
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.2, Problem 2.14P
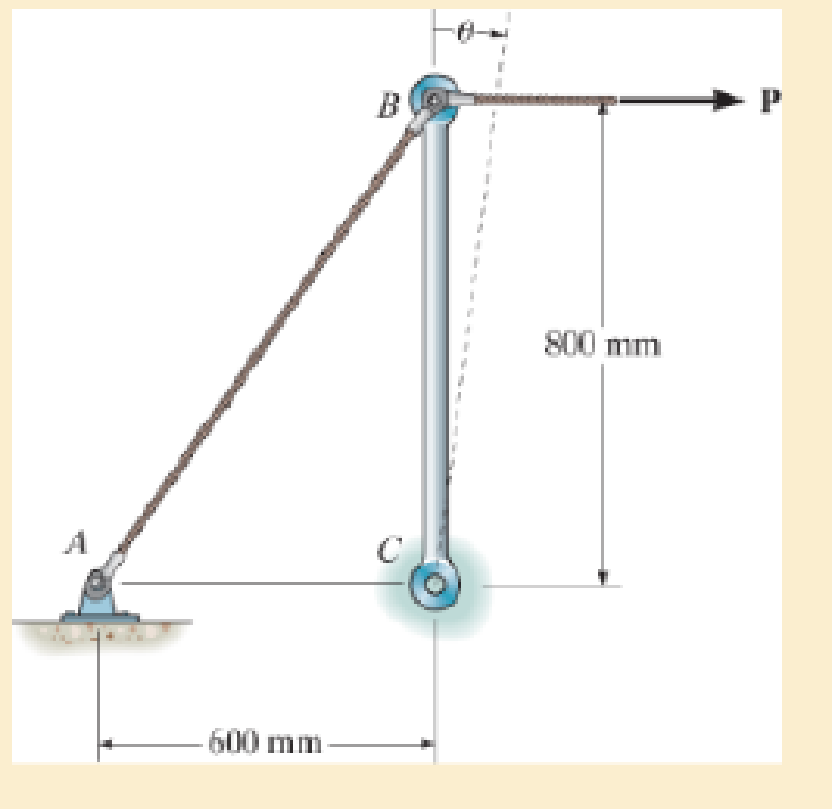
Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists of a rigid member CB and a flexible cable AB. If a force is applied to the end B of the member and causes it to rotate by θ = 0.5°, determine the normal strain in the cable. Originally the cable is unstretched.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule04:15
Students have asked these similar questions
First, define the coordinate system XY with its origin at O2 and X-axis passing through O4 asshown above, then based on the provided steps Perform coordinate transformation from XY to xy to get the trajectory of point P. Show all the steps and calcualtions
I don't know how to solve this
Question 2 (40 Points)
Consider the following double pendulum-like system with links ₁ and 12. The angles 0 and & could have
angular velocities ėêk and êk, respectively, where ②k is a unit vector that points out of the page and is
perpendicular to x and y. They could also have angular accelerations Ök and êk. The angle is
defined relative to the angle 0. The link 12 is a spring and can extend or compress at a rate of 12. It can
also have a rate of extension or compression Ï2.
li
y
êr1
êe
12
χ
3
еф
er2
ده لج
1) Express the velocity of the mass in terms of the unit vectors ê0, êr1, êø, and êr2, and any
extension/contraction of the links (e.g.,. i; and Ï¿) (12 Points)
2) Express the acceleration of the mass in terms of the unit vectors ê¤, ê×1, êp, and êÃ2, and any
extension/contraction of the links (e.g.,. İ; and Ï¿) (12 Points)
3) Express the velocity of the mass in terms of unit vectors î and ĵ that point in the x and y
directions, respectively. Also include the appropriate,…
Chapter 2 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the member to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the mamber to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the wires to elongate into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the block to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the block to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - When force P is applied to the rigid arm ABC,...Ch. 2.2 - If the force P causes the rigid arm ABC to rotate...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The square plate is deformed into the shape shown...
Ch. 2.2 - The square deforms into the position shown by the...Ch. 2.2 - The pin-connected rigid rods AB and BC are...Ch. 2.2 - The wire AB is unstretched when = 45. If a load...Ch. 2.2 - If a horizontal load applied to the bar AC causes...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners A and B...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners D and C...Ch. 2.2 - The material distorts into the dashed position...Ch. 2.2 - The material distorts into the dashed position...Ch. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...Ch. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...Ch. 2.2 - The nylon cord has an original length L and is...Ch. 2.2 - A thin wire, lying along the x axis, is strained...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners A and B...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners D and C...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the average normal strain that occurs...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The polysulfone block is glued at its top and...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The block is deformed into the position shown by...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The nonuniform loading causes a normal strain in...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate undergoes a deformation...Ch. 2.2 - The fiber AB has a length L and orientation . If...Ch. 2.2 - If the normal strain is defined in reference to...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Suppose that we want to compute the geometric mean of a list of positive values. To compute the geometric mean ...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
What is the purpose of an objects sizing handles?
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
In Exercises 41 through 46, identify the errors.
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
F48. Determine the resultant moment produced by the forces about point O.
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Name two different uses for the C++ operator.
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- provide step by step solutions for angles teta 3 and teta 4 by the vector loopmethod. Show work in: vector loop, vector equations, solution procedure.arrow_forward(Manometer) A tank is constructed of a series of cylinders having diameters of 0.35, 0.30, and 0.20 m as shown in the figure below. The tank contains oil, water, and glycerin and a mercury manometer is attached to the bottom as illustrated. Calculate the manometer reading, h. 0.11 m + SAE 30 Oil 0.13 m + Water 0.10 m Glycerin + 0.10 m Mercury h = marrow_forwardP = A piston having a cross-sectional area of 0.40 m² is located in a cylinder containing water as shown in the figure below. An open U-tube manometer is connected to the cylinder as shown. For h₁ = 83 mm and h = 111 mm what is the value of the applied force, P, acting on the piston? The weight of the piston is negligible. Hi 5597.97 N P Piston Water Mercuryarrow_forward
- Student Name: Student Id: College of Applied Engineering Al-Muzahmiyah Branch Statics (AGE 1330) Section-1483 Quiz-2 Time: 20 minutes Date: 16/02/2025 Q.1. A swinging door that weighs w=400.0N is supported by hinges A and B so that the door can swing about a vertical' axis passing through the hinges (as shown in below figure). The door has a width of b=1.00m and the door slab has a uniform mass density. The hinges are placed symmetrically at the door's edge in such a way that the door's weight is evenly distributed between them. The hinges are separated by distance a=2.00m. Find the forces on the hinges when the door rests half-open. Draw Free body diagram also. [5 marks] [CLO 1.2] Mool b ర a 2.0 m B 1.0 marrow_forwardFor the walking-beam mechanism shown in Figure 3, find and plot the x and y coordinates of the position of the coupler point P for one complete revolution of the crank O2A. Use the coordinate system shown in Figure 3. Hint: Calculate them first with respect to the ground link 0204 and then transform them into the global XY coordinate system. y -1.75 Ꮎ Ꮎ 4 = 2.33 0242.22 L4 x AP = 3.06 L2 = 1.0 W2 31° B 03 L3 = 2.06 P 1 8 5 .06 6 7 P'arrow_forwardThe link lengths, gear ratio (2), phase angle (Ø), and the value of 02 for some geared five bar linkages are defined in Table 2. The linkage configuration and terminology are shown in Figure 2. For the rows assigned, find all possible solutions for angles 03 and 04 by the vector loop method. Show your work in details: vector loop, vector equations, solution procedure. Table 2 Row Link 1 Link 2 Link 3 Link 4 Link 5 λ Φ Ө a 6 1 7 9 4 2 30° 60° P y 4 YA B b R4 R3 YA A Gear ratio: a 02 d 05 r5 R5 R2 Phase angle: = 0₂-202 R1 05 02 r2 Figure 2. 04 Xarrow_forward
- Problem 4 A .025 lb bullet C is fired at end B of the 15-lb slender bar AB. The bar is initially at rest, and the initial velocity of the bullet is 1500 ft/s as shown. Assuming that the bullet becomes embedded in the bar, find (a) the angular velocity @2 of the bar immediately after impact, and (b) the percentage loss of kinetic energy as a result of the impact. (c) After the impact, does the bar swing up 90° and reach the horizontal? If it does, what is its angular velocity at this point? Answers: (a). @2=1.6 rad/s; (b). 99.6% loss = (c). Ah2 0.212 ft. The bar does not reach horizontal. y X 4 ft 15 lb V₁ 1500 ft/s 0.025 lb C 30°7 B Aarrow_forwardsubject: combustion please include complete solution, no rounding off, with diagram/explanation etc. In a joule cycle, intake of the compressor is 40,000 cfm at 0.3 psig and 90 deg F. The compression ratio is 6.0 and the inlet temperature at the turbine portion is 1900R while at the exit, it is 15 psi. Calculate for the back work ratio in percent.arrow_forwardsubject: combustion please include complete solution, no rounding off, with diagram/explanation etc. A gasoline engine, utilizing cold air, recorded a work of 431 BTU/lb at a maximum temperature of 3,273 K and 1112 deg F temperature at the beginning of constant volume heat addition. What is the compression ratio?arrow_forward
- subject: combustion please do step by step solution and no rounding off, complete solution with diagram/explanation if needed etc. thank you! Air enters the compressor at 101,320 Pascals, 305.15K, and leaves at a pressure of 0.808MPa. The air is heated to 990.15K in the combustion chamber. For a net output of 2,125,000 Watts, find the rate of flow of air per second.arrow_forwardThe link lengths and the value of 2 and offset for some fourbar crank-slide linkages are defined in Table 1. The linkage configuration and terminology are shown in Figure 1. For the rows assigned, find (a) all possible solutions for angle & and slider position d by vector loop method. (b) the transmission angle corresponding to angle 03. (Hint: Treat the vector R4 as virtual rocker) Show your work in details: vector loop, vector equations, solution procedure. Table 1 Row Link 2 Link 3 Offset Ө a 1.4 4 1 45° b 3 8 2 -30° C 5 20 -5 225° 03 slider axis B X offset Link 2 A R3 Link 3 R4 04 R2 02 R1 d Figure 1. Xarrow_forward4. Two links made of heat treated 6061 aluminum (Sy = 276 MPa, Sys = 160 MPa) are pinned together using a steel dowel pin (Sy = 1398 MPa, Sys = 806 MPa) as shown below. The links are to support a load P with a factor of safety of at least 2.0. Determine if the link will fail first by tearout, direct shear of the pin, bearing stress on the link, or tensile stress at section AA. (Hint: find the load P for each case and choose the case that gives the smallest load.) P 8 mm P 8 mm ¡+A 3 mm →A 10 mm Parrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
An Introduction to Stress and Strain; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aQf6Q8t1FQE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY