
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.2, Problem 2.21P
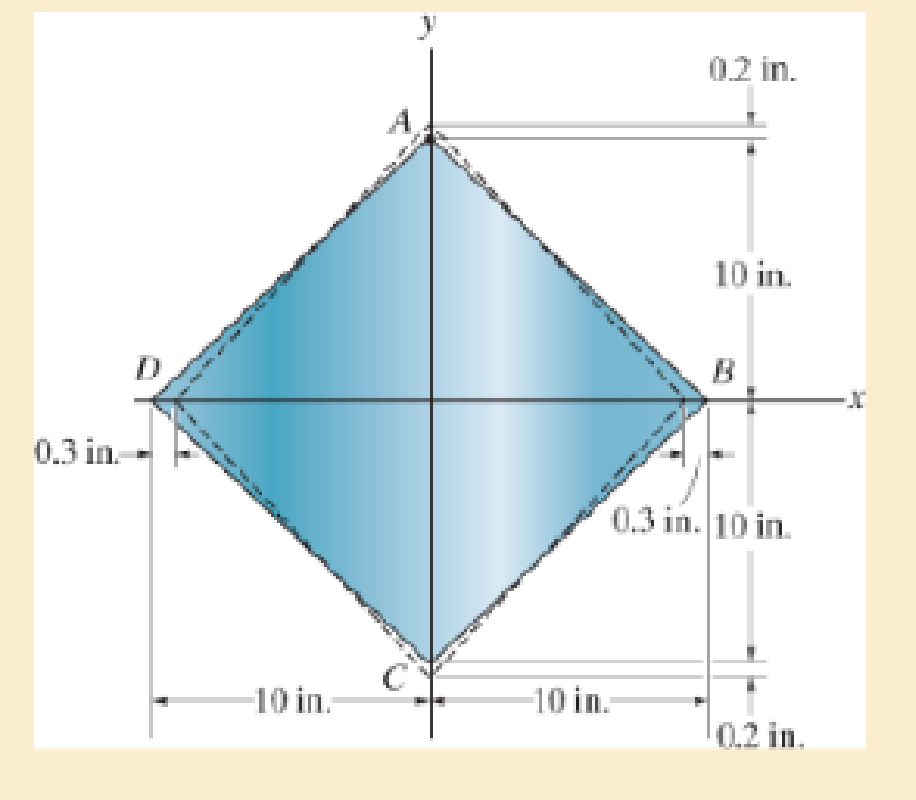
The corners of the square plate are given the displacements indicated. Determine the average normal strains εx and εy along the x and y axes.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
1. A loading causes the member to deform into the dashed shape. Explain how to
determine the normal strains ɛcd and ɛAB. The displacement A and the lettered
dimensions are known.
B
L.
L/2
A
2 L
(а)
L.
B
L/2
A
2 L
(b)
For the state of a plane strain with εx, εy and γxy components: (a) construct Mohr’s circle and (b) determine the equivalent in-plane strains for an element oriented at an angle of 30° clockwise. εx = 255 × 10-6 εy = -320 × 10-6 γxy = -165 × 10-6
Consider the given loading on a pipe. A rectangular rosette (45 degree apart) is placed on a point (K) which is located on the half length of the pipe as shown below. Note that the second gage (b) is parallel to the z-axis . When the load is applied, the strain gages read εa=80 µS, εb=60 µS, εc=20 µS. The pipe have an elastic modulus of Est=201 GPa.
a. Determine the in-plane principal strains and the principal strain directions for the given set of strains (Use Mohr circle)
Chapter 2 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the member to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the mamber to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the wires to elongate into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the block to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the block to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - When force P is applied to the rigid arm ABC,...Ch. 2.2 - If the force P causes the rigid arm ABC to rotate...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The square plate is deformed into the shape shown...
Ch. 2.2 - The square deforms into the position shown by the...Ch. 2.2 - The pin-connected rigid rods AB and BC are...Ch. 2.2 - The wire AB is unstretched when = 45. If a load...Ch. 2.2 - If a horizontal load applied to the bar AC causes...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners A and B...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners D and C...Ch. 2.2 - The material distorts into the dashed position...Ch. 2.2 - The material distorts into the dashed position...Ch. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...Ch. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...Ch. 2.2 - The nylon cord has an original length L and is...Ch. 2.2 - A thin wire, lying along the x axis, is strained...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners A and B...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners D and C...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the average normal strain that occurs...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The polysulfone block is glued at its top and...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The block is deformed into the position shown by...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The nonuniform loading causes a normal strain in...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate undergoes a deformation...Ch. 2.2 - The fiber AB has a length L and orientation . If...Ch. 2.2 - If the normal strain is defined in reference to...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The strain components at a point in a body subjected to plane strain are & 850μ, Ey -300μ, and Yay 400μ. Determine the principal strains and the maximum shearing strain at the point. Show the principal strain deformations and the maximum shearing strain distortion on a sketch. = = =arrow_forwardFor the given plane strain state, use Mohr's circle to determine the strain state associated with the x' and y' axes rotated to θ indicated in the table: \epsilon_x \epsilon_y \gamma_{xy} θ -500\mu 250\mu 120\mu -15°arrow_forwardThe piece of plastic is originally rectangular. Determine the average normal strain that occurs along the diagonals AC and DB. Determine the shear strain at corners A and B if the plastic distorts as shown by the dashed lines.arrow_forward
- Determine the shear strain gxy at corners D and C if the plate distorts as shown by the dashed lines.arrow_forwardThe strain components e x, e y, and γ xy are given for a point in a body subjected to plane strain. Using Mohr’s circle, determine the principal strains, the maximum in-plane shear strain, and the absolute maximum shear strain at the point. Show the angle θ p, the principal strain deformations, and the maximum in-plane shear strain distortion in a sketch. Ex Ey Yxy −1,570 με -430με -950 μradarrow_forwardThe strain components Ex, Ey, and Yxy are given for a point in a body subjected to plane strain. Using Mohr's circle, determine the principal strains, the maximum in-plane shear strain, and the absolute maximum shear strain at the point. Show the angle 0p, the principal strain deformations, and the maximum in-plane shear strain distortion in a sketch. Ex = 0 μE, Ey = 310 με, Yxy = 280 μrad. Enter the angle such that -45° ≤ 0,≤ +45° Answer: Ep1 = Ep2 = Ymax in-plane = Yabsolute max. = 0p = με με urad uradarrow_forward
- The strain components εx, εy, and γxy are given for a point in a body subjected to plane strain. Using Mohr’s circle, determine the principal strains, the maximum in-plane shear strain, and the absolute maximum shear strain at the point. Show the angle θp, the principal strain deformations, and the maximum in-plane shear strain distortion in a sketch. εx = 350 με, εy = -540 με, γxy = -890 μrad. Enter the angle such that -45°≤θp≤ +45°.arrow_forwardThe strain components ɛx, Ey, and yxy are given for a point in a body subjected to plane strain. Using Mohr's circle, determine the principal strains, the maximum in-plane shear strain, and the absolute maximum shear strain at the point. Show the angle 0p, the principal strain deformations, and the maximum in-plane shear strain distortion in a sketch. Ex = 0 HE, ɛy = 380 µɛ, Yxy = 230 µrad. Enter the angle such that -45° s 0,s+45°. Answer: Ep1 = με Ep2 = με Ymax in-plane = prad Yabsolute max. = prad 0, =arrow_forwardDetermine the shear strain gxy at corners D and C if the plastic distorts as shown by the dashed lines.arrow_forward
- The block is deformed into the position shown by the dashed lines. Determine the average normal strain along with line AB.arrow_forwardThe strain components ɛ, Ey, and yy are given for a point in a body subjected to plane strain. Using Mohr's circle, determine the principal strains, the maximum in-plane shear strain, and the absolute maximum shear strain at the point. Show the angle 0, the principal strain deformations, and the maximum in-plane shear strain distortion in a sketch. Ex = 300 µe, ɛ, = -710 pe, Vxy = -440 urad. Enter the angle such that -45°s0,s +45°. Answer: Ep1= pe Ep2= με Ymax in-plane = prad Yabsolute max. prad Əp =arrow_forwardThe material distorts into the dashed position shown. Determine the average normal strains Px, Py and the shear strain gxy at A, and the average normal strain along line BE.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Lec21, Part 5, Strain transformation; Author: Mechanics of Materials (Libre);https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sgJvz5j_ubM;License: Standard Youtube License