
Concept explainers
In Fig. 21-41, three identical
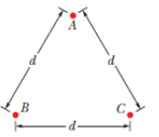
Figure 21-41 Problem 48.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- Snoop Dogg, in an effort to get laid back (with his mind on his money and his money on his mind) pours himself a gin and juice. He mixes 0.124 kg (about 3 shots) of gin with 0.576 kg (about a pint) of orange juice. The gin starts at 20.0˚C, room temperature. The juice is refrigerated and starts at 2.89 ˚C. What is the final temperature after mixing of the gin and juice? The specific heat of gin is 3460 J/kg˚C and the specific heat of orange juice is 3730 J/kg˚C.arrow_forwardA sword is heated up to 226 °C, it is put into a nearby barrel of water that is at 18.4 °C. What mass of water would be needed to cool the sword to 30.0˚C, bringing the system to thermal equilibrium? The sword is 35.4 kg and is made of steel. The specific heat of water is = 4186 J/kg ˚C. The specific heat of steel is = 502 J/kg ˚Carrow_forwardYou are planning on installing a new above-ground swimming pool in your backyard. The pool will be rectangular with dimensions 32.0 m x 10.0 m. It will be filled with fresh water to a depth of 2.20 m. In order to provide the appropriate structural support, you wish to determine the following. (a) Determine the force exerted on the bottom of the pool by the water (in N). (No Response) N (b) Determine the force exerted on each end of the pool by the water (in N). (Assume the end is the 10.0 m wall.) (No Response) N (c) Determine the force exerted on each side of the pool by the water (in N). (Assume the side is the 32.0 m wall.) (No Response) N (d) You wish to have swimming parties with your children and grandchildren. At a given time, you might have 23 people with an average mass of 75.0 kg in the pool. You need to determine if such parties will affect your calculations for the required strength of materials supporting your pool. The parties will not affect the required strength since…arrow_forward
- The construction of a water pistol is shown in the figure below. The cylinder with cross-sectional area A₁ is filled with water and when the piston is pushed (by pulling the trigger), water is forced out the tube with cross-sectional area A2. The radius of the cylinder and tube are, respectively, 1.30 cm and 1.10 mm, and the center of the tube is a height h = 3.00 cm above the center of the cylinder. (Assume atmospheric pressure is 1.013 × 105 Pa.) A2 A₁ (a) If the pistol is fired horizontally at a height of 1.30 m, determine the time interval (in s) required for water to travel from the nozzle to the ground. Neglect air resistance. (No Response) s (b) If the desired range of the stream is 7.50 m, with what speed ✓2 (in m/s) must the stream leave the nozzle? (No Response) m/s (c) At what speed v₁ (in m/s) must the plunger be moved to achieve the desired range? (No Response) m/s (d) What is the pressure (in Pa) at the nozzle? (No Response) Pa (e) Find the pressure (in Pa) needed in the…arrow_forwardA high-speed lifting mechanism supports a(n) 700-kg object with a steel cable that is 34.0 m long and 4.00 cm² in cross-sectional area. (a) Determine the elongation of the cable. (Enter your answer to at least two decimal places.) (No Response) mm (b) By what additional amount does the cable increase in length if the object is accelerated upwards at a rate of 2.5 m/s²? (No Response) mm (c) What is the greatest mass that can be accelerated upward at 2.5 m/s² if the stress in the cable is not to exceed the elastic limit of the cable, which is 2.2 × 108 Pa? (No Response) kgarrow_forwardA square metal sheet 2.5 cm on a side and of negligible thickness is attached to a balance and inserted into a container of fluid. The contact angle is found to be zero, as shown in Figure a, and the balance to which the metal sheet is attached reads 0.42 N. A thin veneer of oil is then spread over the sheet, and the contact angle becomes 180°, as shown in Figure b. The balance now reads 0.41 N. What is the surface tension of the fluid? x Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. N/m a barrow_forward
- A helium-filled balloon (whose envelope has a mass of m₁ = 0.260 kg) is tied to a uniform string of length l = 2.70 m and mass m = 0.050 6 kg. The balloon is spherical with a radius of r = 0.399 m. When released in air of temperature 20°C and density Pair = 1.20 kg/m³, it lifts a length h of string and then remains stationary as shown in the figure below. We wish to find the length of string lifted by the balloon. He (a) When the balloon remains stationary, what is the appropriate analysis model to describe it? Oa particle in equilibrium model a particle under constant acceleration model a particle under constant velocity model the ideal fluid model (b) Write a force equation for the balloon from this model in terms of the buoyant force B, the weight F of the balloon, the weight Fe of the helium, and the weight F of the segment of string of length h. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: π. Follow the sign convention that upward is the positive…arrow_forwardAssume that if the shear stress in steel exceeds about 4.00 × 108 N/m², the steel ruptures. (a) Determine the shearing force necessary to shear a steel bolt 1.50 cm in diameter. (No Response) N (b) Determine the shearing force necessary to punch a 1.50-cm-diameter hole in a steel plate 0.650 cm thick. (No Response) Narrow_forward= = You are preparing your house for a party with your classmates and friends, and want to set up an impressive light display to entertain them. From your study of fluids, you have come up with the idea based on the water flowing from the tank in the figure. You set up the tank as shown in the figure, filled to a depth h 1.15 m, and sitting on a stand of height { 0.300 m. You punch a hole in the tank at a height of Y1 = 0.102 m above the stand. (Ignore the thickness of the tank in your calculation.) You want to punch a second hole higher on the tank so that the streams of water from the two holes arrive at the same position on the table, in a catch basin at a distance d from the right edge of the stand. A pump will continuously carry water from the catch basin back up to the top of the tank to keep the water level fixed. Then, you will use laser pointers on the left side of the tank to light the two streams of water, which will capture the light (see the section on total internal…arrow_forward
- A square metal sheet 2.5 cm on a side and of negligible thickness is attached to a balance and inserted into a container of fluid. The contact angle is found to be zero, as shown in Figure a, and the balance to which the metal sheet is attached reads 0.42 N. A thin veneer of oil is then spread over the sheet, and the contact angle becomes 180°, as shown in Figure b. The balance now reads 0.41 N. What is the surface tension of the fluid? N/m aarrow_forwardSucrose is allowed to diffuse along a 12.0-cm length of tubing filled with water. The tube is 6.1 cm² in cross-sectional area. The diffusion coefficient is equal to 5.0 × 10-10 m²/s, and 8.0 × 10−14 x transported along the tube in 18 s. What is the difference in the concentration levels of sucrose at the two ends of the tube? .00567 kg isarrow_forwardneed help part a and barrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





