
Concept explainers
In Fig. 28-44, a metal wire of mass m = 24.1 mg can slide with negligible friction on two horizontal parallel rails separated by distance d = 2.56 cm. The track lies in a vertical uniform magnetic field of magnitude 56.3 mT. At time t = 0, device G is connected to the rails, producing a constant current i = 9.13 mA in the wire and rails (even as the wire moves). At t = 61.1 ms, what are the wire’s (a) speed and (b) direction of motion (left or right)?
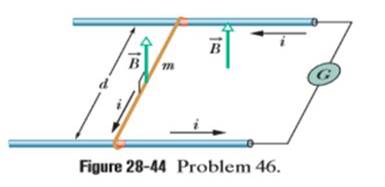
Figure 28-44 Problem 46.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 28 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS (LLF)+WILEYPLUS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Physics (5th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
- Assume the region to the right of a certain plane contains a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.00 mT and the field is zero in the region to the left of the plane as shown in Figure P22.71. An electron, originally traveling perpendicular to the boundary plane, passes into the region of the field. (a) Determine the time interval required for the electron to leave the field-filled region, noting that the electrons path is a semicircle. (b) Assuming the maximum depth of penetration into the field is 2.00 cm, find the kinetic energy of the electron.arrow_forwardA magnetic field directed into the page changes with time according to B = 0.030 0t2 + 1.40, where B is in teslas and t is in seconds. The field has a circular cross section of radius R = 2.50 cm (see Fig. P23.28). When t = 3.00 s and r2 = 0.020 0 m, what are (a) the magnitude and (b) the direction of the electric field at point P2?arrow_forwardA mass spectrometer (Fig. 30.40, page 956) operates with a uniform magnetic field of 20.0 mT and an electric field of 4.00 103 V/m in the velocity selector. What is the radius of the semicircular path of a doubly ionized alpha particle (ma = 6.64 1027 kg)?arrow_forward
- An election moves through a uniform electric field E = (2.50i + 5.00j) V/m and a uniform magnetic field B = 0.400k T. Determine the acceleration of the electron when it has a velocity v = 10.0i m/s.arrow_forwardHow many turns must be wound on a flat, circular coil of radius 20 cm in order to produce a magnetic field of magnitude 4.0105 T at the center of the coil when the current through it is 0.85 A?arrow_forwardSolenoid A has length L and N turns, solenoid B has length 2L and N turns, and solenoid C has length L/2 and 2N turns. If each solenoid carries the same current, rank the magnitudes of the magnetic fields in the centers of the solenoids from largest to smallest.arrow_forward
- Sketch a plot of the magnitude of the magnetic field as a function of position r for a coax (Fig. P31.27).arrow_forwardA square loop whose sides are 6.0-cm long is made with copper wire of radius 1.0 mm. If a magnetic field perpendicular to the loop is changing at a rate of 5.0 mT/s, what is the current in the loop?arrow_forwardA circular coil of radius 5.0 cm is wound with five turns and carries a current of 5.0 A. If the coil is placed in a uniform magnetic field of strength 5.0 T, what is the maximum torque on it?arrow_forward
- A proton (charge +e, mass mp), a deuteron (charge +e, mass 2mp), and an alpha particle (charge +2e, mass 4mp) are accelerated from rest through a common potential difference V. Each of the particles enters a uniform magnetic field B, with its velocity in a direction perpendicular to B. The proton moves in a circular path of radius p. In terms of p, determine (a) the radius rd of the circular orbit for the deuteron and (b) the radius r for the alpha particle.arrow_forwardFigure CQ19.7 shows a coaxial cable carrying current I in its inner conductor and a return current of the same magnitude in the opposite direction in the outer conductor. The magnetic field strength at r = r0 is Find the ratio B/B0, at (a) r = 2r0 and (b) r = 4r0. Figure CQ19.7arrow_forwardCalculate the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point 25.0 cm from a long, thin conductor carrying a current of 2.00 A.arrow_forward

 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





