
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781938168000
Author: Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 26, Problem 31PE
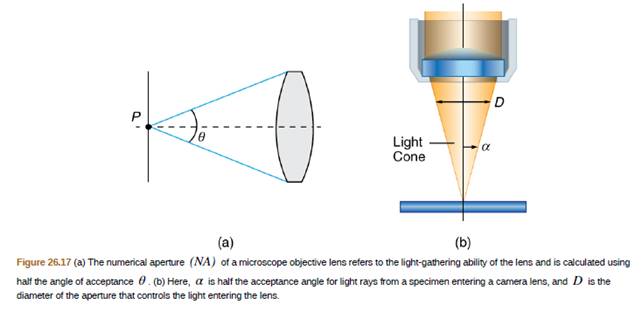
You are using a standard microscope with a
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 26 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 26 - If the lens of a person’s eye is removed because...Ch. 26 - A cataract is cloudiness in the lens of the eye....Ch. 26 - When laser light is shone into a relaxed...Ch. 26 - How does the power of a dry contact lens compare...Ch. 26 - Why is your vision so blurry when you open your...Ch. 26 - It has become common to replace the...Ch. 26 - If the cornea is to be reshaped (this can be done...Ch. 26 - If there is a fixed percent uncertainty in LASIK...Ch. 26 - A person with presbyopia has lost some or all of...Ch. 26 - A pure red object on a black background seems to...
Ch. 26 - What is color constancy, and what are its...Ch. 26 - There are different types of color blindness...Ch. 26 - Propose a way to study the function of the rods...Ch. 26 - Geometric optics describes the interaction of...Ch. 26 - The image produced by the microscope in Figure...Ch. 26 - Why not have the objective at a microscope form a...Ch. 26 - What advantages do oil immersion objectives offer?Ch. 26 - How does the NA of a microscope compare wi1h the...Ch. 26 - If you want your microscope or telescope to...Ch. 26 - List the various types of aberrations. What causes...Ch. 26 - What is the power of the eye when viewing an...Ch. 26 - Calculate the power at the eye when viewing an...Ch. 26 - (a) The print in many books averages 3.50 mm in...Ch. 26 - Suppose a certain person’s visual acuity is such...Ch. 26 - People who do very detailed work close up, such as...Ch. 26 - What is the far point of a person whose eyes have...Ch. 26 - What is the near point of a person whose eyes have...Ch. 26 - (a) A laser vision correction reshaping the cornea...Ch. 26 - In a LASIK vision correction, the power of a...Ch. 26 - What was the previous far point of a patient who...Ch. 26 - A severely myopic patient has a far point of 5.00...Ch. 26 - A student’s eyes, while reading the blackboard,...Ch. 26 - The power of a physician’s eyes is 53.0 D while...Ch. 26 - A young woman with normal distant vision has a...Ch. 26 - The far point of a myopic administrator is 50.0...Ch. 26 - A very myopic man has afar point of 20.0 cm. What...Ch. 26 - Repeat the previous problem for eyeglasses held...Ch. 26 - A myopic person sees that her contact lens...Ch. 26 - Repeat the previous problem for glasses that are...Ch. 26 - The contact lens prescription for a mildly...Ch. 26 - A nearsighted man cannot see objects clearly...Ch. 26 - A mother sees that her child's contact lens...Ch. 26 - Repeat the previous problem for glasses that are...Ch. 26 - The contact lens prescription for a nearsighted...Ch. 26 - Unreasonable Results A boy has a near point of 50...Ch. 26 - A microscope with an overall magnification of 800...Ch. 26 - (a) What magnification is produced by a 0.150 cm...Ch. 26 - (a) Where does an object need to be placed...Ch. 26 - You switch from a 1.40NA60X oil immersion...Ch. 26 - An amoeba is 0.305 cm away from the 0.300 cm focal...Ch. 26 - You are using a standard microscope with a...Ch. 26 - Unreasonable Results Your friends show you an...Ch. 26 - What is the angular magnification of a telescope...Ch. 26 - Find the distance between the objective and...Ch. 26 - A large reflecting telescope has an objective...Ch. 26 - A small telescope has a concave mirror with a 2.00...Ch. 26 - A 7.5x binocular produces an angular magnification...Ch. 26 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider a telescope of...Ch. 26 - Integrated Concepts (a) During laser vision...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. If an object is not moving, does that mean that there are no forces acting on it? Explain.
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
30. Consider the unbalanced equation for the reaction of aluminum with sulfuric acid:
a. Balance the equation...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Where is transitional epithelium found and what is its importance at those sites?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
5. In a type of parakeet known as a “budgie,” feather color is controlled by two genes. A yellow pigment is syn...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
When Mendel did crosses of true-breeding purple- and white-flowered pea plants, the white-flowered trait disapp...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
MAKE CONNECTIONS Review the description of meiosis (see Figure 10.8) and Mendels laws of segregation and indepe...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax
Convex and Concave Lenses; Author: Manocha Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CJ6aB5ULqa0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY