
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The reaction between
Concept introduction:
Deuterium is an isotope of hydrogen. Deuterium contains one neutron and one proton in its nucleus while hydrogen has only one proton in its nucleus but the number of electrons in hydrogen and deuterium is one.
Isotopic substitution is a reaction in which one isotope is substituted by the other
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction between
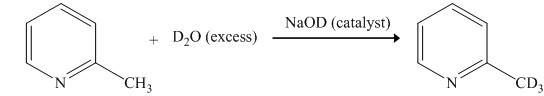
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
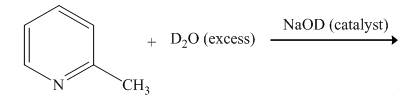
Figure 1
When

Figure 2
The complete reaction between
(b)
Interpretation:
The reaction between
Concept introduction:
Phenyllithium is an organometallic agent which is used to introduce metal into an organic compound during synthesis. It is used to give nucleophilic addition and substitution reactions.
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction between
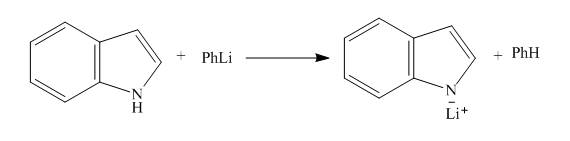
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
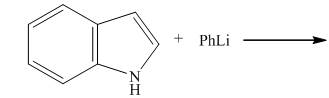
Figure 3
When indole reacts with phenyllithium, phenyllithium abstracts a proton bonded to nitrogen atom and a lithium salt of indole is formed as a conjugate base. The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 4
The complete reaction between
(c)
Interpretation:
The reaction of
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction involves the substitution of an electrophile on an aromatic ring. The
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction of
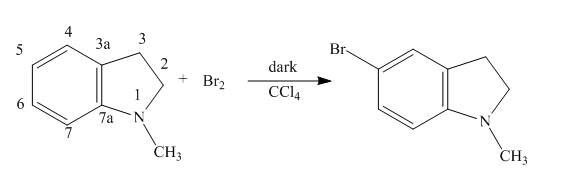
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
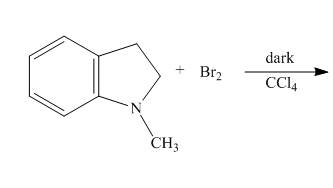
Figure 5
When
The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 6
The complete reaction of
(d)
Interpretation:
The reaction of pyrrolizine with hydrogen in presence of platinum and carbon catalyst is to be completed by giving the major product.
Concept introduction:
Catalytic hydrogenation is a reduction process of addition of hydrogen atoms in an
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction of pyrrolizine with hydrogen in presence of platinum and carbon catalyst is shown below.
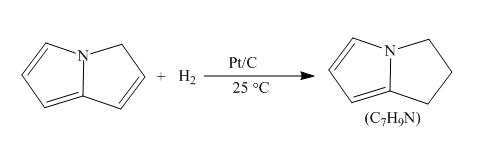
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
c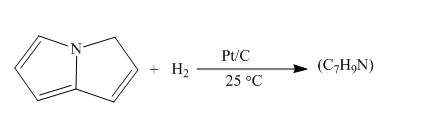
Figure 7
When pyrrolizine reacts with hydrogen in presence of

Figure 8
The complete reaction of pyrrolizine with hydrogen in presence of platinum and carbon catalyst is shown in Figure 8.
(e)
Interpretation:
The reaction of
Concept introduction:
Nitration is a process in which an
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction of
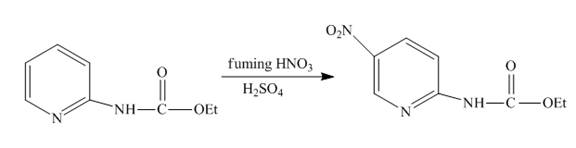
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
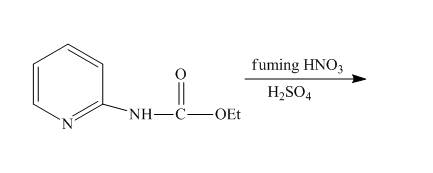
Figure 9
Nitration occurs when

Figure 10
The complete reaction of
(f)
Interpretation:
The reaction between
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction involves the substitution of an electrophile on an aromatic ring. The
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction between
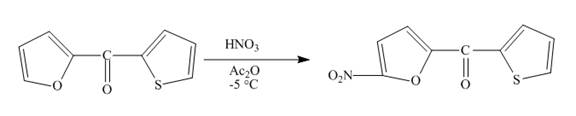
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
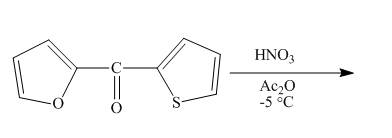
Figure 11
Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction will occur in Furan since it is more reactive than thiophene. Therefore, nitration will occur at carbon

Figure 12
The complete reaction between
(g)
Interpretation:
The reaction of
Concept introduction:
Nitration is a process in which an aromatic compound is nitrated by electrophilic substitution mechanism in presence of concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid. Electron donating groups substituted on the aromatic ring are those which donates electron to the aromatic ring. Electron donating groups are ortho and para-directing.
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction of
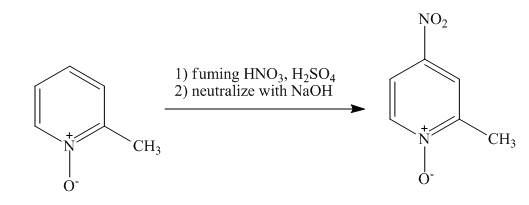
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
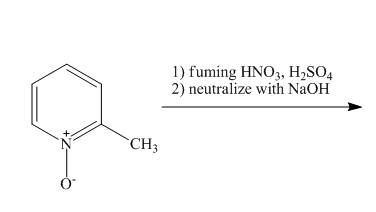
Figure 13
The pyridine ring activates towards electrophilic aromatic substitution due to the presence of pyridinium

Figure 14
The complete reaction of
(h)
Interpretation:
The reaction of
Concept introduction:
Wolff Kishner reduction is a reaction in which
Answer to Problem 26.34AP
The complete reaction of
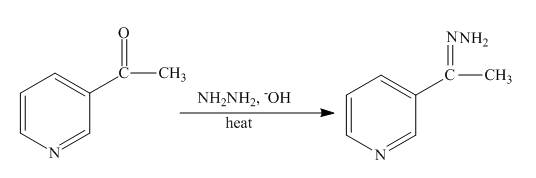
Explanation of Solution
The reaction to be completed is shown below.
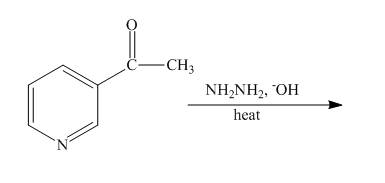
Figure 15
The Wolff-Kishner reduction takes place when

Figure 16
The complete reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- ASP please....arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardConsider the structure of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane. Part 1 of 2 Draw the Newman projection for the anti conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. ✡ ぬ Part 2 of 2 H H F Br H H ☑ Draw the Newman projection for the gauche conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. H F Br H Harrow_forward
- Please help me answer this question. I don't understand how or where the different reagents will attach and it's mostly due to the wedge bond because I haven't seen a problem like this before. Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how it can happen and what the final product will look like.arrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds is the most acidic in the gas phase? Group of answer choices H2O SiH4 HBr H2Sarrow_forwardWhich of the following is the most acidic transition metal cation? Group of answer choices Fe3+ Sc3+ Mn4+ Zn2+arrow_forward
- Based on the thermodynamics of acetic acid dissociation discussed in Lecture 2-5, what can you conclude about the standard enthalpy change (ΔHo) of acid dissociation for HCl? Group of answer choices You cannot arrive at any of the other three conclusions It is a positive value It is more negative than −0.4 kJ/mol It equals −0.4 kJ/molarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal structure corresponding to the following IUPAC name: 7-isopropyl-3-methyldecanearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





