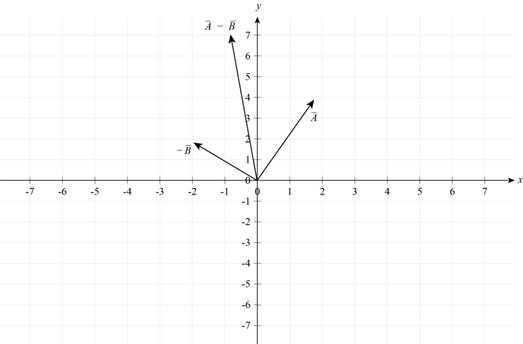
Figure II
Conclusion:
Therefore, the vector diagram for vector difference,
(b)
The vectors
Answer to Problem 26P
The vectors
Explanation of Solution
Section 1:
To determine: The vector
Answer: The vector
Given information:
Vector
Formula to calculate the
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the vector
Section 2:
To determine: The vector
Answer: The vector
Given information:
Vector
Formula to calculate the
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the vectors
(c)
The vectors
Answer to Problem 26P
The vectors
Explanation of Solution
Section 1:
To determine: The vector
Answer: The vector
Given information:
Vector
The vector
Formula to calculate the first polar coordinate is,
Substitute
Formula to calculate the second polar coordinate is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the vector
Section 2:
To determine: The vector
Answer: The vector
Given information:
Vector
The vector
Formula to calculate the first polar coordinate is,
Substitute
Formula to calculate the second polar coordinate is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the vectors
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
- look at answer show all work step by steparrow_forwardLook at the answer and please show all work step by steparrow_forward3. As a woman, who's eyes are h = 1.5 m above the ground, looks down the road sees a tree with height H = 9.0 m. Below the tree is what appears to be a reflection of the tree. The observation of this apparent reflection gives the illusion of water on the roadway. This effect is commonly called a mirage. Use the results of questions 1 and 2 and the principle of ray reversibility to analyze the diagram below. Assume that light leaving the top of the tree bends toward the horizontal until it just grazes ground level. After that, the ray bends upward eventually reaching the woman's eyes. The woman interprets this incoming light as if it came from an image of the tree. Determine the size, H', of the image. (Answer 8.8 m) please show all work step by steparrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning




