Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.3, Problem 5P
Solve 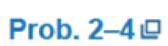 with F = 350 lb.
with F = 350 lb.
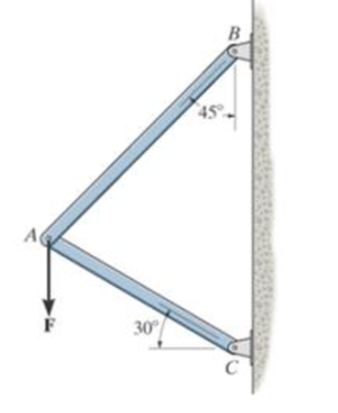
Prob. 2-4/5
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Q
Derive (continuity equation)?
I want to derive clear mathematics.
motor supplies 200 kW at 6 Hz to flange A of the shaft shown in Figure. Gear B transfers 125 W of power to operating machinery in the factory, and the remaining power in the shaft is mansferred by gear D. Shafts (1) and (2) are solid aluminum (G = 28 GPa) shafts that have the same diameter and an allowable shear stress of t= 40 MPa. Shaft (3) is a solid steel (G = 80 GPa) shaft with an allowable shear stress of t = 55 MPa. Determine:
a) the minimum permissible diameter for aluminum shafts (1) and (2)
b) the minimum permissible diameter for steel shaft (3).
c) the rotation angle of gear D with respect to flange A if the shafts have the minimum permissible diameters as determined in (a) and (b).
First monthly exam
Gas dynamics
Third stage
Q1/Water at 15° C flow through a 300 mm diameter riveted steel pipe, E-3 mm with a head loss of 6 m in
300 m length. Determine the flow rate in pipe. Use moody chart.
Q2/ Assume a car's exhaust system can be approximated as 14 ft long and 0.125 ft-diameter cast-iron pipe (
= 0.00085 ft) with the equivalent of (6) regular 90° flanged elbows (KL = 0.3) and a muffler. The
muffler acts as a resistor with a loss coefficient of KL= 8.5. Determine the pressure at the beginning of the
exhaust system (pl) if the flowrate is 0.10 cfs, and the exhaust has the same properties as air.(p = 1.74 ×
10-3 slug/ft³, u= 4.7 x 10-7 lb.s/ft²) Use moody chart
(1)
MIDAS
Kel=0.3
Q3/Liquid ammonia at -20°C is flowing through a 30 m long section of a 5 mm diameter copper tube(e =
1.5 × 10-6 m) at a rate of 0.15 kg/s. Determine the pressure drop and the head losses.
.μ= 2.36 × 10-4 kg/m.s)p = 665.1 kg/m³
Chapter 2 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 2.3 - In each case, construct the parallelogram law to...Ch. 2.3 - In each case, show how to resolve the force F into...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.3 - Two forces act on the hook. Determine the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the 30-lb force into components along the...Ch. 2.3 - The force F = 450 lb acts on the frame. Resolve...Ch. 2.3 - If force F is to have a component along the u axis...Ch. 2.3 - If = 60 and F = 450 N, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the magnitude of the resultant force is to be...
Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - The vertical force F acts downward at A on the...Ch. 2.3 - Solve with F = 350 lb. Prob. 2-4/5Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force F1 into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force F2 into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force acting on the support is to...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - The plate is subjected to the two forces at A and...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the angle for connecting member A to...Ch. 2.3 - The force acting on the gear tooth is F = 20lb....Ch. 2.3 - The component of force F acting along line aa is...Ch. 2.3 - Force F acts on the frame such that its component...Ch. 2.3 - Force F acts on the frame such that its component...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the design angle (0 90) for strut AB...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the design angle (0 90) between...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - Prob. 22PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 23PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 24PCh. 2.3 - If F1 = 30 lb and F2 = 40 lb, determine the angles...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of FA SO...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction, measured...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of force F so that the...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force of the two tugboats is 3...Ch. 2.3 - If FB = 3 kN and = 45, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force of the two tugboats is...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve each force acting on the post into its x...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 9FPCh. 2.4 - If the resultant force acting on the bracket is to...Ch. 2.4 - If the magnitude of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 33PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 34PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve each force acting on the gusset plate into...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 38PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 39PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Express F1, F2, and F3 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 43PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 44PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 45PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and orientation of FB so...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and orientation. measured...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 49PCh. 2.4 - Express F1, F2, and F3 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 51PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 52PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 53PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 54PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 55PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 56PCh. 2.4 - If the resultant force acting on the bracket is...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 58PCh. 2.4 - If F = 5 kN and = 30, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.6 - Sketch the following forces on the x, y, z...Ch. 2.6 - In each case, establish F as a Cartesian vector,...Ch. 2.6 - Show how to resolve each force into its x, y, z...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of the...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 14FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 15FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 16FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 17FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 18FPCh. 2.6 - The force F has a magnitude of 80 lb and acts...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 61PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 62PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 63PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 64PCh. 2.6 - The screw eye is subjected to the two forces...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 66PCh. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Specify the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 72PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 73PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 74PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 75PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 76PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 77PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 78PCh. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of the...Ch. 2.6 - The bracket is subjected to the two forces shown....Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 81PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 82PCh. 2.6 - If the direction of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 84PCh. 2.6 - The pole is subjected to the force F which has...Ch. 2.8 - In each case, establish a position vector from...Ch. 2.8 - In each case, express F as a Cartesian vector....Ch. 2.8 - Express the position vector rAB in Cartesian...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 20FPCh. 2.8 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 22FPCh. 2.8 - Prob. 23FPCh. 2.8 - Prob. 24FPCh. 2.8 - Determine the length of the connecting rod AB by...Ch. 2.8 - Express force F as a Cartesian vector; then...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 88PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 89PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 90PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 91PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 92PCh. 2.8 - If FB = 560 N and FC = 700 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - If FB = 700 N, and FC = 560 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - The plate is suspended using the three cables...Ch. 2.8 - The three supporting cables exert the forces shown...Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 98PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 99PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 100PCh. 2.8 - The two mooring cables exert forces on the stern...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 102PCh. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - If the force in each cable tied to the bin is 70...Ch. 2.8 - If the resultant of the four forces is FR = {360k}...Ch. 2.9 - P2.8. in each case set up the dot product to find...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 9PPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 25FPCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 27FPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 28FPCh. 2.9 - Find the magnitude of the projected component of...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 30FPCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of the...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 106PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 107PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 108PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 109PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 110PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 111PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 112PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of F =...