
Webassign Printed Access Card For Katz's Physics For Scientists And Engineers: Foundations And Connections, 1st Edition, Single-term
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781337684637
Author: Debora M. Katz
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 25, Problem 7PQ
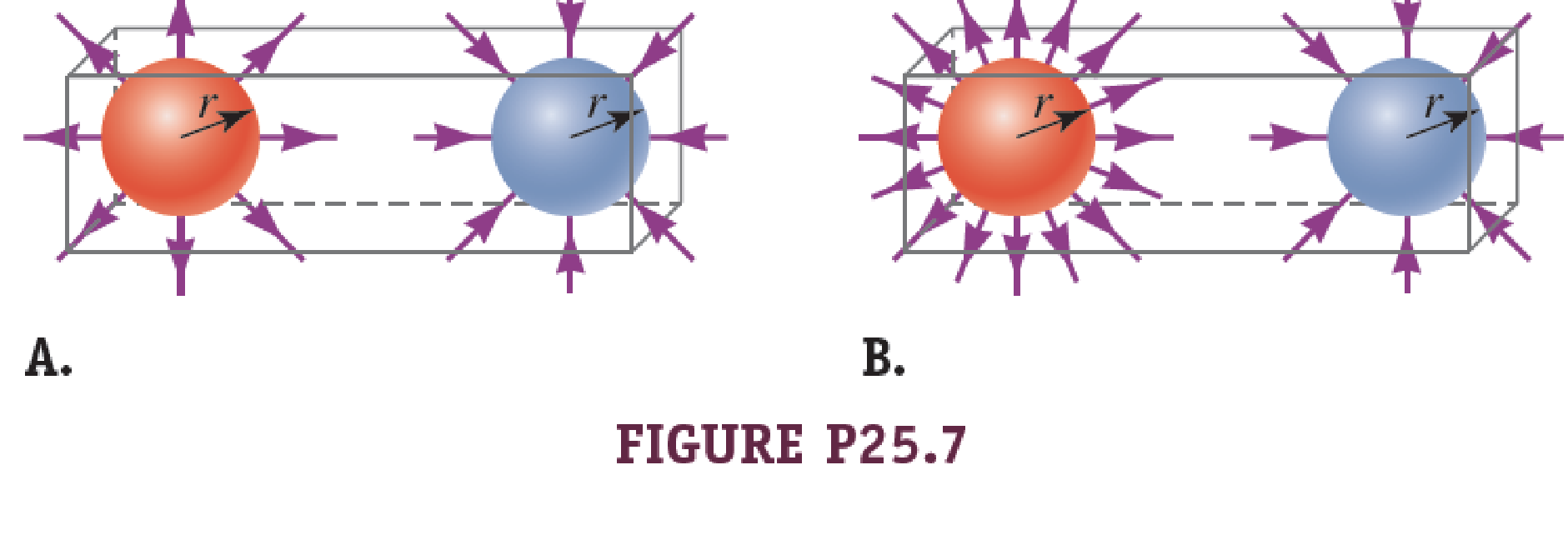
A positively charged sphere and a negatively charged sphere are in a sealed container. The only way the charged spheres can be examined is by observing the electric field outside the container.
- a. Given the depiction of the electric fields in Figure P25.7A, is the net electric flux through the container zero, positive, or negative? Explain your answer.
- b. Two different spheres are placed inside a container. Given the depiction of the electric fields in Figure P25.7B, is the net electric flux through the container zero, positive, or negative? Explain your answer.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A shere of radius R = 0.35 m has a volume charge distribution described by: ρ(r) = ρ0 (1− r/R) for r ≤ R, where ρ0 = 18.5 μC/m3.
a. What is the total charge on the sphere?
b. What is the strength of the electric field produced by the charge distribution at a distance 0.21 m from the center of the sphere?
c. What is the strength of the electric field produced by the charge distribution at a distance 0.4025 m from the center of the sphere?
d. Graph the electric field as a function of r between r = 0 and r =0.4025 m.
A hollow, conducting sphere with an outer radius of 0.240 mm and an inner radius of 0.200 mm has a uniform surface charge density of +6.27 ×10−6 C/m2. A charge of -0.600 μC is now introduced into the cavity inside the sphere.
a. What is the new charge density on the outside of the sphere?
b. Calculate the strength of the electric field just outside the sphere.
c. What is the electric flux through a spherical surface just inside the inner surface of the sphere?
A pair of parallel conducting plates are given charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign to create a uniform electric field with magnitude 38 N/C. A rectangular surface with dimensions 4.2cm×1.2cm is located in the gap between the parallel plates.
a. What is the magnitude of the electric flux, in newton squared meters per coulomb, through the rectangular surface if it is parallel to the charged plates?
b. What is the magnitude of the electric flux, in newton squared meters per coulomb, through the rectangular surface if it is perpendicular to the charged plates?
c. What is the magnitude of the electric flux, in newton squared meters per coulomb, through the rectangular surface if the angle between its normal and the electric field is 25∘?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Webassign Printed Access Card For Katz's Physics For Scientists And Engineers: Foundations And Connections, 1st Edition, Single-term
Ch. 25.1 - a. List all the uppercase letters that have the...Ch. 25.2 - The terms electric force, electric field, and...Ch. 25.2 - Prob. 25.3CECh. 25.3 - Which of the following expressions are correct...Ch. 25.3 - Find the electric flux through the three Gaussian...Ch. 25.4 - Prob. 25.6CECh. 25.7 - Is it possible for the charged solid sphere in...Ch. 25 - Which word or name has the same symmetry as the...Ch. 25 - Prob. 2PQCh. 25 - Prob. 3PQ
Ch. 25 - Prob. 4PQCh. 25 - Prob. 5PQCh. 25 - Prob. 6PQCh. 25 - A positively charged sphere and a negatively...Ch. 25 - A circular hoop of radius 0.50 m is immersed in a...Ch. 25 - Prob. 9PQCh. 25 - If the hemisphere (surface C) in Figure 25.10...Ch. 25 - A Ping-Pong paddle with surface area 3.80 102 m2...Ch. 25 - Prob. 12PQCh. 25 - A pyramid has a square base with an area of 4.00...Ch. 25 - Prob. 14PQCh. 25 - Prob. 15PQCh. 25 - A circular loop with radius r is rotating with...Ch. 25 - A circular loop with radius r is rotating with...Ch. 25 - Prob. 18PQCh. 25 - What is the net electric flux through each of the...Ch. 25 - Prob. 20PQCh. 25 - The colored regions in Figure P25.21 represent...Ch. 25 - Prob. 22PQCh. 25 - Prob. 23PQCh. 25 - Three particles and three Gaussian surfaces are...Ch. 25 - A Using Gausss law, find the electric flux through...Ch. 25 - Three point charges q1 = 2.0 nC, q2 = 4.0 nC, and...Ch. 25 - Prob. 27PQCh. 25 - A very long, thin wire fixed along the x axis has...Ch. 25 - Figure P25.29 shows a wry long tube of inner...Ch. 25 - Two very long, thin, charged rods lie in the same...Ch. 25 - Prob. 31PQCh. 25 - Two long, thin rods each have linear charge...Ch. 25 - Figure P25.33 shows a very long, thick rod with...Ch. 25 - A very long line of charge with a linear charge...Ch. 25 - Two infinitely long, parallel lines of charge with...Ch. 25 - An infinitely long wire with uniform linear charge...Ch. 25 - Prob. 37PQCh. 25 - Prob. 38PQCh. 25 - Prob. 39PQCh. 25 - Prob. 40PQCh. 25 - Two uniform spherical charge distributions (Fig....Ch. 25 - FIGURE P25.41 Problems 41 and 42. Two uniform...Ch. 25 - The nonuniform charge density of a solid...Ch. 25 - Prob. 44PQCh. 25 - What is the magnitude of the electric field just...Ch. 25 - Prob. 46PQCh. 25 - The infinite sheets in Figure P25.47 are both...Ch. 25 - Prob. 48PQCh. 25 - Prob. 49PQCh. 25 - Prob. 50PQCh. 25 - A very large, flat slab has uniform volume charge...Ch. 25 - FIGURE P25.41 Problems 51 and 52. Find the surface...Ch. 25 - Prob. 53PQCh. 25 - Prob. 54PQCh. 25 - If the magnitude of the surface charge density of...Ch. 25 - A spherical conducting shell with a radius of...Ch. 25 - A charged rod is placed in the center along the...Ch. 25 - A charged rod is placed in the center along the...Ch. 25 - A thick spherical conducting shell with an inner...Ch. 25 - A thick spherical conducting shell with an inner...Ch. 25 - A rectangular plate with sides 0.60 m and 0.40 m...Ch. 25 - Prob. 62PQCh. 25 - Prob. 63PQCh. 25 - A uniform spherical charge distribution has a...Ch. 25 - A rectangular surface extends from x = 0 to x =...Ch. 25 - A uniform electric field E = 1.57 104 N/C passes...Ch. 25 - A solid plastic sphere of radius R1 = 8.00 cm is...Ch. 25 - Examine the summary on page 780. Why are...Ch. 25 - Prob. 69PQCh. 25 - Prob. 70PQCh. 25 - Prob. 71PQCh. 25 - A coaxial cable is formed by a long, straight wire...Ch. 25 - Prob. 73PQCh. 25 - Prob. 74PQCh. 25 - A solid sphere of radius R has a spherically...Ch. 25 - A solid sphere of radius R has a spherically...Ch. 25 - A very large, horizontal conducting square plate...Ch. 25 - Prob. 78PQCh. 25 - A particle with charge q = 7.20 C is surrounded by...Ch. 25 - A sphere with radius R has a charge density given...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A Ping-Pong paddle with surface area 3.80 102 m2 is placed in a uniform electric field of magnitude 1.10 106 N/C. a. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the paddle when the electric field is parallel to the paddles surface? b. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the paddle when the electric field is perpendicular to the paddles surface?arrow_forwardThe colored regions in Figure P25.21 represent four three-dimensional Gaussian surfaces A through D. The regions may also contain three charged particles, with qA + +5.00 nC, qB = 5.00 nC, and qC = +8.00 nC, that are nearby as shown. What is the electric flux through each of the four surfaces? FIGURE P25.21arrow_forwardWhat is the electric field at point A in Figure P24.30 if d = 1.40 m, R = 0.500 m, q1 = 15.0 nC, and q2 = 25.0 nC? Assume the positive x axis points to the right, through the center of the rings.arrow_forward
- Figure P24.20 shows three charged spheres arranged along the y axis. a. What is the electric field at x = 0, y = 3.00 m? b. What is the electric field at x = 3.00 m, y = 0? FIGURE P24.20arrow_forwardA solid, insulating sphere of radius a has a uniform charge density throughout its volume and a total charge Q. Concentric with this sphere is an uncharged, conducting, hollow sphere whose inner and outer radii are b and e as shown in Figure P24.45. We wish to understand completely the charges and electric fields at all locations. (a) Find the charge contained within a sphere of radius r a. (b) From this value, find the magnitude of the electric field for r a. (c) What charge is contained within a sphere of radius r when a r b? (d) From this value, find the magnitude of the electric field for r when a r b. (e) Now consider r when b r c. What is the magnitude of the electric field for this range of values of r? (f) From this value, what must be the charge on the inner surface of the hollow sphere? (g) From part (f), what must be the charge on the outer surface of the hollow sphere? (h) Consider the three spherical surfaces of radii a, b, and c. Which of these surfaces has the largest magnitude of surface charge density? Figure P24.45 Problems 43 and 47.arrow_forwardFigure P25.29 shows a wry long tube of inner radius a and outer radius b that has uniform volume charge density . Find an expression for the electric field between the walls of the tubethat is, for a r b. Figure P25.29arrow_forward
- What is the net electric flux through each of the four surfaces shown in Figure P25.19?arrow_forwardA charged rod is curved so that it is part of a circle of radius R (Fig. P24.32). The excess positive charge Q is uniformly distributed on the rod. Find an expression for the electric field at point A in the plane of the curved rod in terms of the parameters given in the figure.arrow_forwardTwo positively charged spheres are shown in Figure P24.70. Sphere 1 has twice as much charge as sphere 2. If q = 6.55 nC, d = 0.250 m, and y = 1.25 m, what is the electric field at point A?arrow_forward
- A very long, thin wire fixed along the x axis has a linear charge density of 3.2 C/m. a. Determine the electric field at point P a distance of 0.50 m from the wire. b. If there is a test charge q0 = 12.0 C at point P, what is the magnitude of the net force on this charge? In which direction will the test charge accelerate?arrow_forwardA positively charged disk of radius R = 0.0366 m and total charge 56.8 C lies in the xz plane, centered on the y axis (Fig. P24.35). Also centered on the y axis is a charged ring with the same radius as the disk and a total charge of 34.1 C. The ring is a distance d = 0.0050 m above the disk. Determine the electric field at the point P on the y axis, where P is y = 0.0100 m above the origin. FIGURE P24.35 Problems 35 and 36.arrow_forwardA very long, uniformly charged cylinder has radius R and linear charge density λ. a. Find the cylinder's electric field strength outside the cylinder, r≥R. Give your answer as a multiple of λ/ε0. Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables R, r, and the constant π. b. Find the cylinder's electric field strength inside the cylinder, r≤R. Give your answer as a multiple of λ/ε0. Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables R, r, and the constant π.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY