
The IUPAC rules permit the use of common names for a number of familiar phenols and aryl ethers. These common names are listed here along with their systematic names. Write the structure of each compound.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
Interpretation:
The structures of the given compounds are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is done by using IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of an organic compound is done in such a way that the structure of the organic compound is correctly interpreted from its name.
In order to determine the structure of an organic compound from its name, first the root word in the name is identified. The suffixes like
In the next step of structure identification of the organic compound from its name, the position, location and number of the substituents bonded to the carbon chain are determined.
Answer to Problem 12P
Solution:
a) The structure of
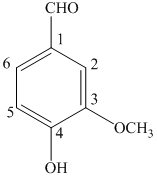
b) The structure of
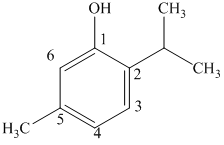
c) The structure of
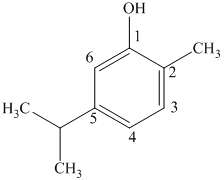
d) The structure of
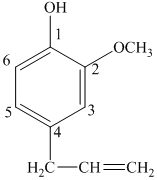
e) The structure of
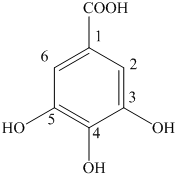
f) The structure of
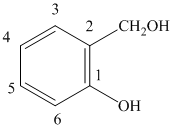
Explanation of Solution
a) The structure of
The given compound is

b) The structure of
The given compound is

c) The structure of
The given compound is

d) The structure of
The given compound is

e) The structure of
The given compound is

f) The structure of is
The given compound is

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Provide the IUPAC name for each of the following compounds. Pay attention to stereochemistry. (c) (a) (Б) О NO2 OH NH2 ОН NH2arrow_forwardGive IUPAC names for the following alkyl halides: (please answer letters d, c, d)arrow_forwardArrange the alkenes in each set in order of increasing rate of reaction with HI and explain the basis for your ranking. Draw the structural formula of the major product formed in each case. (a) and (b) H3CH₂CHC=CH₂ and (H3C) 2C=CHCH3arrow_forward
- 8arrow_forwardMany ethers, including diethyl ether, are effective as general anesthetics. Because simple ethers are quite flammable, their place in medical practice has been taken by highly halogenated nonflammable ethers. Two such general anesthetic agents are isoflurane and enflurane. These compounds are isomeric; isoflurane is 1-chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether; enflurane is 2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether. Write the structural formulas of isoflurane and enflurane.arrow_forwardPhenylethanol can be oxidised to phenylethanal or phenylethanoic acid, depending on the reagents used (both the alcohol and the aldehyde are of interest for their antimicrobial properties, while the acid is used to treat type II hyperammonemia): A (a) (b) (c) CoH,CH,CHO phenylethanal B C6H5CH₂CH₂OHC₂H₂CH₂CO₂H phenylethanol Suggest reagents (shown as A and B in the scheme above) that could be used to carry out the oxidation of the alcohol to the aldehyde and the acid, respectively. C6H5CH₂- Suggest two other syntheses of phenylethanoic acid, in each case indicating the starting materials and other reagents required, but not giving details of mechanism. One of your proposed syntheses must start with a compound which only contains seven carbon atoms (the acid product contains eight carbon atoms). phenylethanoic acid Phenylethanal can be converted to a hydrate in the presence of aqueous acid, though the position of equilibrium is very far to the left: H H+/H₂O OH C6H5CH₂-C-H OH Explain why…arrow_forward
- Give an IUPAC substitutive name for each of the following alcohols.arrow_forward1B. Provide the IUPAC name of the following compounds, with clear indication of stereochemistry for stereocenters and alkene. Me. (a) (b) (c) (d) Br "Ме CIarrow_forward1. Give the IUPAC names for the following alcohols. (a) OH OH (b) ОН (c) HO CH3CHCH2CHCHCH3 CH2CH2CCH3 -CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 (d) (e) (f) CH3 HO HO OHarrow_forward
