
POWER FROM THE SEA.
Ocean thermal energy conversion is a process that uses the temperature difference between the warm surface water of tropical oceans and the cold deep-ocean water to run a
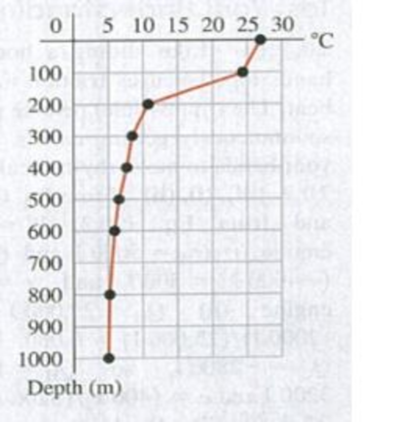
20.59 If the power plant uses a Carnot cycle and the desired theoretical efficiency is 6.5%, from what depth must cold water be brought? (a) 100 m; (b) 400 m; (c) 800 m; (d) deeper than 1000m.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective
Physics (5th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
- (a) How much food energy will a man metabolize in the process of doing 35.0 kJ of work with an efficiency of 5.00%? (b) How much heal transfer occurs to the environment to keep his temperature constant? Explicitly show how you follow the steps in the Problem—Solving Strategy for thermodynamics found in Problem-Solving Strategies for Thermodynamics.arrow_forwardIf a gas is compressed isothermally, which of the following statements is true? (a) Energy is transferred into the gas by heat. (b) No work is done on the gas. (c) The temperature of the gas increases. (d) The internal energy of the gas remains constant. (e) None of those statements is true.arrow_forward(a) A cyclical heat engine, operating between temperatures of 450C and 150C produces 4.00 MJ of work on a heat transfer of 5.00 MJ into the engine. How much heat transfer occurs to the environment? (b) What is unreasonable about the engine? (c) Which premise is unreasonable?arrow_forward
- Unreasonable Results (a) What is the temperature increase of an 80.0 kg person who consumes 2500 kcal of food in one day with 95.0% of the energy transferred as heat to the body? (b) What is unreasonable about this result? (c) Which premise or assumption is responsible?arrow_forward(a) How long will the energy in a 1470kJ (350kcal) cup of yogurt last in a woman doing work at the rate of 150 W with an efficiency of 20.0% (such as in leisurely climbing stairs)? (b) Does the time found in part (a) imply that it is easy to consume more food energy than you can reasonably expect to work off with exercise?arrow_forwardA 2.00-mol sample of a diatomic ideal gas expands slowly and adiabatically from a pressure of 5.00 atm and a volume of 12.0 L to a final volume of 30.0 L. (a) What is the final pressure of the gas? (b) What are the initial and final temperatures? Find (c) Q, (d) Eint, and (e) W for the gas during this process.arrow_forward
- A person inhales and exhales 2.00 L of 37.0C air, evaporating 4.00102g of water from the lungs and breathing passages with each breath. (a) How much heat transfer occurs due to evaporation in each breath? (b) What is the rate of heat transfer in watts if the person is breathing at a moderate rate of 18.0 breaths per minute? (c) If the inhaled air had a temperature of 20.0C, what is the rate of heat transfer for warming the air? (d) Discuss the total rate of heat transfer as it relates to typical metabolic rates. Will this breathing be a major form of heat transfer for this person?arrow_forward(a) How much heat must be added to raise the temperature of 1.5 mol of air 25.0 to 33.0 at constant volume? Assume air is completely diatomic. (b) Repeat the problem for the same number of moles of xenon, Xe.arrow_forwardA certain ideal gas has a molar specific heat of Cv = 72R. A 2.00-mol sample of the gas always starts at pressure 1.00 105 Pa and temperature 300 K. For each of the following processes, determine (a) the final pressure, (b) the final volume, (c) the final temperature, (d) the change in internal energy of the gas, (e) the energy added to the gas by heat, and (f) the work done on the gas. (i) The gas is heated at constant pressure to 400 K. (ii) The gas is heated at constant volume to 400 K. (iii) The gas is compressed at constant temperature to 1.20 105 Pa. (iv) The gas is compressed adiabatically to 1.20 105 Pa.arrow_forward
- In a cylinder of an automobile engine, immediately after combustion the gas is confined to a volume of 50.0 cm3 and has an initial pressure of 3.00 106 Pa. The piston moves outward to a final volume of 300 cm3, and the gas expands without energy transfer by heat, (a) What is the final pressure of the gas? (b) How much work is done by the gas in expanding?arrow_forward(a) An ideal gas expands adiabatically from a volume of 2.0103 m3 to 2.5103 m3. If the initial pressure and temperature 5.0105 Pa and 300 K, respectively, what are the final pressure and temperature of the gas? Use =5/3 for the gas. (b) In an isothermal process, an ideal gas expands from a of 2.0103 m3 to 2.5103 m3. If the initial pressure and temperature were 5.0105 Pa and 300 K, respectively, what are the final pressure and temperature of the gas?arrow_forward(a) What is the average metabolic rate in watts of a man who metabolizes 10,500 kJ of feed energy in one day? (b) What is the maximum amount of work in joules he can do without breaking down fat, assuming a maximum eficiency of 20.0%? (c) Compare his work output with the daily output of a 187W (0.250horsepower) motor.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





