
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The type of reaction that occurs in step 1 of a turn of the
Concept Introduction:
The
Dehydrogenation reaction, hydration reaction, and thiolysis reactions occur in the
In dehydrogenation reaction, hydrogen molecule
(a)
Answer to Problem 25.30EP
Dehydrogenation reaction occurs in step 1 of a turn of the
Explanation of Solution
In step 1 of a turn of the
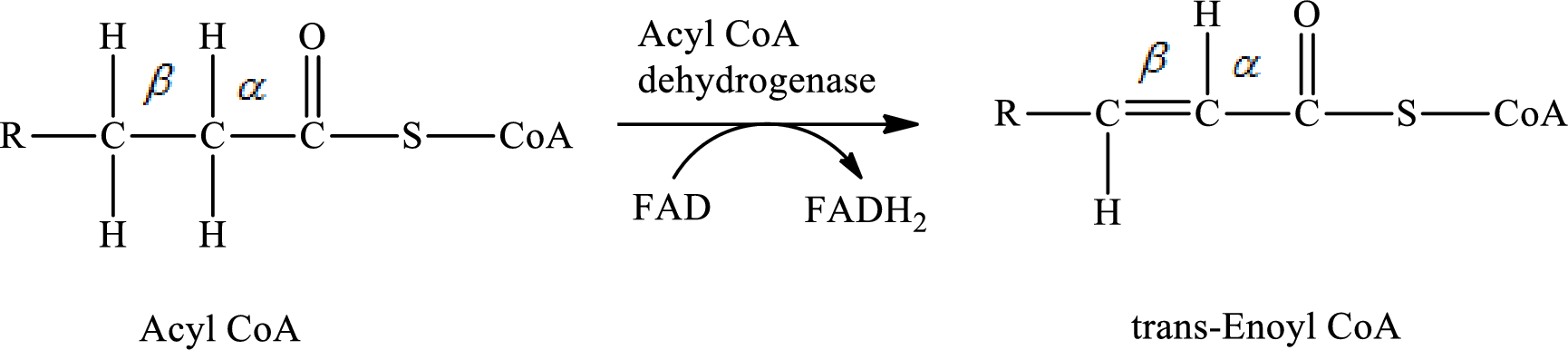
The hydrogen molecule is removed from
(b)
Interpretation:
The type of reaction that occurs in step 2 of a turn of the
Concept Introduction:
The
Dehydrogenation reaction, hydration reaction, and thiolysis reactions occur in the
In dehydrogenation reaction, hydrogen molecule
(b)
Answer to Problem 25.30EP
Hydration reaction occurs in step 2 of a turn of the
Explanation of Solution
In step 2, a water
The reaction for step 2 is as follows:
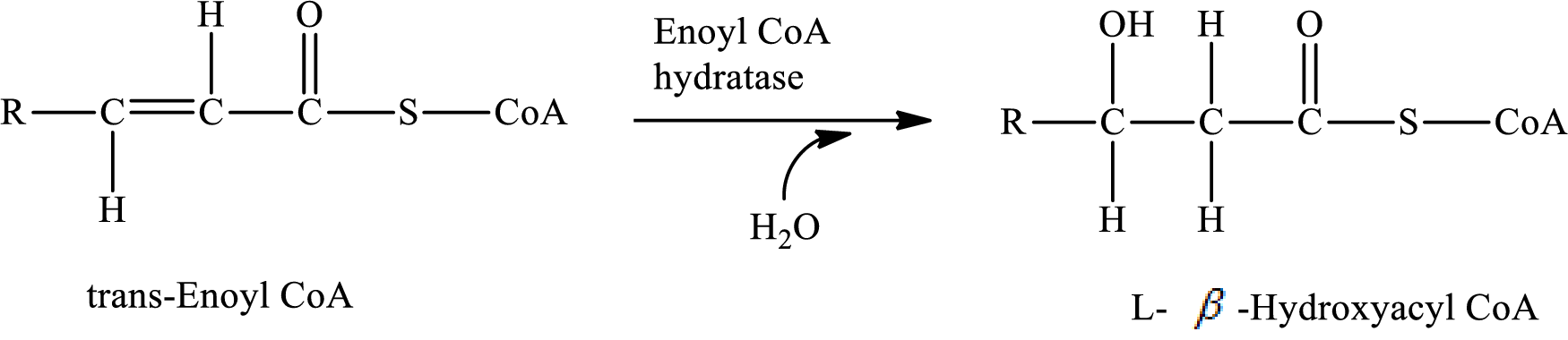
A water molecule is added in step 2, therefore; the reaction in step 2 of a turn of the
(c)
Interpretation:
The type of reaction that occurs in step 3 of a turn of the
Concept Introduction:
The
Dehydrogenation reaction, hydration reaction, and thiolysis reactions occur in the
In dehydrogenation reaction, hydrogen molecule
(c)
Answer to Problem 25.30EP
Dehydrogenation reaction occurs in step 3 of a turn of the
Explanation of Solution
In step 3 of a turn of the
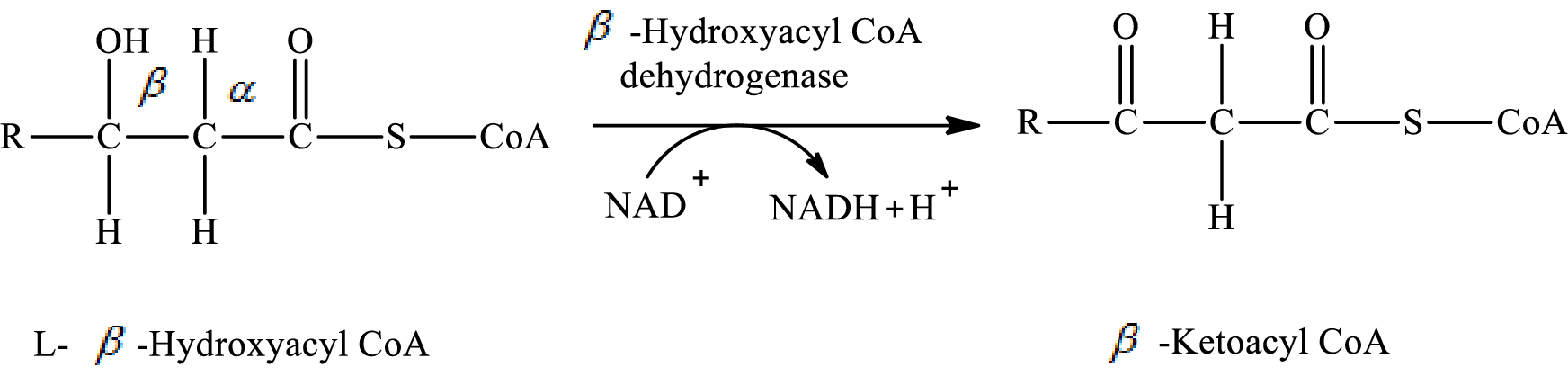
The hydrogen
(d)
Interpretation:
The type of reaction that occurs in step 4 of a turn of the
Concept Introduction:
The
Dehydrogenation reaction, hydration reaction, and thiolysis reactions occur in the
In dehydrogenation reaction, hydrogen molecule
(d)
Answer to Problem 25.30EP
Thiolysis reaction occurs in step 4 of a turn of the
Explanation of Solution
In step 4 of a turn of the
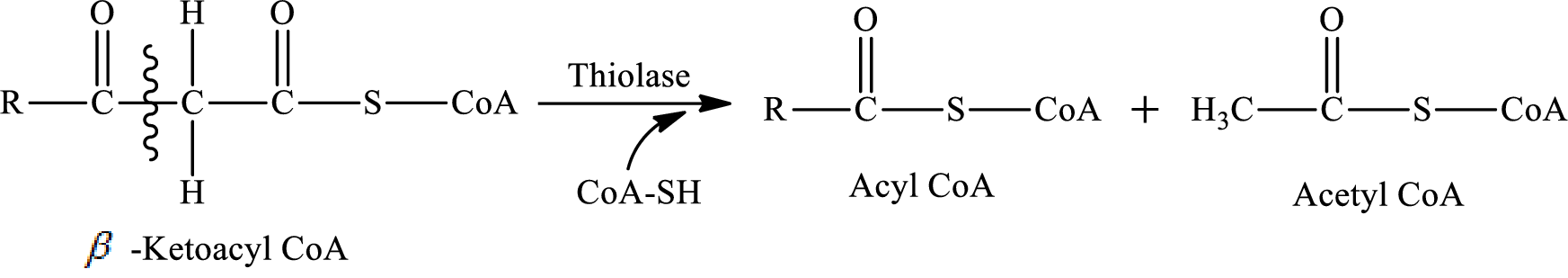
