
Concept explainers
What two
a. an R-group and a hydroxyl group
b. an N–H group and a carbonyl group
c. an amino group and a hydroxyl group
d. an amino group and a carboxyl group
Introduction:
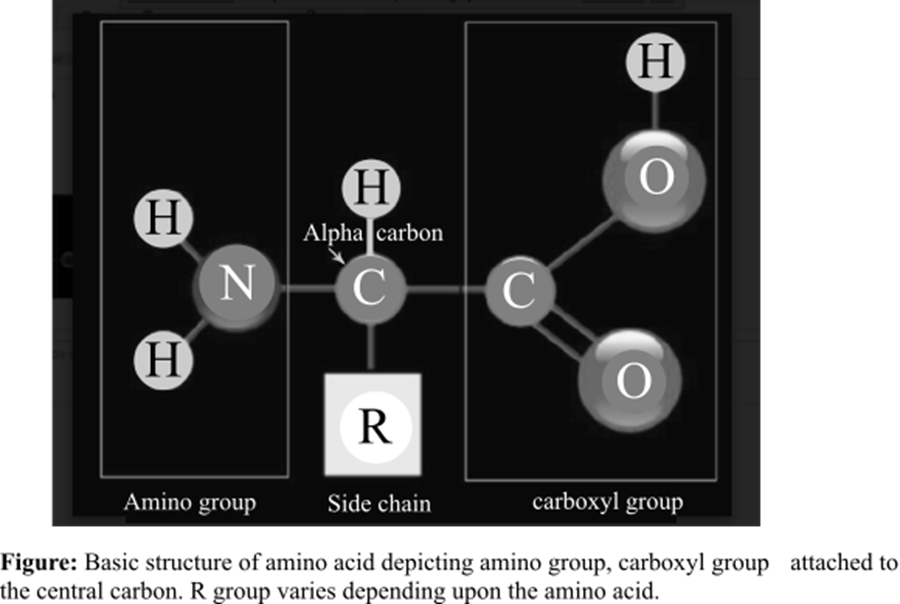
The amino acid is the basic structural unit of the proteins. There are total 20 amino acids found in the living system. At isoelectric point (pH or potential of hydrogen), an amino acid does not have any net charge. The basic structure of amino acids is shown below:
Answer to Problem 1TYK
Correct answer:
An amino group and a carboxyl group
Explanation of Solution
Explanation/Justification for the correct answer:
Option (d) is given as a carboxyl group along with an amino group. Functional groups of amino acids are responsible for bonding between two amino acids. The polypeptide chain consists of several amino acids. When a peptide bond is formed, a hydroxyl (–OH) group is lost from the carboxyl group of an amino acid and an H (hydrogen atom) from the amino group of another amino acid is also lost. This dehydration (loss of one H2O molecule) reaction results in a peptide bond. Hence, option (d) is correct.
Explanation for incorrect answers:
Option (a) is given as an R- group and a hydroxyl group. R group or side chain decides the identity of an amino acid, for example, glycine, which is the simplest amino acid, has a hydrogen atom as its R group. So, it is a wrong answer.
Option (b) is given as an N-H group and a carbonyl group. Any functional group, which has an O (oxygen) atom attached to the C (carbon) atom through double bond (-C=O) is called carbonyl group. COOH (carboxylic acid) is also a type of the carbonyl group. So, it is a wrong answer.
Option (c) is given as an amino group and a hydroxyl group. The carboxylic acid of the amino acid contains one hydroxyl group, which gets lost when the amino acid undergoes peptide bond formation with an amino group of another amino acid. So, it is a wrong answer.
Hence, options (a), (b), and (c) are incorrect.
The amino group and a carboxyl group are functional groups bounded to the central carbon of every free amino acid monomer.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
- Global climate change is expected to result in drastic changes in precipitation patterns. This might mean that, due to the rain shadow effect, the windward sides of mountains might be wetter, while the leeward sides of mountains might be drier. Using what you know about plant taxonomy and ecological relationships, propose a justified, ecological hypothesis on how plant community composition would change on each side of the mountain. Your answer should contain two parts: The hypothesis and the ecological justification addressing the bold points above.arrow_forwardExplain why homologies are used in constructing phylogenetic trees (2 pts). Give two specific examples of how using analogous characters would result in a tree depicting incorrect evolutionary relationships (4 pts). Aarrow_forwardD B - E C - A - Farrow_forward
- Discuss briefly the research on the effects of marijuana smoking on the functioning of the immune system.arrow_forward1) Describe how you would test the hypothesis that lobe eyes are a dominant lethal gene. Run the experiment and see if your hypothesis is correct. b) What are the possible body colors in fruit flies? Place an asterisk next to the wild type body color. c) Draw a fly with star-shaped eyes next to one with lobe eyes and insert your drawing below.arrow_forwardUtilizing the following pedigree, and the key for phenotypes, to the right of it, determine the genotypes of the individuals in the pedigree for blood type inheritance. Individual Blood Type I1 I2 II1 II2 II3 II4 III1 III2 III3 III4 III5 III6arrow_forward
- a)At what wavelength (nm) on a spectrometer can this color be quantified? b) Record your results. Indicate on this page which boxes turned color. A B C + - 1:2 1:10 1:100 c) Based on these results, which patient(s) definitely have lupus, which definitely do not, and which require further testing?arrow_forwarda) Which dog breed has the ancestral allele for all three genes, similar to gray wolves? b)Which dog breeds have a more recent allele for FGF5 but an ancestral allele for KRT71? c)Which coat type is the ancestral allele of the KRT71 gene associated with? d)How might understanding the functions of genes in dogs help us better understand human health?arrow_forwardIf a girl has ptosis and then she marries a man who is a normal eyes, what will be the phenotypic and genotypic ratio of their offspring? 2) Create a small pedigree, noting sex of each individual as well as whether or not they are affected with ptosisarrow_forward
- a) Which types of SNPs might be identified in a GWAS? b)Give two possible reasons for why a SNP would be associated with a trait like fur color. c)Which SNP in Table 1 do you think is completely associated with fur color? Explain the reasoning for your choice.arrow_forwarda) Which SNPs in Table 1 do you think are completely unassociated with fur color? Explain the reasoning for your choices. (Hint: There are five in total.) b) Which SNP in Table 1 do you think has the next strongest association with fur color, after the completely associated SNP you identified two questions ago? Explain the reasoning for your choice. c) Describe a specific problem or question that you could investigate by doing a GWAS with the organism you want to discussarrow_forwarda) What has happened in Bernalillo County to the number of cases of COVID-19 since 01.01.21? b) What is the basis of a traditional vaccine compared to the two top most common SARS-CoV-2 vaccines? c) What is a good resource to use when determining current risks and trends in COVID-19 numbers?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





