
Concept explainers
Sustainable Use of Horseshoe Crabs Horseshoe crab blood clots immediately upon exposure to bacterial toxins, so it can be used to test injectable drugs for the presence of dangerous bacteria. To keep horseshoe crab populations stable, blood is extracted from captured animals, which are then returned to the wild. Concerns about the survival of animals after bleeding led researchers to do an experiment. They compared survival of animals captured and maintained in a tank with that of animals captured, bled, and kept in a similar tank. FIGURE 24.28 shows the results.
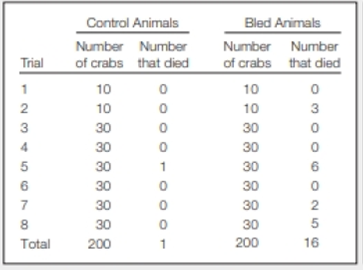
FIGURE 24.28 Mortality of young male horseshoe crabs kept in tanks during the 2 weeks after their capture. Half the animals were bled on the day of their capture. Control animals were handled, but not bled. This procedure was repeated 8 times with different sets of horseshoe crabs.
In which trial did the most control crabs die? In which did the most bled crabs die?
To explain: The trial in which the most control crabs died.
Introduction: Horseshoe crabs belong to the Phylum Arthropod. They are normally found around shallow ocean waters. Horseshoe crabs are living fossils. The horseshoe crabs though they look like crustaceans are marine arachnids.
Explanation of Solution
The uniqueness of horseshoe crabs is that they clot upon encountering bacteria. Therefore, they are used in experiments where highly virulent bacteria are involved. The blood of horseshoe crabs is taken and then let out in their habitat in order to conserve their population, but this might also lead to their death. Therefore, experiments were conducted to check their survival after taking their blood.
In trial 5, the number of control crabs is 30, and 1 crab died out of it.
The trial group 5 marked the highest number of control crabs that died.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physical Universe
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- What are biofertilizers and mention the significancearrow_forwardPCBs and River Otters: Otters in Washington State’s Green-Duwamish River have high levels of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in their livers. PCBs can bind to the estrogen receptors in animals and disrupt the endocrine system of these otters. The PCBs seem to increase the estrogen to androgen ratio, skewing the ratio toward too much estrogen. How would increased estrogen affect the river otter population? Based on your reading of the materials in this unit, what factors can affect fertility in humans? Explain how each of the factors affecting human fertility that you described can disrupt the human endocrine system to affect reproduction.arrow_forwardOther than oil and alcohol, are there other liquids you could compare to water (that are liquid at room temperature)? How is water unique compared to these other liquids? What follow-up experiment would you like to do, and how would you relate it to your life?arrow_forward
- Selection of Traits What adaptations do scavengers have for locating and feeding on prey? What adaptations do predators have for capturing and consuming prey?arrow_forwardCompetition Between Species What natural processes limit populations from growing too large? What are some resources organisms can compete over in their natural habitat?arrow_forwardSpecies Interactions Explain how predators, prey and scavengers interact. Explain whether predators and scavengers are necessary or beneficial for an ecosystem.arrow_forward
- magine that you are conducting research on fruit type and seed dispersal. You submitted a paper to a peer-reviewed journal that addresses the factors that impact fruit type and seed dispersal mechanisms in plants of Central America. The editor of the journal communicates that your paper may be published if you make ‘minor revisions’ to the document. Describe two characteristics that you would expect in seeds that are dispersed by the wind. Contrast this with what you would expect for seeds that are gathered, buried or eaten by animals, and explain why they are different. (Editor’s note: Providing this information in your discussion will help readers to consider the significance of the research).arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between Uniporters, Symporters and Antiporters? Which of these are examples of active transport?arrow_forwardWhat are coupled transporters?arrow_forward
 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





