
Concept explainers
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of a nitrile to give a
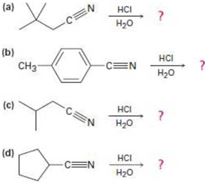
a)
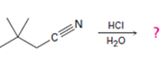
Interpretation:
The products of the reaction, the acid-catalyzed nitrile hydrolysis, along with all the steps involved using curved arrows to represent electron flow in each step, is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The acid protonates the nitrogen of the nitrile group initially. The nucleophilic attack by water and subsequent proton transfer will yield an intermediate. Another nucleophilic attack by water on the intermediate and yet another proton transfer produces another intermediate. The intermediate loses ammonia to produce the protonated acid which deprotonates to yield the acid.
To give:
The products of the reaction, the acid-catalyzed nitrile hydrolysis, along with all the steps involved using curved arrows to represent electron flow in each step.
Answer to Problem 25MP
The products of the reaction are ammonia and 2,2-dimethylbutanoic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.
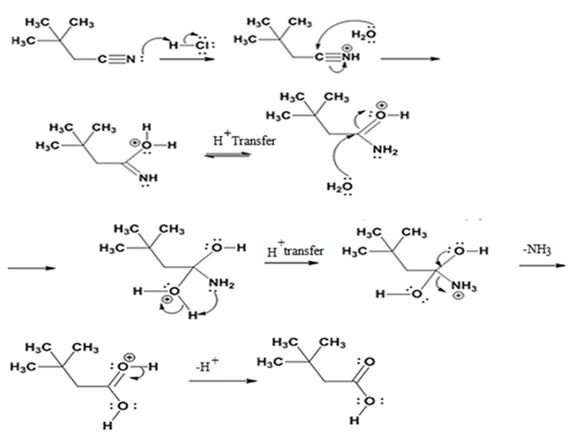
Explanation of Solution
In the first step, 2,2-dimethylbutane nitrile is protonated by HCl. In the next step, the nucleophilic attack of water on the protonated nitrile occurs and the accompanying proton transfer yields a protonated aminoketone. Another nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the protonated aminoketone in the next step and the subsequent proton transfer yields a protonated diol intermediate which eliminates ammonia and a proton in the subsequent steps to yield 2,2-dimethylbutanoic acid.
The products of the reaction are ammonia and 2,2-dimethylbutanoic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.

b)
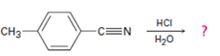
Interpretation:
The products of the reaction, the acid-catalyzed nitrile hydrolysis, along with all the steps involved using curved arrows to represent electron flow in each step, is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The acid protonates the nitrogen of the nitrile group initially. The nucleophilic attack by water and subsequent proton transfer will yield an intermediate. Another nucleophilic attack by water on the intermediate and yet another proton transfer produces another intermediate. The intermediate loses ammonia to produce the protonated acid which deprotonates to yield the acid.
To give:
The products of the reaction, the acid-catalyzed nitrile hydrolysis, along with all the steps involved using curved arrows to represent electron flow in each step.
Answer to Problem 25MP
The products of the reaction are ammonia and p-methylbenzoic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.
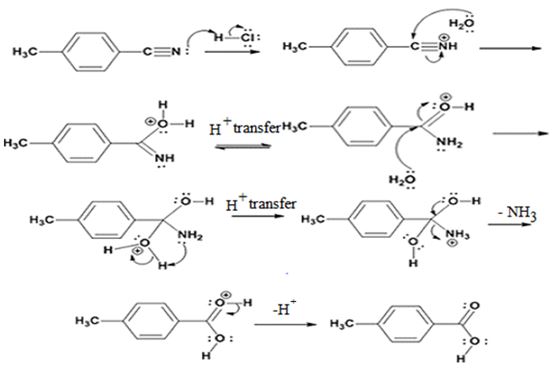
Explanation of Solution
In the first step, p-methylbenzonitrile is protonated by HCl. In the next step, the nucleophilic attack of water on the protonated nitrile occurs and the accompanying proton transfer yields a protonated aminoketone. Another nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the protonated aminoketone in the next step and the subsequent proton transfer yields a protonated diol intermediate which eliminates ammonia and a proton in the subsequent steps to yield p-methylbenzoic acid.
The products of the reaction are ammonia and p-methylbenzoic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.

