
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24, Problem 50P
In Fig. 24-54, how much work must we do to bring a particle, of charge Q = +16e and initially at rest, along the dashed line from infinity to the indicated point near two fixed particles of charges q1 = +4e and q2 = -q1
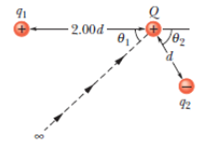
Figure 24-54 Problem 50.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
14
Z
In figure, a closed surface with q=b=
0.4m/
C =
0.6m
if the left edge
of the closed surface at position X=a,
if E is non-uniform and is given by
€ = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the
(3+2x²)
net electric flux leaving the closed
surface.
No chatgpt pls will upvote
suggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 24 - Figure 24-24 shows eight particles that form a...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-25 shows three sets of cross sections of...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-26 shows four pairs of charged...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-27 gives the electric potential V as a...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-28 shows three paths along which we can...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-29 shows four arrangement? of charged...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-30 shows a system of three charged...Ch. 24 - In the situation of Question 7, is the work done...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-26 shows four pairs of charged particles...Ch. 24 - a In Fig. 24-31a, what is the potential at point P...
Ch. 24 - Figure 24-32 shows a thin, uniformly charged rod...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-33, a particle is to be released at...Ch. 24 - SSM A particular 12 V car battery can send a total...Ch. 24 - The electric potential difference between the...Ch. 24 - Suppose that in a lightning flash the potential...Ch. 24 - Two large, parallel, conducting plates are 12 cm...Ch. 24 - SSM An infinite nonconducting sheet has a surface...Ch. 24 - When an electron moves from A to B along an...Ch. 24 - The electric field in a region of space has the...Ch. 24 - A graph of the x component of the electric field...Ch. 24 - An infinite nonconducting sheet has a surface...Ch. 24 - GO Two uniformly charged, infinite, nonconducting...Ch. 24 - A nonconducting sphere has radius R = 2.31 cm and...Ch. 24 - As a space shuttle moves through the dilute...Ch. 24 - What are a the change and b the charge density on...Ch. 24 - Consider a particle with charge q = 1.0 C, point A...Ch. 24 - SSM ILW A spherical drop of water carrying a...Ch. 24 - GO Figure 24-37 shows a rectangular array of...Ch. 24 - GO In Fig.24-33, what is the net electric...Ch. 24 - GO Two charged particles are shown in Fig. 24-39a....Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-40, particles with the charges q1 = 5e...Ch. 24 - Two particles, of charges q1 and q2, are separated...Ch. 24 - ILW The ammonia molecule NH3 has a permanent...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-41a, a particle of elementary charge e...Ch. 24 - a Figure 24-42a shows a nonconducting rod of...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 21-43, a plastic rod having a uniformly...Ch. 24 - A plastic rod has been bent into a circle of...Ch. 24 - GO Figure 24-45 shows a thin rod with a uniform...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-46, three thin plastic rods form...Ch. 24 - GO Figure 24-47 shows a thin plastic rod of length...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-48, what is the net electric potential...Ch. 24 - GO The smiling face of Fig. 24-49 consists of...Ch. 24 - SSM WWW A plastic disk of radius R = 64.0 cm is...Ch. 24 - GO A non uniform linear charge distribution given...Ch. 24 - GO The thin plastic rod shown in Fig. 24-47 has...Ch. 24 - Two large parallel metal plates are 1.5 cm apart...Ch. 24 - The electric potential al points in an xy plane is...Ch. 24 - The electric potential V in the space between two...Ch. 24 - SSM What is the magnitude of the electric field at...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-47 shows a thin plastic rod of length L...Ch. 24 - An electron is placed in an xy plane where I he...Ch. 24 - GO The thin plastic rod of length L = 10.0 cm in...Ch. 24 - A particle of charge 7.5 C is released from rest...Ch. 24 - a What is the electric potential energy of two...Ch. 24 - How much work is required to set up the...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-53, seven charged particles are fixed...Ch. 24 - ILW A particle of charge q is fixed at point P,...Ch. 24 - A charge of 9.0 nC is uniformly distributed around...Ch. 24 - GO What is the escape speed for an electron...Ch. 24 - A thin, spherical conducting shell of radius R is...Ch. 24 - GO Two electrons are fixed 2.0 cm apart. Another...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-54, how much work must we do to bring a...Ch. 24 - GO In the rectangle of Fig. 24-55, the sides have...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-56a shows an electron moving along an...Ch. 24 - Two tiny metal sphere? A and B, mass mA = 5.00 g...Ch. 24 - GO A positron charge e, mass equal to the electron...Ch. 24 - An electron is projected with an initial speed of...Ch. 24 - Particle 1 with a charge of 5.0 C and particle 2...Ch. 24 - SSM Identical 50 C charges are fixed or an x axis...Ch. 24 - GO Proton in a well. Figure 24-59 shows electric...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-60, a charged particle either an...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-61a, we move an electron from an...Ch. 24 - Suppose N electrons can be placed in either of two...Ch. 24 - Sphere 1 with radius R1 has positive charge q....Ch. 24 - SSM WWW Two metal spheres, each of radius 3.0 cm,...Ch. 24 - A hollow metal sphere has a potential of 400 V...Ch. 24 - SSM What is the excess charge on a conducting...Ch. 24 - Two isolated, concentric, conducting spherical...Ch. 24 - A metal sphere of radius 15 cm has a net charge of...Ch. 24 - Here are the charges and coordinates of two...Ch. 24 - SSM A long, solid, conducting cylinder has a...Ch. 24 - The chocolate crumb mystery. This story begins...Ch. 24 - SSM Starting from Eq. 24-30, derive an expression...Ch. 24 - The magnitude E of an electric field depends on...Ch. 24 - a If an isolated conducting sphere 10 cm in radius...Ch. 24 - Three particles, charge q1 = 10 C, q2 = 20 C, and...Ch. 24 - An electric field of approximately 100 V/m is...Ch. 24 - A Gaussian sphere of radius 4.00 cm is centered or...Ch. 24 - In a Millikan oil-drop experiment Module 22-6, a...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-63 shows three circular, nonconducting...Ch. 24 - An electron is released from rest on the axis of...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-64 shows a ring of outer radius R = 13.0...Ch. 24 - GO Electron in a well. Figure 24-65 shows electric...Ch. 24 - a If Earth had a uniform surface charge density of...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-66, point P is at distance d1 = 4.00 m...Ch. 24 - A solid conducting sphere of radius 3.0 cm has a...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-67, we move a particle of charge 2e in...Ch. 24 - Figure 24-68 shows a hemisphere with a charge of...Ch. 24 - SSM Three 0.12 C charges form an equilateral...Ch. 24 - Two charges q = 2.0 C are fixed a distance d = 2.0...Ch. 24 - Initially two electrons are fixed in place with a...Ch. 24 - A particle of positive charge Q is fixed at point...Ch. 24 - Two charged, parallel, flat conducting surfaces...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-70, point P is at the center of the...Ch. 24 - SSM A uniform charge of 16.0 C is on a thin...Ch. 24 - Consider a particle with charge q = 150 108 C,...Ch. 24 - SSM A thick spherical shell of charge Q and...Ch. 24 - A charge q is distributed uniformly throughout a...Ch. 24 - SSM A solid copper sphere whose radius is 1.0 cm...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-71, a metal sphere with charge q = 5.00...Ch. 24 - a Using Eq. 24-32, show that the electric...Ch. 24 - An alpha particle which has two protons is seat...Ch. 24 - In the quark model of fundamental particles, a...Ch. 24 - A charge of 1.50 108 C lies on an isolated metal...Ch. 24 - In Fig. 24-72, two particles of charges q1 and q2...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
16.
a. Calculate the standard free energy change as a pair of electrons is transferred from succinate to mole...
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. The reason we do not have a solar ecli...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
3. In a test of his chromosome theory of heredity, Morgan crossed an F1 female Drosophila with red eyes to a m...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
A horizontal spring with spring constant 100 N/m is compressed 20 cm and used to launch a 2.5 kg box across a f...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Which tarsal bone articulates with both the tibia and fibula?
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Name the process by which sediment is transformed into sedimentary rocks.
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Checkpoint 4 The figure shows four orientations of an electric di- pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta- tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di- pole, greatest first. (1) (2) E (4)arrow_forwardWhat is integrated science. What is fractional distillation What is simple distillationarrow_forward19:39 · C Chegg 1 69% ✓ The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take F=1700 lb. (Figure 1) Figure 800 lb ||-5- F 600 lb بتا D E C BO 10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft- Solved Part A The compound beam is fixed at E and... Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm Problem A-12 % Chia sẻ kip 800 lb Truy cập ) D Lưu of C 600 lb |-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft D E 5 ft- Trying Cheaa Những kết quả này có hữu ích không? There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!) Chegg Solved The compound b... Có Không ☑ ||| Chegg 10 וחarrow_forward
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY