
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 55PQ
Three small metallic spheres with identical mass m and identical charge +q are suspended by light strings from the same point (Fig. P23.55). The left-hand and right-hand strings have length L and make an angle θ with the vertical. What is the value of q in terms of k, g, m, L, and θ?
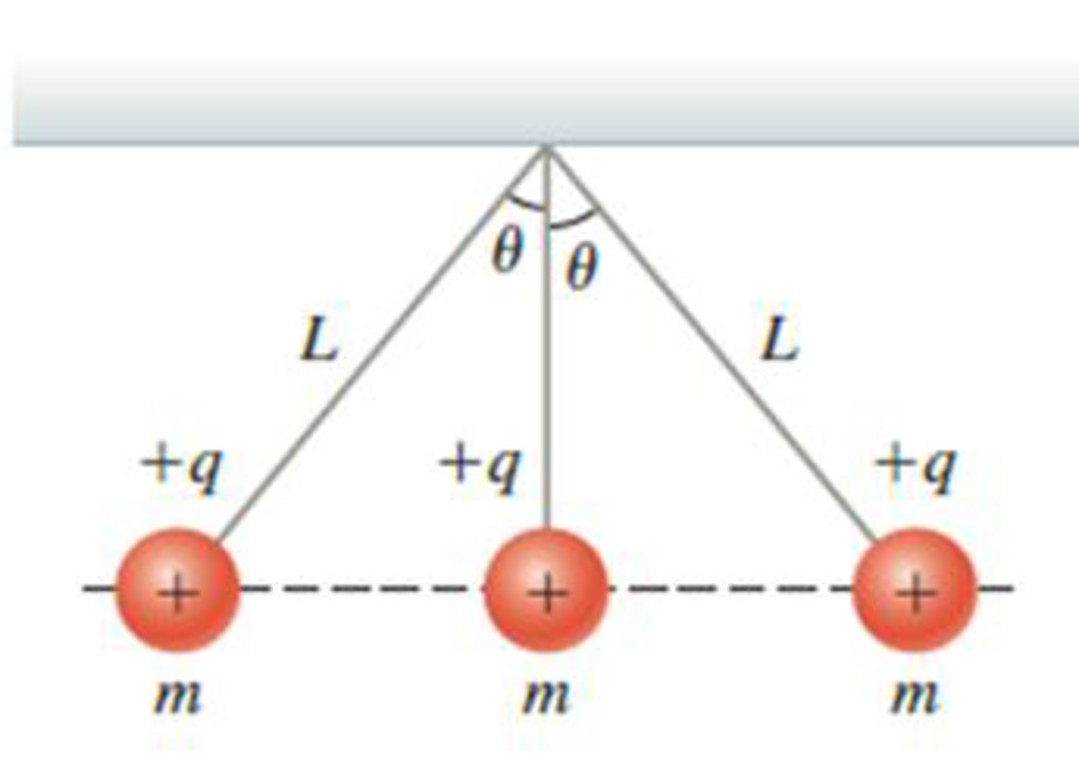
Figure P23.55
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
19:39 ·
C
Chegg
1 69%
✓
The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take
F=1700 lb. (Figure 1)
Figure
800 lb
||-5-
F
600 lb
بتا
D
E
C
BO
10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft-
Solved Part A The compound
beam is fixed at E and...
Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm
Problem
A-12
% Chia sẻ
kip
800 lb
Truy cập )
D Lưu
of
C
600 lb
|-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft
D
E
5 ft-
Trying
Cheaa
Những kết quả này có
hữu ích không?
There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!)
Chegg
Solved The compound b...
Có Không ☑
|||
Chegg
10
וח
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 23 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 23.2 - Initially a glass rod and a piece of silk are...Ch. 23.3 - a. In Figure 23.8, why are there three plus signs...Ch. 23.3 - When wool is rubbed against amber, the wool...Ch. 23.3 - Prob. 23.4CECh. 23.4 - The following scenarios involve a metal ball and a...Ch. 23.4 - Prob. 23.6CECh. 23 - What is the difference between a contact force and...Ch. 23 - Many textbooks claim Franklin decided that moving...Ch. 23 - An object has a charge of 35 nC. How many excess...Ch. 23 - As part of a demonstration, a physics professor...
