
Core Skill: Modeling The goal of this modeling challenge is to make a simplified model of the one shown in Figure 28.29, to determine if the latter represents a life cycle that is diploid dominant, haploid dominant, or an alternation of generations.
Modeling Challenge: Chapter 16 describes the three basic types of eukaryotic sexual life cycles (refer back to Figure 16.14). These cycles are modeled by circular diagrams that show life phases connected by the processes of fertilization, meiosis, and mitotic cell divisions. Animals display a diploid-dominant life cycle;
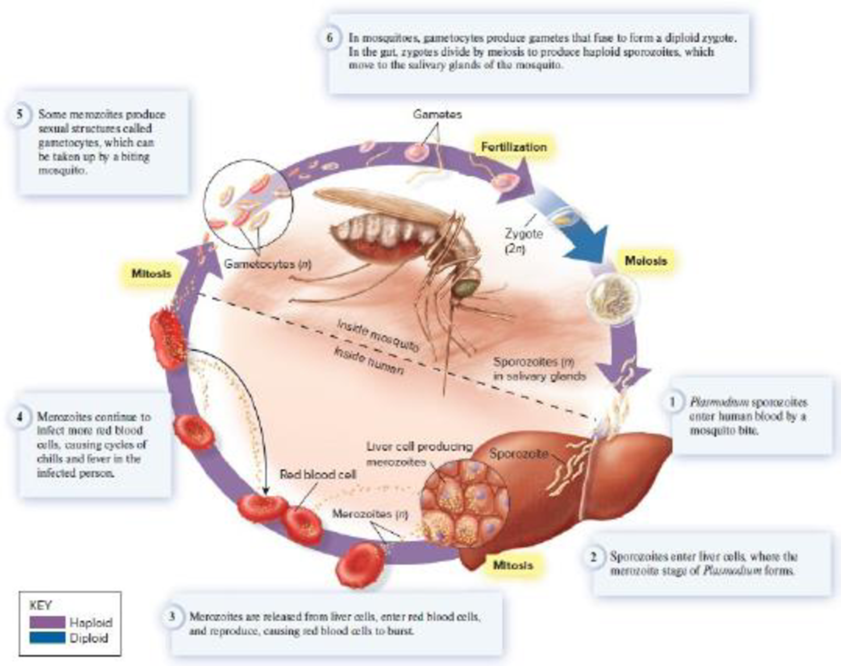
Figure 28.29 Diagram of the life cycle of Plasmodium falciparum, a species that causes malaria in humans. This life cycle requires two alternate hosts, humans and Anopheles mosquitoes.
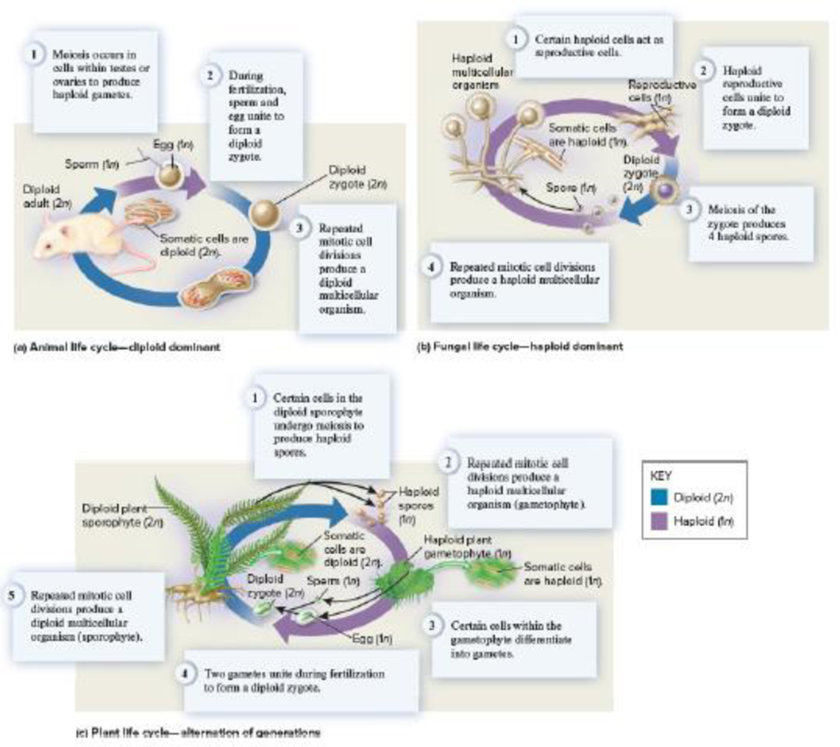
Figure 16.14 A comparison of three types of life cycles for sexually reproducing organisms.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
Biology
- Which of the following is the process that is "capable of destroying all forms of microbial life"? Question 37 options: Surgical scrub Sterilization Chemical removal Mechanical removalarrow_forwardAfter you feel comfortable with your counting method and identifying cells in the various stages of mitosis, use the four images below of whitefish blastula to count the cells in each stage until you reach 100 total cells, recording your data below in Data Table 1. (You may not need to use all four images. Stop counting when you reach 100 total cells.) After totaling the cells in each stage, calculate the percent of cells in each stage. (Divide total of stage by overall total of 100 and then multiply by 100 to obtain percentage.) Data Table 1Stage Totals PercentInterphase Mitosis: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis Totals 100 100% To find the length of time whitefish blastula cells spend in each stage, multiply the percent (recorded as a decimal, in other words take the percent number and divide by 100) by 24 hours. (Example: If percent is 20%, then Time in Hours = .2 * 24 = 4.8) Record your data in Data…arrow_forwardWhat are Clathrin coated vesicles and what is their function?arrow_forward
- How is a protein destined for the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), imported into the ER? Be concise.arrow_forwardFind out about the organisations and the movements aimed at the conservation of our natural resources. Eg Chipko movement and Greenpeace. Make a project report on such an organisation.arrow_forwardWhat are biofertilizers and mention the significancearrow_forward
- PCBs and River Otters: Otters in Washington State’s Green-Duwamish River have high levels of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in their livers. PCBs can bind to the estrogen receptors in animals and disrupt the endocrine system of these otters. The PCBs seem to increase the estrogen to androgen ratio, skewing the ratio toward too much estrogen. How would increased estrogen affect the river otter population? Based on your reading of the materials in this unit, what factors can affect fertility in humans? Explain how each of the factors affecting human fertility that you described can disrupt the human endocrine system to affect reproduction.arrow_forwardOther than oil and alcohol, are there other liquids you could compare to water (that are liquid at room temperature)? How is water unique compared to these other liquids? What follow-up experiment would you like to do, and how would you relate it to your life?arrow_forwardSelection of Traits What adaptations do scavengers have for locating and feeding on prey? What adaptations do predators have for capturing and consuming prey?arrow_forward
- Competition Between Species What natural processes limit populations from growing too large? What are some resources organisms can compete over in their natural habitat?arrow_forwardSpecies Interactions Explain how predators, prey and scavengers interact. Explain whether predators and scavengers are necessary or beneficial for an ecosystem.arrow_forwardmagine that you are conducting research on fruit type and seed dispersal. You submitted a paper to a peer-reviewed journal that addresses the factors that impact fruit type and seed dispersal mechanisms in plants of Central America. The editor of the journal communicates that your paper may be published if you make ‘minor revisions’ to the document. Describe two characteristics that you would expect in seeds that are dispersed by the wind. Contrast this with what you would expect for seeds that are gathered, buried or eaten by animals, and explain why they are different. (Editor’s note: Providing this information in your discussion will help readers to consider the significance of the research).arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