The carbon-carbon bond in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- Which of the following enzyme classes catalyze reactions in which two molecules become covalently linked to each other? A. Kinase B. Hydrolase C. Isomerase D. Ligasearrow_forwardWhich of the following describes a reaction that requires substrate 1 to bind the the enzyme, then substrate 2 binds, and then the products are produced? A. No ternary complex B. Ordered ternary complex C. Ping-Pong D. Random ternary complexarrow_forwardWhich of the following could act as one of the substrates in a reaction catalyzed by a glycosyltransferase? Choose one or more: A. GalNAc ☐ B. galactose C. UDP-GalNAc D. GDP-Mannosearrow_forward
- Which ONE of the following would be most effective as a feedback mechanism for anenzymatic reaction? A. Reduced concentration of the product B. A change in pH C. Increased concentration of substrate D. Temporary binding of a non-substrate molecule in the active binding sitearrow_forwardMatch each reaction description to the type of enzyme that catalyzes the reaction. 1. Oxidation and reduction of compounds 2. Transfers a functional group from one compound to another compound 3. Utilizes water to break bonds within a compound 4. Addition/removal of a group of atoms and bonds within a compound 5. Forms a bond between two compounds A. Ligase B. Transferase C. Hydrolase D. Oxidoreductase E. Isomerase F. Lyasearrow_forwardPotassium cyanide is a poison which combines with cytochrome A3 to prevent binding of oxygen to the enzyme without altering the Km of the reaction with respect to reduced cytochrome c. Which type of inhibition does this represent? c. Competitive inhibition D. Uncompetitive inhibition A. Irreversible inhibition B. Noncompetitive inhibition 10. Which of the following enzyme classes catalyze reactions in which two molecules become dissociated from each other? A. Kinase В. Нydrolase C. Isomerase D. Ligase 11. Which of the following enzyme classes catalyze reactions in which two molecules become covalently linked to each other? C. Isomerase D. Ligase A. Kinase В. Нydrolasearrow_forward
