
Microbiology: An Introduction
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780321929150
Author: Gerard J. Tortora, Berdell R. Funke, Christine L. Case
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 28, Problem 1CAE
Suppose you are culturing a microorganism that produces enough lactic acid to kill itself in a few days.
- a. How can the use of a bioreactor help you maintain the culture for weeks or months? The graph below shows conditions in the bioreactor:
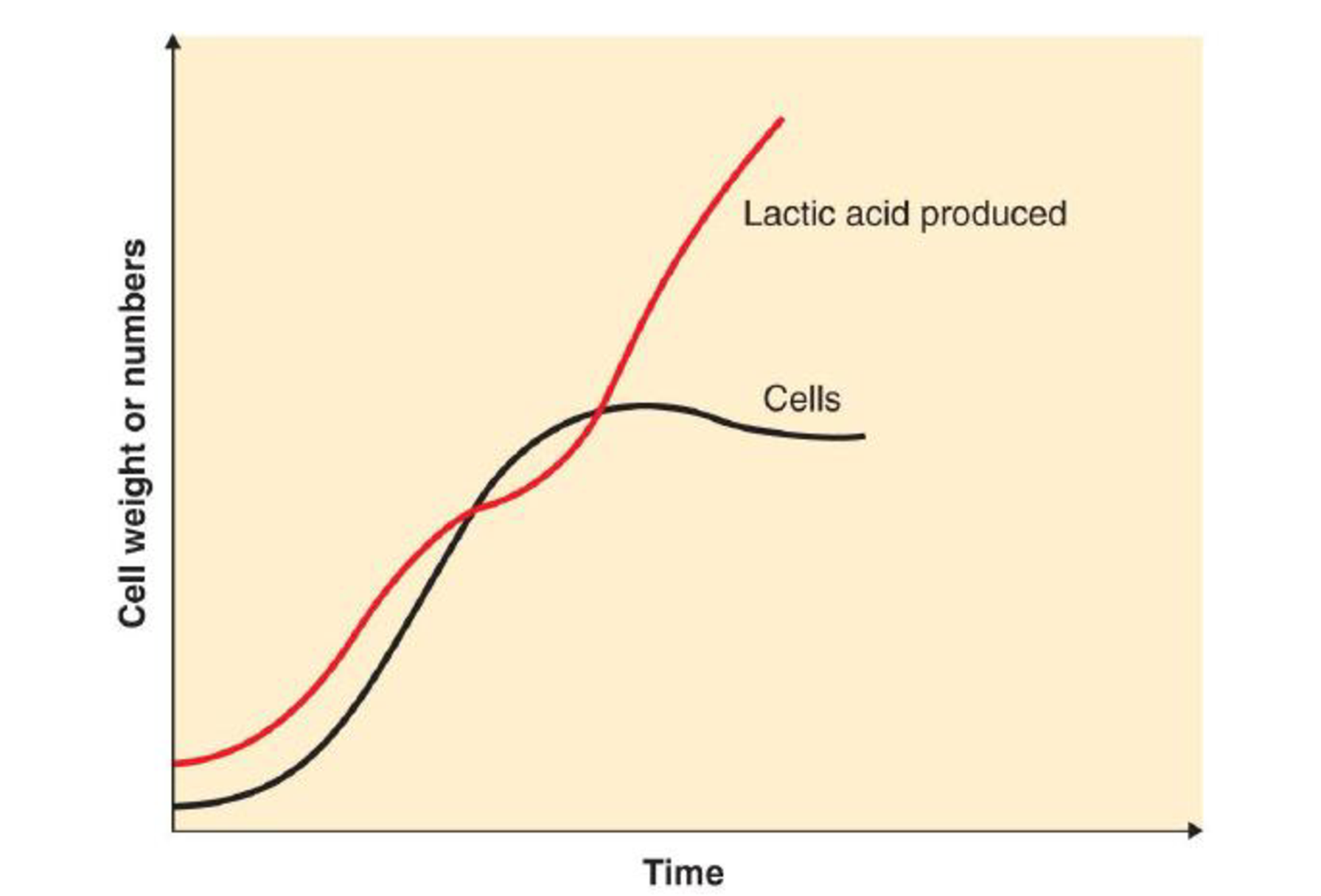
- b. If your desired product is a secondary metabolite, when can you begin collecting it?
- c. If your desired product is the cells themselves and you want to maintain a continuous culture, when can you begin harvesting?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
What is the difference between Uniporters, Symporters and Antiporters? Which of these are examples of active transport?
What are coupled transporters?
What are “domains” and how do they aid in protein function?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Ch. 28 - What is industrial microbiology? Why is it...Ch. 28 - How does commercial sterilization differ from...Ch. 28 - Why is a can of blackberries preserved by...Ch. 28 - Outline the steps in the production of cheese, and...Ch. 28 - Beer is made with water, malt, and yeast; hops are...Ch. 28 - Why is a bioreactor better than a large flask for...Ch. 28 - The manufacture of paper includes the use of...Ch. 28 - Describe an example of bioconversion. What...Ch. 28 - Prob. 9RCh. 28 - NAME IT Van Leeuwenhoek was the first to see this...
Ch. 28 - Foods packed in plastic for microwaving are a....Ch. 28 - Acetobacter is necessary for only one of the steps...Ch. 28 - Use the following choices to answer questions 35:...Ch. 28 - The spoilage of canned foods caused by Geobacillus...Ch. 28 - A heat-resistant fungus that causes spoilage in...Ch. 28 - The term 12D treatment refers to a. heat treatment...Ch. 28 - Which one of the following is not a fuel produced...Ch. 28 - Which type of radiation is used to preserve foods?...Ch. 28 - Which of the following reactions is undesirable in...Ch. 28 - Which of the following reactions is an oxidation...Ch. 28 - Which bacteria seem to be most frequently used in...Ch. 28 - Methylophilus methylotrophus can convert methane...Ch. 28 - Faded worn-look denim is produced with cellulase....Ch. 28 - Suppose you are culturing a microorganism that...Ch. 28 - Researchers at the CDC inoculated apple cider with...Ch. 28 - The antibiotic efrotomycin is produced by...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
The distances you obtained in Question 3 are for only one side of the ridge. Assuming that a ridge spreads equa...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
13. Figure 2.12 shows the results of Mendel’s test-cross analysis of independent assortment. In this experiment...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
APPLY 1.2 Express the following quantities in scientific notation
using fundamental SI units of mass and lengt...
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Q1. Which wavelength of light has the highest frequency?
a) 10 nm
b) 10 mm
c) 1 nm
d) 1 mm
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
27. Consider the reaction.
Express the rate of the reaction in terms of the change in concentration of each of...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What are intrinsically disordered proteins, and how might they be useful for a living system?arrow_forwardWhat are Amyloid Fibrils? What biological functions are these known to perform?arrow_forwardHow do histamine and prostaglandins help in the mobilization of leukocytes to an injury site? What are chemotactic factors? How do they affect inflammation process?arrow_forward
- Compare and contrast neutrophils and macrophages. Describe two ways they are different and two ways they are similar.arrow_forwardDescribe the effects of three cytokines (not involved in the initial inflammation response). What cells release them?arrow_forwardDescribe activation of helper T cells or cytotoxic T cellsarrow_forward
- Compare and contrast MHC 1 and MHC 2. Describe two way they are different and two ways they similar including how they are used in antigen presentation.arrow_forwardDescribe two antimicrobial properties of the skin.arrow_forwardDescribe how the inflammation response starts including the sentinel cells and the chemicals involved. How do pathogens trigger the response particularly in the skin?arrow_forward
- How does complement promote the immune response? Describe three waysarrow_forwardWhich of the following is not a possible mechanism for autoimmunity? Select one: A. Abnormal expression of MHC II molecules in non-antigen-presenting cells B. Activation of polyclonal B cells C. Polymorphism of HLA alleles D. Molecular mimicry E. Release of sequestered antigensarrow_forwardWRITTEN WORK 3: NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS Part A: Complete the Punnett square and calculate for the probability of genotype and phenotype. i i Genotype: Phenotype: 08:55arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning

Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...
Nursing
ISBN:9781305964792
Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Publisher:Cengage Learning
cell culture and growth media for Microbiology; Author: Scientist Cindy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EjnQ3peWRek;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY