
Concept explainers
What is the predominant form of each of the following amino acids at
(a)
Interpretation: The predominant form of threonine at
Concept introduction: At isoelectric point, the amino acids exist in their neutral form. The amine groups exists as
Answer to Problem 29.36P
The predominant form of threonine at
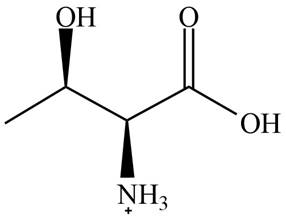
The overall charge on it is
Explanation of Solution
At isoelectric point, the amino acids exist in their neutral form. The amine groups exists as
The isoelectric point of threonine is
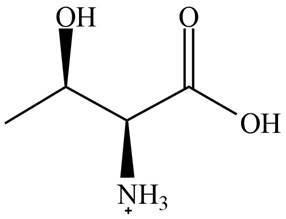
Figure 1
The overall charge on threonine at
The predominant form of threonine at
(b)
Interpretation: The predominant form of methionine at
Concept introduction: At isoelectric point, the amino acids exist in their neutral form. The amine groups exists as
Answer to Problem 29.36P
The predominant form of methionine at
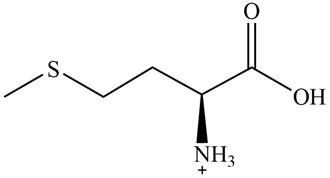
The overall charge on it is
Explanation of Solution
At isoelectric point, the amino acids exist in their neutral form. The amine groups exists as
The isoelectric point of methionine is
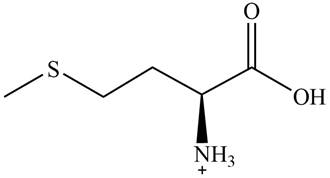
Figure 2
The overall charge on methionine at
The predominant form of methionine at
(c)
Interpretation: The predominant form of aspartic acid at
Concept introduction: At isoelectric point, the amino acids exist in their neutral form. The amine groups exists as
Answer to Problem 29.36P
The predominant form of aspartic acid at
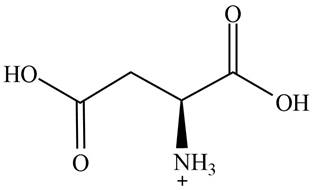
The overall charge on it is
Explanation of Solution
At isoelectric point, the amino acids exist in their neutral form. The amine groups exists as
The isoelectric point of aspartic acid is
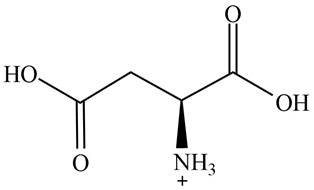
Figure 3
The overall charge on aspartic acid at
The predominant form of aspartic acid at
(d)
Interpretation: The predominant form of arginine at
Concept introduction: At isoelectric point, the amino acids exist in their neutral form. The amine groups exists as
Answer to Problem 29.36P
The predominant form of arginine at
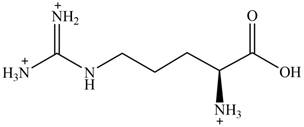
The overall charge on it is
Explanation of Solution
At isoelectric point, the amino acids exist in their neutral form. The amine groups exists as
The isoelectric point of arginine is
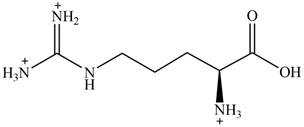
Figure 4
The overall charge on arginine at
The predominant form of arginine at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 29 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