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 114PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 115PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 116PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the projected...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between cables AB and AC....Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 119PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 120PCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the two cables...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the cables AB and AC....Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projection of force...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 126PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 127PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 128PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 130PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 131PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 133PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 134PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 135PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 136PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 137PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 138PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 139PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.9 - Resolve F into components along the u and v axes...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 3RPCh. 2.9 - The cable at the end of the crane boom exerts a...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 5RPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 6RPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 7RPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2/Y Y+1 2Cp Q1/ Show that Cda Az x P1 mactual Cdf Af R/T₁ 2pf(P1-P2-zxgxpf) Q2/ A simple jet carburetor has to supply 5 Kg of air per minute. The air is at a pressure of 1.013 bar and a temperature of 27 °C. Calculate the throat diameter of the choke for air flow velocity of 90 m/sec. Take velocity coefficient to be 0.8. Assume isentropic flow and the flow to be compressible. Quiz/ Determine the air-fuel ratio supplied at 5000 m altitude by a carburetor which is adjusted to give an air-fuel ratio of 14:1 at sea level where air temperature is 27 °C and pressure is 1.013 bar. The temperature of air decreases with altitude as given by the expression The air pressure decreases with altitude as per relation h = 19200 log10 (1.013), where P is in bar. State any assumptions made. t = ts P 0.0065harrow_forward36 2) Use the method of MEMBERS to determine the true magnitude and direction of the forces in members1 and 2 of the frame shown below in Fig 3.2. 300lbs/ft member-1 member-2 30° Fig 3.2. https://brightspace.cuny.edu/d21/le/content/433117/viewContent/29873977/Viewarrow_forwardCan you solve this for me?arrow_forward
- 5670 mm The apartment in the ground floor of three floors building in Fig. in Baghdad city. The details of walls, roof, windows and door are shown. The window is a double glazing and air space thickness is 1.3cm Poorly Fitted-with Storm Sash with wood strip and storm window of 0.6 cm glass thickness. The thickness of door is 2.5 cm. The door is Poor Installation. There are two peoples in each room. The height of room is 280 cm. assume the indoor design conditions are 25°C DBT and 50 RH, and moisture content of 8 gw/kga. The moisture content of outdoor is 10.5 gw/kga. Calculate heat gain for living room : الشقة في الطابق الأرضي من مبنى ثلاثة طوابق في مدينة بغداد يظهر في مخطط الشقة تفاصيل الجدران والسقف والنوافذ والباب. النافذة عبارة عن زجاج مزدوج وسمك الفراغ الهوائي 1.3 سم ضعيف الاحكام مع ساتر حماية مع إطار خشبي والنافذة بسماكة زجاج 0.6 سم سماكة الباب 2.5 سم. الباب هو تركيب ضعيف هناك شخصان في كل غرفة. ارتفاع الغرفة 280 سم. افترض أن ظروف التصميم الداخلي هي DBT25 و R50 ، ومحتوى الرطوبة 8…arrow_forwardHow do i solve this problem?arrow_forwardQ4/ A compressor is driven motor by mean of a flat belt of thickness 10 mm and a width of 250 mm. The motor pulley is 300 mm diameter and run at 900 rpm and the compressor pulley is 1500 mm diameter. The shaft center distance is 1.5 m. The angle of contact of the smaller pulley is 220° and on the larger pulley is 270°. The coefficient of friction between the belt and the small pulley is 0.3, and between the belt and the large pulley is 0.25. The maximum allowable belt stress is 2 MPa and the belt density is 970 kg/m³. (a) What is the power capacity of the drive and (b) If the small pulley replaced by V-grooved pulley of diameter 300 mm, grooved angle of 34° and the coefficient of friction between belt and grooved pulley is 0.35. What will be the power capacity in this case, assuming that the diameter of the large pulley remain the same of 1500 mm.arrow_forward
- You are tasked with designing a power drive system to transmit power between a motor and a conveyor belt in a manufacturing facility as illustrated in figure. The design must ensure efficient power transmission, reliability, and safety. Given the following specifications and constraints, design drive system for this application: Specifications: Motor Power: The electric motor provides 10 kW of power at 1,500 RPM. Output Speed: The output shaft should rotate at 150 rpm. Design Decisions: Transmission ratio: Determine the necessary drive ratio for the system. Shaft Diameter: Design the shafts for both the motor and the conveyor end. Material Selection: Choose appropriate materials for the gears, shafts. Bearings: Select suitable rolling element bearings. Constraints: Space Limitation: The available space for the gear drive system is limited to a 1-meter-long section. Attribute 4 of CEP Depth of knowledge required Fundamentals-based, first principles analytical approach…arrow_forward- | العنوان In non-continuous dieless drawing process for copper tube as shown in Fig. (1), take the following data: Do-20mm, to=3mm, D=12mm, ti/to=0.6 and v.-15mm/s. Calculate: (1) area reduction RA, (2) drawing velocity v. Knowing that: ti: final thickness V. Fig. (1) ofthrearrow_forwardA direct extrusion operation produces the cross section shown in Fig. (2) from an aluminum billet whose diameter 160 mm and length - 700 mm. Determine the length of the extruded section at the end of the operation if the die angle -14° 60 X Fig. (2) Note: all dimensions in mm.arrow_forward
- For hot rolling processes, show that the average strain rate can be given as: = (1+5)√RdIn(+1)arrow_forward: +0 usão العنوان on to A vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2R. Take: -9.81 mis ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forward: +0 العنوان use only In conventional drawing of a stainless steel wire, the original diameter D.-3mm, the area reduction at each die stand r-40%, and the proposed final diameter D.-0.5mm, how many die stands are required to complete this process. онarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY