
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Distribution of d-electrons and the geometry of the complex ion
Concept Introduction:
Complex compounds exist in following geometries - tetrahedral, square planar, octahedral etc.
When ligands approach the metal ion the degeneracy in d-orbitals of the metal ion is destroyed and they split into two different energy levels. In case of tetrahedral complex, the
In case of square planar complex, the 5 d-orbitals split into following pattern and it is given below with increasing order of energy.
(a)
Answer to Problem 22.59QP
The d-electrons are distributed in the complex ion

The complex has square planar geometry.
Explanation of Solution
In the complex ion

The distribution of d-electrons as shown above correlates to that of square planar geometry. Hence the complex ion
Splitting of d-orbitals determines the geometry of the complex.
(b)
Interpretation:
Distribution of d-electrons and the geometry of the complex ion
Concept Introduction:
Complex compounds exist in following geometries - tetrahedral, square planar, octahedral etc.
When ligands approach the metal ion the degeneracy in d-orbitals of the metal ion is destroyed and they split into two different energy levels. In case of tetrahedral complex, the
In case of square planar complex, the 5 d-orbitals split into following pattern and it is given below with increasing order of energy.
(b)
Answer to Problem 22.59QP
The d-electrons are distributed in the complex ion

The complex has square planar geometry.
Explanation of Solution
In the complex ion
Atomic number of Cobalt is

The distribution of d-electrons as shown above correlates to that of square planar geometry. Hence the complex ion
Splitting of d-orbitals determines the geometry of the complex.
(c)
Interpretation:
Distribution of d-electrons and the geometry of the complex ion
Concept Introduction:
Complex compounds exist in following geometries - tetrahedral, square planar, octahedral etc.
When ligands approach the metal ion the degeneracy in d-orbitals of the metal ion is destroyed and they split into two different energy levels. In case of tetrahedral complex, the
In case of square planar complex, the 5 d-orbitals split into following pattern and it is given below with increasing order of energy.
(c)
Answer to Problem 22.59QP
The d-electrons are distributed in the complex ion
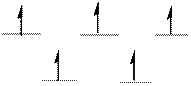
The complex has tetrahedral geometry.
Explanation of Solution
In the complex ion
Atomic number of Iron is

The distribution of d-electrons as shown above correlates to that of tetrahedral geometry. Hence the complex ion
Splitting of d-orbitals determines the geometry of the complex.
(d)
Interpretation:
Distribution of d-electrons and the geometry of the complex ion
Concept Introduction:
Complex compounds exist in following geometries - tetrahedral, square planar, octahedral etc.
When ligands approach the metal ion the degeneracy in d-orbitals of the metal ion is destroyed and they split into two different energy levels. In case of tetrahedral complex, the
In case of square planar complex, the 5 d-orbitals split into following pattern and it is given below with increasing order of energy.
(d)
Answer to Problem 22.59QP
The d-electrons are distributed in the complex ion
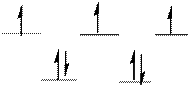
The complex has tetrahedral geometry.
Explanation of Solution
In the complex ion
Atomic number of Cobalt is

The distribution of d-electrons as shown above correlates to that of tetrahedral geometry. Hence the complex ion
Splitting of d-orbitals determines the geometry of the complex.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Bundle: General Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version, 11th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- What types of isomers are possible for the following compounds or complex ions? (a) K[Co(NH3)2Cl4] (b) Pt(en)Cl2 (square-planar) (c) [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+ (d) [Ru(phen)3]Cl3 (e) Na2[MnCl4] (tetrahedral) (f) [Co(NH3)5NO2)2+arrow_forwardFour different octahedral chromium coordination compounds exist that all have the same oxidation state for chromium and have H2O and Cl as the ligands and counterions. When 1 mole of each of the four compounds is dissolved in water, how many moles of silver chloride will precipitate upon addition of excess AgNO3?arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