c)
Interpretation:
The products of the reaction, the acid-catalyzed nitrile hydrolysis, along with all the steps involved using curved arrows to represent electron flow in each step, is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The acid protonates the nitrogen of the nitrile group initially. The nucleophilic attack by water and subsequent proton transfer will yield an intermediate. Another nucleophilic attack by water on the intermediate and yet another proton transfer produces another intermediate. The intermediate loses ammonia to produce the protonated acid which deprotonates to yield the acid.
To give:
The products of the reaction, the acid-catalyzed nitrile hydrolysis, along with all the steps involved using curved arrows to represent electron flow in each step.
Answer to Problem 25MP
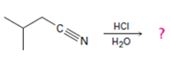
The products of the reaction are ammonia and 2-methylbutanoic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.
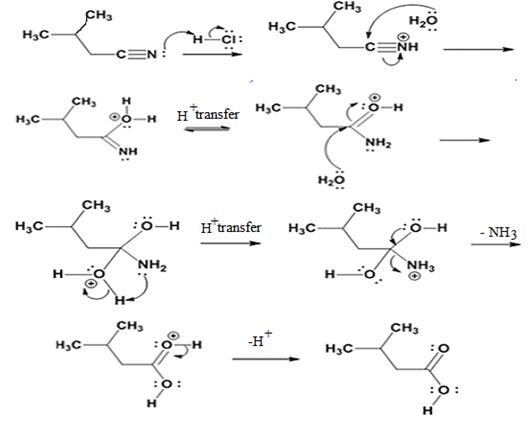
Explanation of Solution
In the first step, 2-methylbutane nitrile is protonated by HCl. In the next step, the nucleophilic attack of water on the protonated nitrile occurs and the accompanying proton transfer yields a protonated aminoketone. Another nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the protonated aminoketone in the next step and the subsequent proton transfer yields a protonated diol intermediate which eliminates ammonia and a proton in the subsequent steps to yield 2-methylbutanoic acid.
The products of the reaction are ammonia and 2-methylbutanoic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.

d)
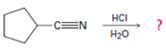
Interpretation:
The products of the reaction, the acid-catalyzed nitrile hydrolysis, along with all the steps involved using curved arrows to represent electron flow in each step, is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The acid protonates the nitrogen of the nitrile group initially. The nucleophilic attack by water and subsequent proton transfer will yield an intermediate. Another nucleophilic attack by water on the intermediate and yet another proton transfer produces another intermediate. The intermediate loses ammonia to produce the protonated acid which deprotonates to yield the acid.
To give:
The products of the reaction, the acid-catalyzed nitrile hydrolysis, along with all the steps involved using curved arrows to represent electron flow in each step.
Answer to Problem 25MP
The products of the reaction are ammonia and cyclopentanecarboxylic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.
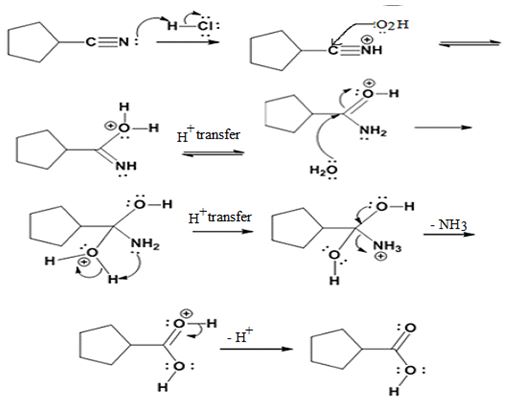
Explanation of Solution
In the first step, cyclopentanenitrile is protonated by HCl. In the next step, the nucleophilic attack of water on the protonated nitrile occurs and the accompanying proton transfer yields a protonated aminoketone. Another nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the protonated ketone in the next step and the subsequent proton transfer yields a protonated aminodiol intermediate which eliminates ammonia and a proton in the subsequent steps to yield cyclopentanecarboxylic acid.
The products of the reaction are ammonia and cyclopentanecarboxylic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Bundle: Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + LMS Integrated for OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- For the photochemical halogenation reaction below, draw both propagation steps and include the mechanism arrows for each step. H CH ot CH3 CI-CI MM hv of CH H-CI CH3 2nd attempt See Periodic Table See Hint Draw only radical electrons; do not add lone pair electrons. Note that arrows cannot meet in "space," and must end at either bonds or at atoms. 1 i Add the missing curved arrow notation to this propagation step. 20 H ن S F P H CI Br 品arrow_forwardThe radical below can be stabilized by resonance. 4th attempt Draw the resulting resonance structure. DOCEarrow_forwardUse curved arrows to generate a second resonance form for the allylic radical formed from 2-methyl-2-pentene. 1 Draw the curved arrows that would generate a second resonance form for this radical. D 2 H S F A Бг Iarrow_forward
- Draw the resulting product(s) from the coupling of the given radicals. Inlcude all applicable electrons and non-zero formal charges. H.C öö- CH3 2nd attempt +1 : 招 H₂C CH CH₂ See Periodic Table See H H C S F P Br CH₂ Iarrow_forwardPlease, help me out with the calculation, step by step on how to find what's blank with the given information.arrow_forwardPredict the following products. Then show the mechanism. H₂N NH2arrow_forward
- BF3, Boron Trifluoride, known to contain three covalent boron-fluorine bonds. suggest and illustrate all of the processes as well as their energetical consequences for the formation of BF3 from its elements.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism of the reaction.arrow_forward9. Draw all of the possible Monochlorination Products that would Result From the Free Radical Chlormation OF 23,4-TRIMethyl Pentane b. Calculate the To Yield For the major • Product given the Following Relative Restritus For 1° 2° and 30 Hydrogens toward Free Radical Chloration 5.0: 38 : 1 30 2° 1° C. what would be the major product in the Free Radical brominator Of the Same Molecule. Explain your Reasoning.arrow_forward
- What is the complete reaction mechanism for the chlorination of Ethane, C2H6?arrow_forwardA 13C NMR spectrum is shown for a molecule with the molecular formula of C6H100. Draw the structure that best fits this data. 220 200 180 160 140 120100 80 60 40 20 Drawingarrow_forwardPlease help me figure out the blan areas with step by step calculations.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


