
(a)
The equivalent resistance between points
(a)
Answer to Problem 17P
The equivalent resistance between points
Explanation of Solution
Consider the circuit diagram as shown below.
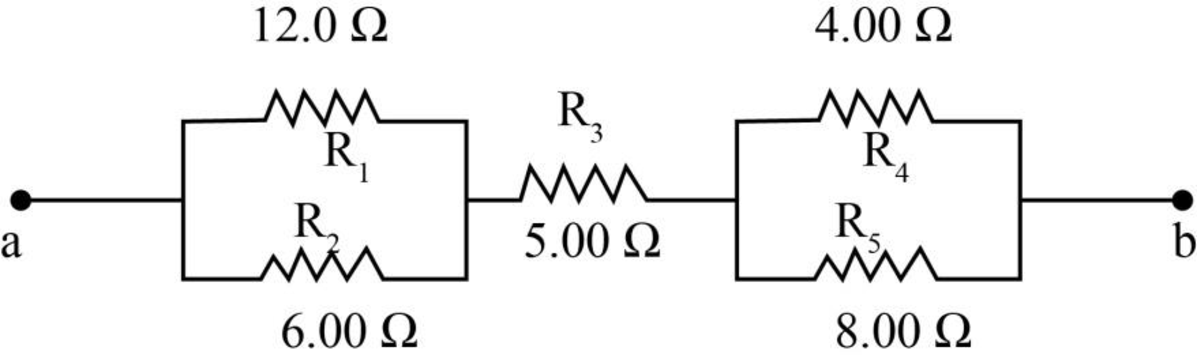
Figure-(1)
Resistors
Write the expression to calculate the equivalent resistance for
Here,
Resistors
Write the expression to calculate the equivalent resistance for
Here,
Write the expression to calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the equivalent resistance between points
(b)
The current in each resistor.
(b)
Answer to Problem 17P
The current across the resistor of
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to calculate the total current.
Here,
Since the resistances
Write the expression to calculate the voltage for resistance
Here,
Since resistors
Write the expression to calculate the voltage for resistance
Here,
Since resistors
Write the expression to calculate the current across resistor
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Current across resistor
Therefore, the current across resistor
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern, Revised Hybrid (with Enhanced WebAssign Printed Access Card for Physics, Multi-Term Courses)
- Figure P29.45 shows five resistors connected between terminals a and b. a. What is the equivalent resistance of this combination of resistors? b. What is the current through each resistor if a 24.0-V battery is connected across the terminals?arrow_forwardA lightbulb is connected to a variable power supply. As the potential across the bulb is varied, the resulting current and the filaments temperature are measured. The data are listed in Table P28.38. a. Find R for each entry in Table P28.38, and then plot R as a function of T. b. Assume that room temperature is at 293 K. Find R0 (resistance at room temperature). Comment on your result.arrow_forwardFigure P29.46 shows a circuit with a 12.0-V battery connected to four resistors. How much power is delivered to each resistor?arrow_forward
- What is the equivalent resistance between points a and b of the six resistors shown in Figure P29.70? FIGURE P29.70arrow_forwardFour resistors are connected to a battery as shown in the figure. The current through the battery is I, the battery's electromotive force (emf) is & = 4.85 V, and the resistor values are R₁ = R, R₂ = 2R, R3 = 4R, and R4 = 3R. Find the voltages across each resistor. V₁ = V₂ = V3 = V4= TOOLS y x10 V V V V R₁ = R www R₂= = 2R R₁=3R ww R₂ = 4Rarrow_forwardThe resistors in the circuit below have the following values: R₁ = 6.70 , R₂ = 7.00 , and R3 = 4.30 . The two batteries each have a voltage of 7.00 V. www R3 www. .E₁ R₁ E₂ (a) Find the current in through R3. 1.8 X Is it possible to reduce the circuit by considering series and/or parallel combination of resistors? What is the total current delivered by the batteries? What is the voltage across R3? Aarrow_forward
- Four resistors are connected to a battery as shown in the figure. The current through the battery is I, the battery's electromotive force (emf) is & = 5.45 V, and the resistor values are R₁ = R, R₂ = 2R, R3 = 4R, and R4 = 3R. Find the voltages across each resistor. V₁ = V₂ = V3 = V4= V V V V R₁ = R E www R₂ = 2R www R₁=3R www R₂ = 4Rarrow_forwardConsider the circuit shown in Figure 4. The emf source has negligible internal resistance. The resistors have resistances R1 = 6 2 and R2 = 4 2. The capacitor has capacitance C = 9 µF. When the capacitor is fully charged, the magnitude of the charge on its plates is Q = 36 µC. Calculate the emf ɛ. R2 Rarrow_forwardWhat is the time constant of the circuit shown in Figure OQ28.7? Each of the five resistors has resistance R. and each of the five capacitors has capacitance C. The internal resistance of the battery is negligible. (a) RC. (b) 5RC. (c) 10RC (d) 25RC (e) none of those answersarrow_forward
- Three resistors, R1 = 17.3, R2 = 13.2, R3 = 78, are connected in series across a 16.6 V battery. What is the voltage drop (in Volts) across R1?arrow_forwardFour resistors are connected to a battery as shown in the R, = 2R figure. The current through the battery is I, the battery's electromotive force (emf) is E = 6.10 V, and the resistor values are R1 = R, R, = 2R, R3 = 4R, and R4 = 3R. Find R, = R the voltages across each resistor. R = 3R V = V V½ = R, = 4R V3 = V V4 = Varrow_forwardThree resistors are connected as shown below. R1 = 3.0 Ω, R2 = 6.0 Ω, and R3 = 8.0 Ω. The voltage across the battery is 60 V. What is the current through R1, in Amperes?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
