
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 21, Problem 7Q
Figure 21-16 shows three situations involving a charged particle and a uniformly charged spherical shell. The charges are given, and the radii of the shells are indicated. Rank the situations according to the magnitude of the force on the particle due to the presence of the shell, greatest first.
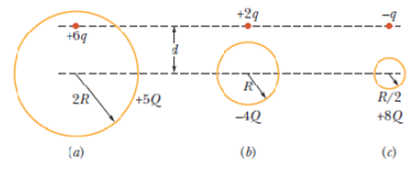
Figure 21-16 Question 7.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 21 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 21 - Figure 21-11 shows 1 four situations in which five...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-12 shows three pairs of identical...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-13 shows four situations in which...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-14 shows two charged particles on an...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-15, a central particle of charge q is...Ch. 21 - A positively charged ball is brought close to an...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-16 shows three situations involving a...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-17 shows four arrangements of charged...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-18 shows four situations in which...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-19, a central particle of charge 2q is...
Ch. 21 - Figure 21-20 shows three identical conducting...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-21 shows four situations in which a...Ch. 21 - SSM ILW Of the charge Q initially on a tiny...Ch. 21 - Identical isolated conducting spheres 1 and 2 have...Ch. 21 - SSM What must be the distance between point charge...Ch. 21 - In the return stroke of a typical lightning bolt,...Ch. 21 - A particle of charge 3.00 106 C is 12.0 cm...Ch. 21 - ILW Two equally chained particles are held 3.2 ...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-23, three charged particles lie on an x...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-24, three identical conducting spheres...Ch. 21 - SSM WWW Two identical conducting spheres, fixed in...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-25, four particles form a square....Ch. 21 - ILW In Fig. 21-25, the particles have charges q1 =...Ch. 21 - Two particles are fixed on an x axis. Particle 1...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-26, particle 1 of charge l.0 C and...Ch. 21 - Three particles are fixed on an x axis. Particle 1...Ch. 21 - GO The charges and coordinates of two charged...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-27a, particle l of charge q1 and...Ch. 21 - In Fig.21-28a, particles 1 and 2 have charge 20.0...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-29a, three positively charged particles...Ch. 21 - SSM WWW In Fig. 21-26, particle 1 of charge q and...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-30a shows an arrangement of three...Ch. 21 - GO A nonconducting spherical shell, with an inner...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-31 shows an arrangement of four...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-32, particles 1 and 2 of charge q1 =...Ch. 21 - Two tiny, spherical water drops, with identical...Ch. 21 - ILW How many electrons would have to be removed...Ch. 21 - Prob. 26PCh. 21 - SSM The magnitude of the electrostatic force...Ch. 21 - A current of 0.300 A through your chest can send...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-33, particles 2 and 4, of charge e,...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-26, particles 1 and 2 are fixed in...Ch. 21 - ILW Earths atmosphere is constantly bombarded by...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-34a shows charged particles 1 and 2...Ch. 21 - Calculate the number of coulombs of positive...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-35 shows electrons 1 and 2 on an x...Ch. 21 - SSM In crystals of the salt cesium chloride,...Ch. 21 - Electrons and positrons are produced by the...Ch. 21 - Prob. 37PCh. 21 - GO Figure 21-37 shows four identical conducting...Ch. 21 - SSM In Fig. 21-38, particle 1 of charge 4e is...Ch. 21 - In Fig, 21-23, particles 1 and 2 are fixed in...Ch. 21 - a What equal positive charges would have to be...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-39, two tiny conducting balls of...Ch. 21 - a Explain what happens to the balls of Problem 42...Ch. 21 - SSM How far apart must two protons be if the...Ch. 21 - How many megacoulombs of positive charge are in...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-40, four particles are fixed along an x...Ch. 21 - GO Point charges of 6.0 C and 4.0 C are placed on...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-41, three identical conducting spheres...Ch. 21 - A neutron consists of ore up quark of charge 2e/3...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-42 shows a long, nonconducting, massless...Ch. 21 - A charged nonconducting rod, with a length of 2.00...Ch. 21 - A particle of charge Q is Fixed at the origin of...Ch. 21 - What would be the magnitude of the electrostatic...Ch. 21 - A charge of 6.0 C is to be split into two parts...Ch. 21 - Of the charge Q on a tiny sphere, a fraction is...Ch. 21 - If a cat repeatedly rubs against your cotton...Ch. 21 - We know that the negative charge on the electron...Ch. 21 - In Fig, 21-26, particle 1 of charge 80.0C and...Ch. 21 - What is the total charge in coulombs of 75.0 kg of...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-43, six charged particles surround...Ch. 21 - Three charged particles form a triangle: particle...Ch. 21 - SSM In Fig. 21-44, what are the a magnitude and b...Ch. 21 - Two point charges of 30 nC and 40 nC are held...Ch. 21 - Two small, positively charged spheres have a...Ch. 21 - The initial charges on the three identical metal...Ch. 21 - An electron is in a vacuum near Earths surface and...Ch. 21 - SSM In Fig. 21-26, particle 1 of charge 5.00q and...Ch. 21 - Two engineering students, John with a mass of 90...Ch. 21 - In the radioactive decay of Eq. 21-13, a 238U...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-25, four particles form a square. The...Ch. 21 - In a spherical metal shell of radius R, an...Ch. 21 - An electron is projected with an initial speed vl...Ch. 21 - In an early model of the hydrogen atom the Bohr...Ch. 21 - A100 W lamp has a steady current of 0.83 A in its...Ch. 21 - The charges of an electron and a positron are e...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Q1. What is the empirical formula of a compound with the molecular formula
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Ahydraulic cylinder has a 125mm diameter piston with an ambient pressure of 1 bar. Assuming standard gravity, f...
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY You are handed a mystery pea plant with tall stems and axial flowers and asked to determine ...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
The genes dumpy (dp), clot (cl), and apterous (ap) are linked on chromosome II of Drosophila. In a series of tw...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
A source of electromagnetic radiation produces infrared light. Which of the following could be the wavelength ...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Why is turbidity not an accurate measurement of viable bacteria in a culture?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY