
Concept explainers
- a. The isoelectric point (pl) of phenylalanine is pH 5.5. Draw the structure of the major form of phenylalanine at pH values of 1, 5.5, and 11.
- b. The isoelectric point of histidine is pH 7 6. Draw the structures of the major forms of histidine at pH values of 1, 4, 7.6, and 11. Explain why the nitrogen in the histidine ring is a weaker base than the α-amino group.
- c. The isoelectric point of glutamic acid is pH 3.2. Draw the structures of the major forms of glutamic acid at pH values of 1,3.2, 7, and 11. Explain why the side-chain
carboxylic acid is a weaker acid than the acid group next to the α-carbon atom.
(a)
Interpretation:
The structures of the major form of phenylalanine at
Concept introduction:
The more acidic strength increases the formation of the hydrogen ions and decreases the
Answer to Problem 24.27SP
The structures of the major form of phenylalanine at
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the major forms of phenylalanine at
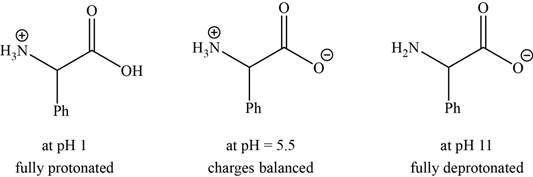
Figure 1
It is conferred from the above reaction that phenylalanine at
(b)
Interpretation:
The structures of the major forms of histidine at
Concept introduction:
The more acidic strength increases the formation of the hydrogen ions and decreases the
Answer to Problem 24.27SP
The structures of the major forms of histidine at
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the major forms of histidine at
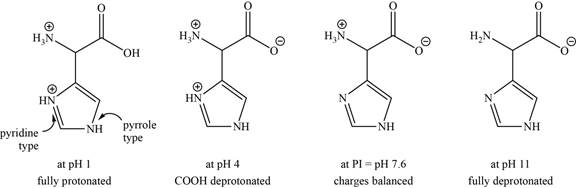
Figure 2
It is conferred from the above reaction that histidine at
(c)
Interpretation:
The structures of the major forms of glutamic acid at
Concept introduction:
The more acidic strength increases the formation of the hydrogen ions and decreases the
Answer to Problem 24.27SP
The structures of the major forms of glutamic acid at
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the major forms of glutamic acid at
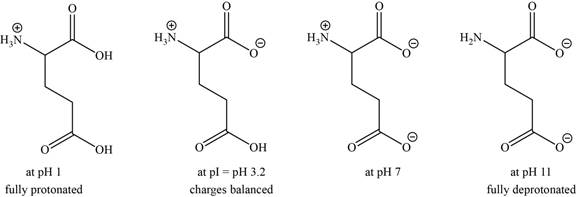
Figure 3
It is conferred from the above reaction that glutamic acid at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
- Laser. Indicate the relationship between metastable state and stimulated emission.arrow_forwardThe table includes macrostates characterized by 4 energy levels (&) that are equally spaced but with different degrees of occupation. a) Calculate the energy of all the macrostates (in joules). See if they all have the same energy and number of particles. b) Calculate the macrostate that is most likely to exist. For this macrostate, show that the population of the levels is consistent with the Boltzmann distribution. macrostate 1 macrostate 2 macrostate 3 ε/k (K) Populations Populations Populations 300 5 3 4 200 7 9 8 100 15 17 16 0 33 31 32 DATO: k = 1,38×10-23 J K-1arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- In an experiment, the viscosity of water was measured at different temperatures and the table was constructed from the data obtained. a) Calculate the activation energy of viscous flow (kJ/mol). b) Calculate the viscosity at 30°C. T/°C 0 20 40 60 80 η/cpoise 1,972 1,005 0,656 0,469 0,356arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardLet's see if you caught the essentials of the animation. What is the valence value of carbon? a) 4 b) 2 c) 8 d) 6arrow_forward
- A laser emits a line at 632.8 nm. If the cavity is 12 cm long, how many modes oscillate in the cavity? How long does it take for the radiation to travel the entire cavity? What is the frequency difference between 2 consecutive modes?(refractive index of the medium n = 1).arrow_forwardA laser emits a line at 632.8 nm. If the cavity is 12 cm long, how many modes oscillate in the cavity? How long does it take for the radiation to travel the entire cavity? What is the frequency difference between 2 consecutive modes?(refractive index of the medium n = 1).arrow_forwardThe number of microstates corresponding to each macrostate is given by N. The dominant macrostate or configuration of a system is the macrostate with the greatest weight W. Are both statements correct?arrow_forward
- For the single step reaction: A + B → 2C + 25 kJ If the activation energy for this reaction is 35.8 kJ, sketch an energy vs. reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction. Be sure to label the following on your diagram: each of the axes, reactant compounds and product compounds, enthalpy of reaction, activation energy of the forward reaction with the correct value, activation energy of the backwards reaction with the correct value and the transition state. In the same sketch you drew, after the addition of a homogeneous catalyst, show how it would change the graph. Label any new line "catalyst" and label any new activation energy.arrow_forwardHow many grams of C are combined with 3.75 ✕ 1023 atoms of H in the compound C5H12?arrow_forwarde. f. CH3O. יון Br NaOCH3 OCH 3 Br H₂Oarrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