- Penicillin functions by inhibiting an enzyme, transpeptidase, that catalyzes the last step in the bacteria's metabolism which synthesises bacterial the cell-wall. Why does inhibition of this enzyme make Penicilin such an effective medicine in humans, with so few side effects? A. Inhibiting enzymes like this always slows the metabolism of an organism. B. The enzyme is not inhibited in humans because we have resistance to the penicillin. C. The enzyme is part of an essential pathway in the bacteria, which does not exist in humans. D. Inhibiting the enzymes stops respiration in the bacteria, killing quickly.arrow_forwardbisphosphoglycerate mutase is an example of Select one: a. transferase b. lyase c. none d. isomerasearrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is TRUE in describing the activity of the lactaseenzyme? A. Lactase is converted to glucoseB. One lactase enzyme can catalyze many reactions C. The shape of lactase does not change during the reaction D. Lactase can function effectively at many different pH levelsarrow_forward
- FoF1 ATPase is the enzyme that catalyzes ATP synthesis. The enzyme itself is deactivated by ATP. What mode of enzyme regulation is being exemplified? Select the correct response: Trasncriptional control Covalent modification Proteolytic modification Allosteric regulation Compartmentationarrow_forwardWhich of the following best explains why enzyme catalysis is affected by a change in pH? A. Change in pH alters ionization states of serine in the active site involved in nucleophilic catalysis B. The ionization states of his, asp and glu involved in acid/base catalysis are altered with change in pH C. Change in pH alters ionization states of contact amino acids in the active site D. All enzymes have optimum pHarrow_forwardDefine the following terms: a. oxidoreductase b. lyase c. ligase d. transferase e. isomerasearrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





