
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given complex the orbital splitting diagram has to be drawn using spectrochemial series.
[Cr(H2O)6]3+
Concept introduction:
The element in the periodic table and count its position in the respective transition series. These elements are in Periods 5 and 6, so the general configuration is
[noble gas]ns2(n− 1)dx.
The spectrochemical series is
I−<Cl−<F−<OH−<H2O<SCN−<en<NO−2<CN−<CO
(a)
Explanation of Solution
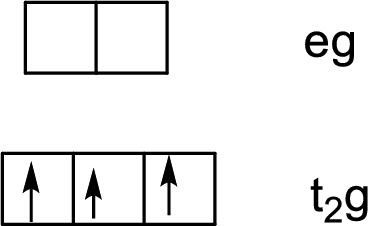
Electron configuration of Cr: [Ar]4s13d5
Charge on Cr: The aqua ligands are neutral, so the charge on Cr is +3.
Electron configuration of Cr3+: [Ar]3d3
Six ligands indicate an octahedral arrangement. Using Hund’s rule, fill the lower energy
t2g orbitals first, filling empty orbitals before pairing electrons within an orbital.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given complex the orbital splitting diagram has to be drawn using spectrochemial series.
[Cu(H2O)4]2+
Concept introduction:
The element in the periodic table and count its position in the respective transition series. These elements are in Periods 5 and 6, so the general configuration is
[noble gas]ns2(n− 1)dx.
The spectrochemical series is
I−<Cl−<F−<OH−<H2O<SCN−<en<NO−2<CN−<CO
(b)
Explanation of Solution
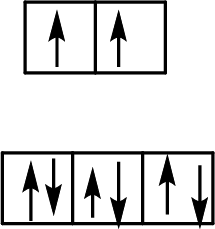
Electron configuration of Cu: [Ar]4s13d10
Charge on Cu: The aqua ligands are neutral, so Cu has a +2 charge.
Electron configuration of Cu2+: [Ar]3d9
Four ligands and a d9 configuration indicate a square planar geometry (only filled d sublevel ions exhibit tetrahedral geometry). Use Hund’s rule to fill in the nine d electrons. Thus, the correct orbital-energy splitting diagram shows one unpaired electron.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given complex the orbital splitting diagram has to be drawn using spectrochemial series.
[FeF6]3−
Concept introduction:
The element in the periodic table and count its position in the respective transition series. These elements are in Periods 5 and 6, so the general configuration is
[noble gas]ns2(n− 1)dx.
The spectrochemical series is
I−<Cl−<F−<OH−<H2O<SCN−<en<NO−2<CN−<CO
(c)
Explanation of Solution
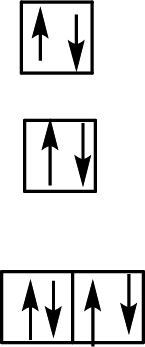
Electron configuration of Fe: [Ar]4s23d6
Charge on Fe: Each fluoride ligand has a –1 charge for a total charge of –6, so Fe has a +3 charge to make the overall complex charge equal to –3.
Electron configuration of Fe3+: [Ar]3d5
Six ligands indicate an octahedral arrangement. Use Hund’s rule to fill the orbitals.
F– is a weak-field ligand, so the splitting energy, Δ, is not large enough to overcome the resistance to electron pairing. The electrons remain unpaired, and the complex is called high-spin.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change
- 5. Please draw in the blanks the missing transition states and the correlated products. Explicitly display relevant absolute stereochemical configuration. MeOH I OMe H Endo transition state, dienophile approaching from the bottom of diene + H ཎྞཾ ཌཱརཱ༔,_o OMe H H OMe Endo transition state, dienophile approaching from the top of diene or from the bottom but horizontally flipped (draw one) + Exo transition state, dienophile approaching from the top of diene or from the bottom but horizontally flipped (draw one) Exo transition state, dienophile approaching from the top of diene or from the bottom but horizontally flipped (draw one) MeO H H MeO H MeO H MeO H Harrow_forwardH H (1) H C. C C .H (2) (3) Cl H The ideal value for bond angle (1) is (Choose one) and the ideal value for bond angle (3) is (Choose one) degrees, the value for bond angle (2) is (Choose one) degrees, degrees.arrow_forwardShow work.....don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Show work. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward10. Complete the following halogenation reactions for alkanes. Draw the structures of one of the many possible products for each reaction. Name the reactant and product. a) CH₂- CH-CH2-CH3 + Br₂ CH₂ UV UV b) + Cl2 c) CH3-CH₂ CHICHCHICH-CH CH₂-CH₂ + F2 UVarrow_forwardWhich of the following processes involves the largest photon energy? Group of answer choices Electron promotion from n=2 to n=5 Electron relaxing from n=4 to n=3 Ionization of an electron from n=2 Ionization of an electron from n=4arrow_forward
- Which of the following compounds does not match atomic ratio expectations in Mendeleev's 1872 periodic table? Group of answer choices NO2 Al2O3 SO3 CaOarrow_forwardNeed help with 14 and 15. 14. bromobenzene + (CHs),CuLi + THF / -78° followed by water quench is a. toluene else!! b. xylene c. cumene d. styrene e. something 15. When cumene + H,SO, / Na,Cr, 0,/water are mixed (refluxed) what is produced? a. 2-phenylpropanol phenol e. styrene b. benzoic acid c. no reaction!arrow_forwardWhich of the following orbitals intersect or overlap the x-axis in the standard cartesian coordinate system used? (Select ALL correct answers.) Group of answer choices px dxz dx2-y2 py dxy sarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





