
(a)
Interpretation:
To identify which of the given set of compounds have pKa value lesser than 20 and to identify the acidic proton in the same
Concept introduction:
pKa is negative base-10 logarithm of the dissociation constant of acid (Ka) of a solution.
pKa is used is to describe acid dissociation because it is expressed in small decimal numbers.
If pKa value is below 20 the compound is said to have acidic proton and vice versa
To identify : The compound pKa value and the most acidic proton
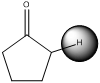
(a)
Answer to Problem 47PP
The pKa value of (a) is just below 20 and it has acidic proton next to carbonyl
Explanation of Solution
Deprotonation of the highlighted hydrogen and resonance stabilization
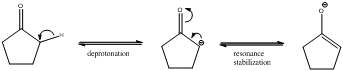
From the above scheme we can infer that the highlighted hydrogen is removed resulting in formation of a conjugate base. The conjugate base is resonance stabilized as the negative charge is delocalized on oxygen atom also. Therefore the highlighted proton is most acidic (pKa value below 20) as the removal of it leads to a stabilized conjugate base.
(b)
Interpretation:
To identify which of the given set of compounds have pKa value lesser than 20 and to identify the acidic proton in the same
Concept introduction:
pKa is negative base-10 logarithm of the dissociation constant of acid (Ka) of a solution.
pKa is used is to describe acid dissociation because it is expressed in small decimal numbers.
If pKa value is below 20 the compound is said to have acidic proton and vice versa
To identify : The compound pKa value and the most acidic proton
(b)
Answer to Problem 47PP
The pKa value of (b) is just above 20 and it does not have acidic proton
No acidic proton is present
Explanation of Solution
The above given compound does not have an acidic proton that can undergo deprotonation. Hence this compound is expected to have pKa above 20.
(c)
Interpretation:
To identify which of the given set of compounds have pKa value lesser than 20 and to identify the acidic proton in the same
Concept introduction:
pKa is negative base-10 logarithm of the dissociation constant of acid (Ka) of a solution.
pKa is used is to describe acid dissociation because it is expressed in small decimal numbers.
If pKa value is below 20 the compound is said to have acidic proton and vice versa
To identify : The compound pKa value and the most acidic proton

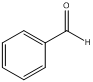
(c)
Answer to Problem 47PP
The pKa value of (c) is just below 20 and it has acidic proton next to carbonyl
Explanation of Solution
Deprotonation of the highlighted hydrogen and resonance stabilization
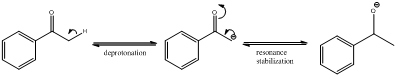
From the above scheme we can infer that the highlighted hydrogen is removed resulting in formation of a conjugate base. The conjugate base is resonance stabilized as the negative charge is delocalized on oxygen atom also. Therefore the highlighted proton is most acidic (pKa value below 20) as the removal of it leads to a stabilized conjugate base.
(d)
Interpretation:
To identify which of the given set of compounds have pKa value lesser than 20 and to identify the acidic proton in the same
Concept introduction:
pKa is negative base-10 logarithm of the dissociation constant of acid (Ka) of a solution.
pKa is used is to describe acid dissociation because it is expressed in small decimal numbers.
If pKa value is below 20 the compound is said to have acidic proton and vice versa
To identify : The compound pKa value and the most acidic proton

(d)
Answer to Problem 47PP
The pKa value of (d) is just below 20 and it has acidic proton next to carbonyl
Explanation of Solution
Deprotonation of the highlighted hydrogen and resonance stabilization
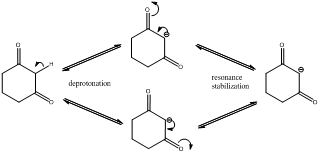
From the above scheme we can infer that the highlighted hydrogen is removed resulting in formation of a conjugate base. The conjugate base is resonance stabilized as the negative charge is delocalized on two oxygen atoms (doubly stabilized enolate ion). Therefore the highlighted proton is most acidic (pKa value below 20) as the removal of it leads to a stabilized conjugate base.
(e)
Interpretation:
To identify which of the given set of compounds have pKa value lesser than 20 and to identify the acidic proton in the same
Concept introduction:
pKa is negative base-10 logarithm of the dissociation constant of acid (Ka) of a solution.
pKa is used is to describe acid dissociation because it is expressed in small decimal numbers.
If pKa value is below 20 the compound is said to have acidic proton and vice versa
To identify : The compound pKa value and the most acidic proton

(e)
Answer to Problem 47PP
The pKa value of (e) is just below 20 and it has acidic proton next to carbonyl
Explanation of Solution
Deprotonation of the highlighted hydrogen

From the above scheme we can infer that the highlighted hydrogen is removed resulting in formation of an alokoxide ion. As such the compound is expected to have pKa lower than 20.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT COMPANION (LL)
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