Ch. 23 - A single coulomb represents a large amount of...Ch. 23 - A sphere has a net charge of 8.05 nC, and a...Ch. 23 - A glass rod is initially neutral. After it is...Ch. 23 - After an initially neutral glass rod is rubbed...Ch. 23 - A 50.0-g piece of aluminum has a net charge of...Ch. 23 - Prob. 10PQCh. 23 - A silk scarf is rubbed against glass, and a wool...Ch. 23 - CASE STUDY A person in Franklins time may have...Ch. 23 - Prob. 13PQCh. 23 - Prob. 14PQCh. 23 - A charge of 36.3 nC is transferred to a neutral...Ch. 23 - Prob. 16PQCh. 23 - Prob. 17PQCh. 23 - An electrophorus is a device developed more than...Ch. 23 - Prob. 19PQCh. 23 - An electroscope is a device used to measure the...Ch. 23 - Two particles with charges of +5.50 nC and 8.95 nC...Ch. 23 - Particle A has a charge of 34.5 nC, and particle B...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23PQCh. 23 - Prob. 24PQCh. 23 - Particle A has charge qA and particle B has charge...Ch. 23 - Two charged particles are placed along the y axis....Ch. 23 - A 1.75-nC charged particle located at the origin...Ch. 23 - A 1.75-nC charged particle located at the origin...Ch. 23 - Two particles with charges q1 and q2 are separated...Ch. 23 - An electron with charge e and mass m moves in a...Ch. 23 - Two electrons in adjacent atomic shells are...Ch. 23 - Two small, identical metal balls with charges 5.0...Ch. 23 - Two identical spheres each have a mass of 5.0 g...Ch. 23 - One end of a light spring with force constant k =...Ch. 23 - Two 25.0-g copper spheres are placed 75.0 cm...Ch. 23 - Three charged particles lie along a single line....Ch. 23 - Given the arrangement of charged particles shown...Ch. 23 - Given the arrangement of charged particles in...Ch. 23 - Given the arrangement of charged particles in...Ch. 23 - Three charged metal spheres are arrayed in the xy...Ch. 23 - Charges A, B, and C are arrayed along the y axis,...Ch. 23 - Three identical conducting spheres are fixed along...Ch. 23 - Charges A, B, and C are arranged in the xy plane...Ch. 23 - Prob. 44PQCh. 23 - A particle with charge q is located at the origin,...Ch. 23 - Figure P23.46 shows four identical conducting...Ch. 23 - Prob. 47PQCh. 23 - Two metal spheres of identical mass m = 4.00 g are...Ch. 23 - Figure P23.49 shows two identical small, charged...Ch. 23 - Two small spherical conductors are suspended from...Ch. 23 - Four equally charged particles with charge q are...Ch. 23 - Four charged particles q, q, q, and q are Fixed...Ch. 23 - A metal sphere with charge +8.00 nC is attached to...Ch. 23 - Prob. 54PQCh. 23 - Three small metallic spheres with identical mass m...Ch. 23 - How does a negatively charged rubber balloon stick...Ch. 23 - How many electrons are in a 1.00-g electrically...Ch. 23 - Prob. 58PQCh. 23 - Prob. 59PQCh. 23 - Prob. 60PQCh. 23 - Three charged particles are arranged in the xy...Ch. 23 - A We saw in Figure 23.16 that a neutral metal can...Ch. 23 - Prob. 63PQCh. 23 - A Figure P23.65 shows two identical conducting...Ch. 23 - Two helium-filled, spherical balloons, each with...Ch. 23 - Two small metallic spheres, each with a mass of...Ch. 23 - A Two positively charged spheres with charges 4e...Ch. 23 - Prob. 69PQCh. 23 - Three charged spheres are at rest in a plane as...Ch. 23 - Prob. 71PQCh. 23 - Three particles with charges of 1.0 C, 1.0 C, and...Ch. 23 - A Two positively charged particles, each with...Ch. 23 - Prob. 74PQCh. 23 - Eight small conducting spheres with identical...Ch. 23 - Prob. 76PQCh. 23 - Prob. 77PQCh. 23 - Prob. 78PQCh. 23 - Prob. 79PQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardair is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forward
- Calculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardCan you help me solve the questions pleasearrow_forward
- Can you help me solve these questions please so i can see how to do itarrow_forwardHow can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY