
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780131495081
Author: Douglas C. Giancoli
Publisher: Addison-Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 21, Problem 74GP
Estimate the net force between the CO group and the HN group shown in Fig. 21–70. The С and О have charges ±0.40e, and the H and N have charges ± 0.20e, where e = 1.6 × 10−19 С. [Hint: Do not include the “internal” forces between С and O, or between Η and N.]
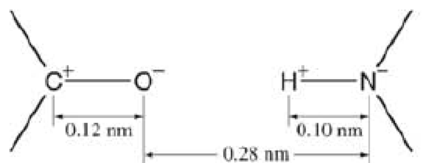
FIGURE 21–70
Problem 74.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Estimate the net force between the CO group and the HN
group shown in Fig. 16–63. The C and O have charges
+ 0.40e, and the H and N have charges ± 0.20e, where
e = 1.6 x 10-19 C. [Hint: Do not include the "internal"
forces between C and O, or between H and N.]
H EN
*0.12 nm
0.10 nm
0.28 nm
FIGURE 16–63 Problem 50.
In a small lead sphere with a mass of 8.00 g are placed surplus electrons, so that its net charge is -3.20 x 10-9 C.
a) Find the number of excess electrons in the sphere.
b) How many excess electrons are there per atom?
Excess electrons are there per lead atom? The atomic number of lead is 82, and its atomic mass is 207 g/mol.
(a) Two insulated charged copper spheres A and B have their centers separated by a
distance of 50 cm. What is the mutual force of electrostatic repulsion if the charge on
each is 6.5 x 10-7 C? The radii of A and B are negligible compared to the distance of
Chapter 21 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Ch. 21.5 - Return to the Chapter-Opening Question, page 559,...Ch. 21.5 - What is the magnitude of F12 (and F21) in Example...Ch. 21.5 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the net...Ch. 21.5 - (a) Consider two point charges of the same...Ch. 21.6 - Four charges of equal magnitude, but possibly...Ch. 21 - If you charge a pocket comb by rubbing it with a...Ch. 21 - Why does a shirt or blouse taken from a clothes...Ch. 21 - Explain why fog or rain droplets tend to form...Ch. 21 - A positively charged rod is brought close to a...Ch. 21 - Why does a plastic ruler that has been rubbed with...
Ch. 21 - Contrast the net charge on a conductor to the free...Ch. 21 - Figures 217 and 218 show how a charged rod placed...Ch. 21 - When an electroscope is charged, the two leaves...Ch. 21 - The form of Coulombs law is very similar to that...Ch. 21 - We are not normally aware of the gravitational or...Ch. 21 - Is the electric force a conservative force? Why or...Ch. 21 - What experimental observations mentioned in the...Ch. 21 - When a charged ruler attracts small pieces of...Ch. 21 - Explain why the test charges we use when measuring...Ch. 21 - When determining an electric field, must we use a...Ch. 21 - Draw the electric field lines surrounding two...Ch. 21 - Assume that the two opposite charges in Fig. 2134a...Ch. 21 - Consider the electric field at the three points...Ch. 21 - Why can electric field lines never cross?Ch. 21 - Given two point charges, Q and 2Q, a distance ...Ch. 21 - Suppose the ring of Fig. 2128 has a uniformly...Ch. 21 - Consider a small positive test charge located on...Ch. 21 - We wish to determine the electric field at a point...Ch. 21 - In what ways does the electron motion in Example...Ch. 21 - Describe the motion of the dipole shown in Fig....Ch. 21 - Explain why there can be a net force on an...Ch. 21 - (I) What is the magnitude of the electric force of...Ch. 21 - (I) How many electrons make up a charge of 38.0 C?Ch. 21 - (I) What is the magnitude of the force a + 25 C...Ch. 21 - (I) What is the repulsive electrical force between...Ch. 21 - (II) When an object such as a plastic comb is...Ch. 21 - (II) Two charged dust particles exert a force of...Ch. 21 - (II) Two charged spheres are 8.45 cm apart. They...Ch. 21 - (II) A person scuffing her feet on a wool rug on a...Ch. 21 - (II) What is the total charge of all the electrons...Ch. 21 - (II) Compare the electric force holding the...Ch. 21 - (II) Two positive point charges are a fixed...Ch. 21 - (II) Particles of charge +75, +48, and 85 C are...Ch. 21 - (II) Three charged particles are placed at the...Ch. 21 - (II) Two small nonconducting spheres have a total...Ch. 21 - (II) A charge of 4.15 mC is placed at each corner...Ch. 21 - (II) Two negative and two positive point charges...Ch. 21 - (II) A charge Q is transferred from an initially...Ch. 21 - (III) Two charges, Q0 and 4Q0, are a distance ...Ch. 21 - (III) Two positive charges +Q are affixed rigidly...Ch. 21 - (III) Two small charged spheres hang from cords of...Ch. 21 - (I) What are the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 21 - (I) A proton is released in a uniform electric...Ch. 21 - (I) Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 21 - (I) A downward electric force of 8.4 N is exerted...Ch. 21 - (I) The electric force on a +4.20-C charge is...Ch. 21 - (I) What is the electric field at a point when the...Ch. 21 - (II) Draw, approximately, the electric field lines...Ch. 21 - (II) What is the electric field strength at a...Ch. 21 - (II) A long uniformly charged thread (linear...Ch. 21 - (II) The electric field midway between two equal...Ch. 21 - (II) Calculate the electric field at one corner of...Ch. 21 - (II) Calculate the electric field at the center of...Ch. 21 - (II) Determine the direction and magnitude of the...Ch. 21 - (II) Two point charges, Q1 = 25 and Q2 = +45 ,...Ch. 21 - (II) A very thin line of charge lies along the x...Ch. 21 - (II) (a) Determine the electric field E at the...Ch. 21 - (II) Draw, approximately, the electric field lines...Ch. 21 - (II) Two parallel circular rings of radius R have...Ch. 21 - (II) You are given two unknown point charges, Q1...Ch. 21 - (II) Use Coulombs law to determine the magnitude...Ch. 21 - (II) (a) Two equal charges Q are positioned at...Ch. 21 - (II) At what position, x = xM, is the magnitude of...Ch. 21 - (II) Estimate the electric field at a point 2.40...Ch. 21 - (II) The uniformly charged straight wire in...Ch. 21 - (II) Use your result from Problem 46 to find the...Ch. 21 - (II) Determine the direction and magnitude of the...Ch. 21 - (II) A thin rod bent into the shape of an arc of a...Ch. 21 - (III) A thin glass rod is a semicircle of radius...Ch. 21 - (III) Suppose a uniformly charged wire starts at...Ch. 21 - (III) Suppose in Example 2111 that x = 0.250m. Q =...Ch. 21 - (III) A thin rod of length carries a total charge...Ch. 21 - (III) Uniform plane of charge. Charge is...Ch. 21 - (III) Suppose the charge Q on the ring of Fig....Ch. 21 - (II) An electron with speed v0 = 27.5 106 m/s is...Ch. 21 - (II) An electron has an initial velocity...Ch. 21 - (II) An electron moving to the right at 7.5 105...Ch. 21 - (II) At what angle will the electrons in Example...Ch. 21 - (II) An electron is traveling through a uniform...Ch. 21 - (II) A positive charge q is placed at the center...Ch. 21 - (II) A dipole consists of charges +e and e...Ch. 21 - (II) The HCl molecule has a dipole moment of about...Ch. 21 - (II) Suppose both charges in Fig. 2145 (for a...Ch. 21 - (II) An electric dipole, of dipole moment p and...Ch. 21 - (III) Suppose a dipole p is placed in a nonuniform...Ch. 21 - (III) (a) Show that at points along the axis of a...Ch. 21 - How close must two electrons be if the electric...Ch. 21 - Given that the human body is mostly made of water,...Ch. 21 - A 3.0-g copper penny has a positive charge of 38...Ch. 21 - Measurements indicate that there is an electric...Ch. 21 - (a) The electric field near the Earths surface has...Ch. 21 - A water droplet of radius 0.018 mm remains...Ch. 21 - Estimate the net force between the CO group and...Ch. 21 - Suppose that electrical attraction, rather than...Ch. 21 - In a simple model of the hydrogen atom, the...Ch. 21 - A positive point charge Q1 = 2.5 105 C is fixed...Ch. 21 - When clothes are removed from a dryer, a 40-g sock...Ch. 21 - A small lead sphere is encased in insulating...Ch. 21 - A large electroscope is made with leaves that are...Ch. 21 - Dry air will break down and generate a spark if...Ch. 21 - Two pint charges, Q1 = 6.7 and Q2 = 1.8 C, are...Ch. 21 - Packing material made of pieces of foamed...Ch. 21 - One type of electric quadrupole consists of two...Ch. 21 - Suppose electrons enter a uniform electric field...Ch. 21 - An electron moves in a circle of radius r around a...Ch. 21 - Three very large square planes of charge are...Ch. 21 - A point charge (m = 1.0 g) at the end of an...Ch. 21 - Four equal positive point charges, each of charge...Ch. 21 - Two small, identical conducting spheres A and B...Ch. 21 - A point charge of mass 0.210 kg, and net charge...Ch. 21 - A one-dimensional row of positive ions, each with...Ch. 21 - (III) A thin ring-shaped object of radius a...Ch. 21 - (III) An 8.00 C charge is on the x axis of a...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The distance at which the finger should be placed to play the note C.
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Estimate the average temperature of the air inside a hot-air balloon (see Figure 1.1). Assume that the total ma...
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Whether the diver can begins to rotate by folding into a tucked position or not.
Physics (5th Edition)
22.14 A solid metal sphere with radius 0.450 m carries a net charge of 0.250 nC. Find the magnitude of the ele...
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
36.30 CDs and DVDs as Diffraction Gratings. A laser beam of wavelength ? = 632.8 nm shines at normal incidence ...
University Physics (14th Edition)
When the momentum of an object or system of objects does not change with time, the momentum of the object or sy...
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (a) Two insulated charged copper spheres A and B have their centres separated by a distance of 50 cm. What is the mutual force of electrostatic repulsion if the charge on each is 6.5 x 10-7 C? The radii of A and B are negligible compared to the distance of separation.arrow_forwardExcess electrons are placed on a small lead sphere with mass 8.00 g so that its net chargeis -3.20 x 10-9 C. (a) Find the number of excess electrons on the sphere. (b) How many excess electrons are there per lead atom? The atomic number of lead is 82, and its atomicmass is 207 g/mol.arrow_forward(b) Three point charges are at the corners of a equilateral triangle as shown in figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant electrostatic force on +7uC charge. [Given Data, Coulomb constant ke 8.99x10° Nm2/C'] [5 Marks] 7.00 µC 0.300 m 60.0° 500 µC -6.00 µCarrow_forward
- I need a solution for this question.arrow_forwardThree distribution of charges are present in free space with: iC/m lies along z-axis. 5 Cm A uniform line charge of pL = 3 A concentric circular cylinder of radius 2 m has es A concentric circular cylinder of radius 4arrow_forward.ylsts Aia) Sib 2843 bluos r "(b91c M (O 26uq An initially neutral piece of plastic is has 1.09 x 1015 electrons removed from it. Determine the net charge of the plastic (in μC). no :(a)s 31 LOL OUGarrow_forwardThe magnitude of the electric fie ld at a distance r from a point charge O is equal to O/4πεor2. How close to a water molecule (of polarizability volume 1.48 x 1-30 m3) must a proton approach before the dipole moment it induces is equal to the permanent dipole moment of the molecule (1.85 D)?arrow_forwardThree distribution of charges are present in free: space with: A uniform line charge of p₁ = 3 μC/m lies along z-axis. MC/m 3 μC / m 3 A concentric circular cylinder of radius 2 m has p, = 5 A concentric circular cylinder of radius 4 ≤r ≤ 5 has pv Find D at a) r=1 b) r-3 c) r=6 (a) 0.0477*10^-6 C/m^2, (b) 3.05*10^-6 C/m^2, (c) 0.0022*10^-6 O C/m^2 (a) 4.77*10^-6 C/m^2, (b) 3.5*10^-6 O C/m^2, (c) 0.22*10^-6 C/m^2 (a) 0.477*10^-6 C/m^2, (b) 3.5*10^-6 C/m^2, (c) 0.022*10^-6 C/m^2 (a) 0.477*10^-5 C/m^2, (b) 3.5*10^-6 C/m^2, (c) 0.022*10^-5 O C/m^2arrow_forwardThree distribution of charges are present in free space with: A uniform line charge of p = 3 4/m lies along z-axis. A concentric circular cylinder of radius 2 m has p, = 5 HC/m A concentric circular cylinder of radius 4arrow_forwardTwo small charged spheres hang from cords of equal length l as shown in Fig. 16–64 and make small angles 01 and 02 with the vertical. (a) If Q1 = Q, Q2 = 2Q, and m1 = m2 = m, determine the ratio 01/02. (b) Estimate the distance between the spheres. FIGURE 16–64 Problem 52. Q1 Q2arrow_forward(III) The dipole moment, considered as a vector, points from the negative to the positive charge. The water molecule, Fig. 17-42, has a dipole moment p which can be considered as the vector sum of the two dipole moments, P¡ and pP2, as shown. The distance between each H and the O is about 0.96 x 10-10 m. The lines joining the center of the O atom with each H atom make an angle of 104°, as shown, and the net dipole moment has been mea- sured to be p = 6.1 × 10-30 C · m. Determine the charge q on each H atom. 104° H+ FIGURE 17-42 Problem 34. P2 A water molecule, H2O.arrow_forwardPoint charges of 5.00μC and -3.00μC are placed 0.25 m apart. (a) Where can a third charge be placed so that the net force on it is zero? (b) What if both charges are positive?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY